|
Pylyp Orlyk
Pylyp Stepanovych Orlyk (; ; – May 26, 1742) was a Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack statesman, diplomat and member of Cossack starshyna who served as the Hetman of Zaporizhian Cossacks, hetman in exile from 1710 to 1742. He was a close associate of Ivan Mazepa and the author of the Constitution of Pylyp Orlyk. Biography Pylyp Orlyk was born in the village of , Ashmyany county, Grand Duchy of Lithuania (Vileyka district of modern-day Belarus), on November 1, 1673. Pylyp Orlik came from an old noble family of the Nowina coat of arms. The family name appeared in the form Orlik or Orlicki. The family most likely came to the Kingdom of Poland from Bohemia in the 15th century, then settled in western Belarus. Pylyp's father Stefan Orlik was killed in the Battle of Khotyn (1673), Battle of Chocim against the Turks on November 11, 1673, fighting in the ranks of the Polish-Lithuanian army, a year after his son's birth. Pylyp's mother was Irena née Małachowski of the Hrym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hetman Of The Zaporozhian Host
The Hetman of the Zaporozhian Host (, ) was the head of state of the Cossack Hetmanate. The office was abolished by the Russian government in 1764. Brief history The position was established by Bohdan Khmelnytsky during the Cossack Hetmanate in the mid 17th century. During that period the office was electoral. All elections, except for the first one, took place in the Senior Council in Chyhyryn which, until 1669, served as the capital of the Hetmanate. After the Pereiaslav Agreement of 1654, several senior cossacks sided with the Tsardom of Russia and, in 1663, they convened the Black Council of 1663 in Nizhyn which elected Ivan Briukhovetsky as an alternative hetman. Since the defeat of Petro Doroshenko in 1669, the title hetman was adapted by pro-Russian elected hetmans who resided in Baturyn. In the course of the Great Northern War one of them, Ivan Mazepa, decided to revolt against Russian rule in 1708, which later drew terrible consequences for the Cossack Hetmanate as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Khotyn (1673)
The Battle of Khotyn or Battle of Chocim, also known as the Hotin War, took place on 11 November 1673 in Khotyn, where the forces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth under the Hetmans of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Grand Hetman of the Polish Crown John III Sobieski, John Sobieski defeated Ottoman Empire forces, with Moldavian and Wallachian regiments, led by Hüseyin Pasha. It reversed the fortunes of the previous year, when Commonwealth weakness led to the signing of the Treaty of Buchach, and allowed John Sobieski to win the upcoming Royal elections in Poland, royal election and become the King of Poland. Name Khotyn (; ; ; ) was conquered and controlled by many states, resulting in many name changes. Other name variations include ''Chotyn'', or ''Choczim'' (especially in Polish language, Polish). Battle The Polish-Lithuanian army, numbering some 30,000 soldiers, under the command of Grand Crown Hetman John III Sobieski, John Sobieski, besieged the Khotyn fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cossacks
The Cossacks are a predominantly East Slavic languages, East Slavic Eastern Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of eastern Ukraine and southern Russia. Cossacks played an important role in defending the southern borders of Ukraine and Russia, Cossack raids, countering the Crimean-Nogai slave raids in Eastern Europe, Crimean-Nogai raids, alongside economically developing steppes, steppe regions north of the Black Sea and around the Azov Sea. Historically, they were a semi-nomadic and semi-militarized people, who, while under the nominal suzerainty of various Eastern European states at the time, were allowed a great degree of self-governance in exchange for military service. Although numerous linguistic and religious groups came together to form the Cossacks, most of them coalesced and became East Slavic languages, East Slavic–speaking Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christians. The rulers of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russian Empire en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
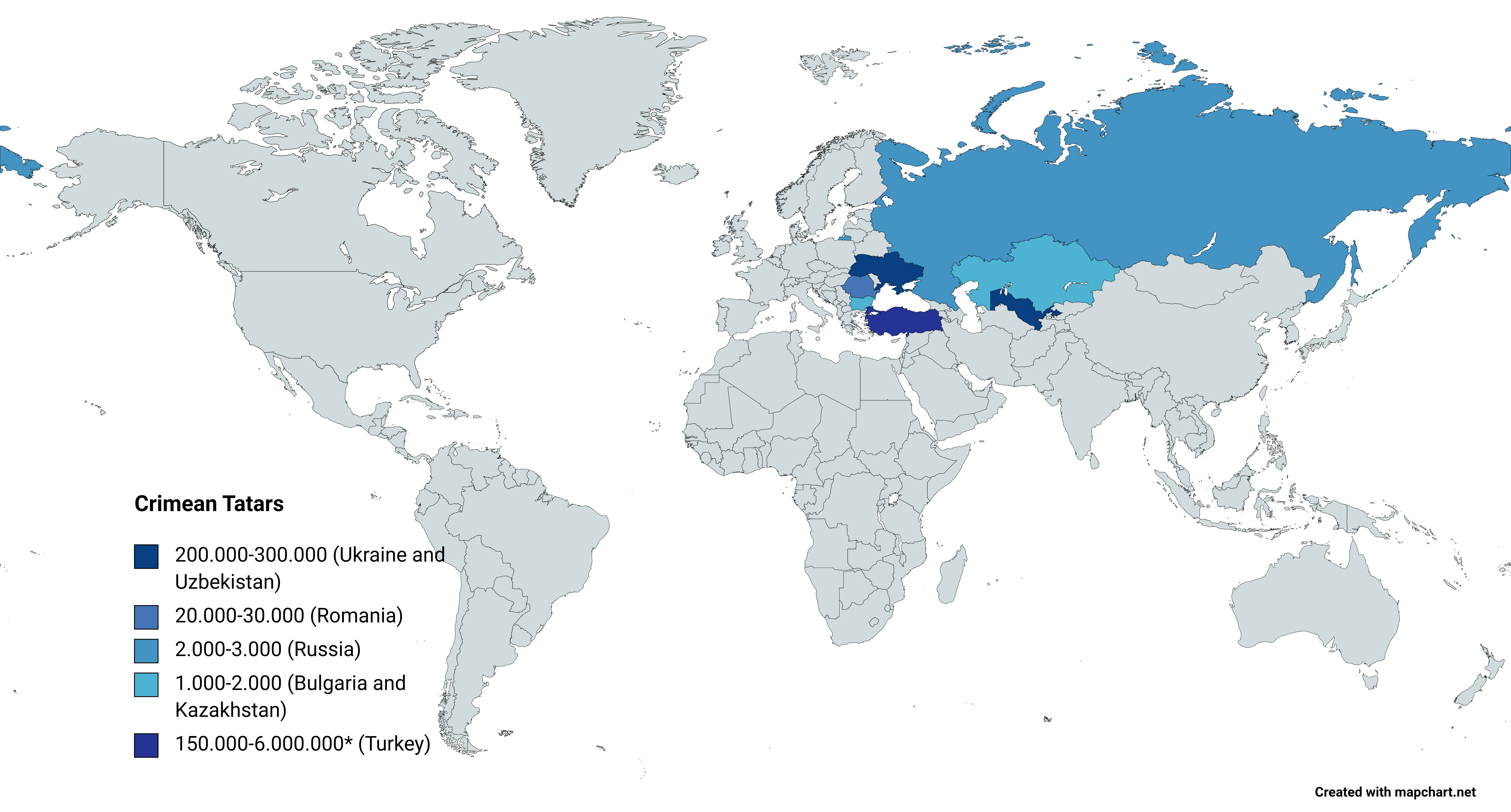
Crimean Tatars
Crimean Tatars (), or simply Crimeans (), are an Eastern European Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group and nation indigenous to Crimea. Their ethnogenesis lasted thousands of years in Crimea and the northern regions along the coast of the Black Sea, uniting Mediterranean basin, Mediterranean populations with those of the Eurasian Steppe.''Агджоян А. Т., Схаляхо Р. А., Утевская О. М., Жабагин М. К., Тагирли Ш. Г., Дамба Л. Д., Атраментова Л. А., Балановский О. П.'Генофонд крымских татар в сравнении с тюркоязычными народами Европы, 2015 Genome-wide study of the Crimean Tatars unveiled connections between them and the genomes of individuals from the Steppe during the Bronze Age, specifically those associated with the Yamnaya culture, Yamnaya archaeological culture. Until the 20th century, Crimean Tatars were the most populous demographic cohort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Moldavia
Moldavia (, or ; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ) is a historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially independent and later autonomous state, it existed from the 14th century to 1859, when it united with Wallachia () as the basis of the modern Romanian state; at various times, Moldavia included the regions of Bessarabia (with the Budjak), all of Bukovina and Hertsa region , Hertsa. The region of Pokuttya was also part of it for a period of time. The Moldavia (region of Romania) , western half of Moldavia is now part of Romania, the eastern side belongs to the Moldova , Republic of Moldova, and the Chernivtsi Oblast , northern and Budjak , southeastern parts are territories of Ukraine. Name and etymology The original and short-lived reference to the region was ''Bogdania'', after Bogdan I, the founding figure of the principality. The name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tighina
Bender (, ) or Bendery (, ; ), also known as Tighina ( mo-Cyrl, Тигина, links=no), is a city within the internationally recognized borders of Moldova under ''de facto'' control of the unrecognized Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (Transnistria) (PMR) since 1992. It is located on the western bank of the river Dniester in the historical region of Bessarabia. Together with its suburb Proteagailovca, the city forms a municipality, which is separate from Transnistria (as an administrative unit of Moldova) according to Moldovan law. Bender is located in the buffer zone established at the end of the 1992 War of Transnistria. While the Joint Control Commission has overriding powers in the city, Transnistria has ''de facto'' administrative control. The fortress of Tighina was one of the important historic fortresses of the Principality of Moldova until 1812. Name First mentioned in 1408 as ''Tyagyanyakyacha'' () in a document in Old Slavonic (the term has Cuman origins), t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles XII Of Sweden
Charles XII, sometimes Carl XII () or Carolus Rex (17 June 1682 – 30 November 1718 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.), was King of Sweden from 1697 to 1718. He belonged to the House of Palatinate-Zweibrücken, a branch line of the House of Wittelsbach. Charles was the only surviving son of Charles XI of Sweden, Charles XI and Ulrika Eleonora the Elder. He assumed power, after a seven-month caretaker government, at the age of fifteen. In 1700, a triple alliance of Denmark–Norway, Electorate of Saxony, Saxony–Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Poland–Lithuania and Tsardom of Russia, Russia launched a threefold attack on the Swedish protectorate of Holstein-Gottorp and provinces of Swedish Livonia, Livonia and Swedish Ingria, Ingria, aiming to take advantage of the Swedish Empire being unaligned and ruled by a young and inexperienced king, thus initiating the Great Northern War. Leading the Swedish army against the alliance, Charles won multiple victories despite being si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
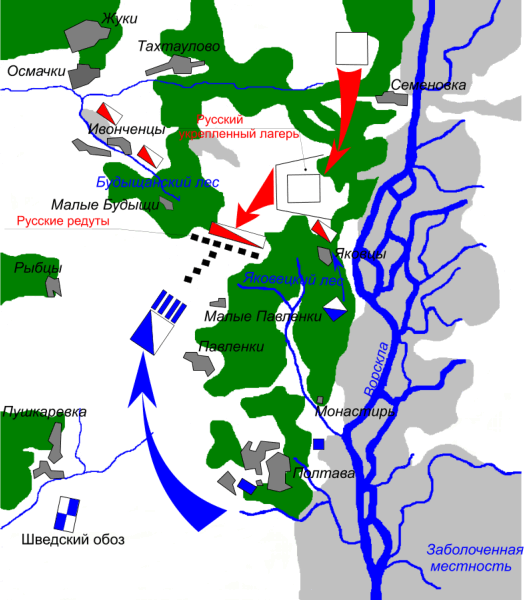
Battle Of Poltava
The Battle of Poltava took place 8 July 1709, was the decisive and largest battle of the Great Northern War. The Russian army under the command of Tsar Peter I defeated the Swedish army commanded by Carl Gustaf Rehnskiöld. The battle would lead to the Swedish Empire losing its status as a European great power and also marked the beginning of Russian supremacy in eastern Europe. During the course of six years in the initial stages of the war, King Charles XII and the Swedish Empire had defeated almost all participants in the anti-Swedish coalition, which initially consisted of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Denmark-Norway and the Tsardom of Russia. The latter, under , was the only one still fighting. Charles therefore chose to invade Russia in the autumn of 1707 and march towards Moscow with a large Swedish army. However, the campaign was complicated by harsh weather conditions and by Russian scorched earth tactics and surprise attacks, which forced Charles to interr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mazepa
Ivan Stepanovych Mazepa (; ; ) was the Hetman of the Zaporozhian Host and the Left-bank Ukraine in 1687–1708. The historical events of Mazepa's life have inspired many literary, artistic and musical works. He was famous as a patron of the arts. Mazepa played an important role in the Battle of Poltava (1709), where after learning that Tsar Peter I intended to relieve him as acting hetman of Zaporozhian Host and to replace him with Alexander Menshikov, he defected from his army and sided with King Charles XII of Sweden. The political consequences and interpretation of this defection have resonated in the national histories both of Russia and of Ukraine. The Russian Orthodox Church laid an anathema (excommunication) on Mazepa's name in 1708 and still refuses to revoke it. The anathema was not recognized by the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, which considers it uncanonical and imposed with political motives as a means of political and ideological repression, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hetman
''Hetman'' is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders (comparable to a field marshal or imperial marshal in the Holy Roman Empire). First used by the Czechs in Bohemia in the 15th century, it was the title of the second-highest military commander after the king in the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from the 16th to 18th centuries. Hetman was also the title of the head of the Cossack state in Ukraine after the Khmelnytsky Uprising of 1648. Throughout much of the history of Romania and the Moldavia, hetmans were the second-highest army rank. In the modern Czech Republic, the title is used for regional governors. Etymology The term ''hetman'' was a Polish borrowing, most likely stemming via Czech from the Turkic title ''ataman'' (literally 'father of horsemen'), however it could also come from the German – captain. Since hetman as a title first appeared in Czechia in the 15th century, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kiev
Kyiv, also Kiev, is the capital and most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city of Ukraine. Located in the north-central part of the country, it straddles both sides of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2022, its population was 2,952,301, making Kyiv the List of European cities by population within city limits, seventh-most populous city in Europe. Kyiv is an important industrial, scientific, educational, and cultural center. It is home to many High tech, high-tech industries, higher education institutions, and historical landmarks. The city has an extensive system of Transport in Kyiv, public transport and infrastructure, including the Kyiv Metro. The city's name is said to derive from the name of Kyi, one of its four legendary founders. During History of Kyiv, its history, Kyiv, one of the oldest cities in Eastern Europe, passed through several stages of prominence and obscurity. The city probably existed as a commercial center as early as the 5th century. A Slav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |