|
Protoplanet
A protoplanet is a large planetary embryo that originated within a protoplanetary disk and has undergone internal melting to produce a differentiated interior. Protoplanets are thought to form out of kilometer-sized planetesimals that gravitationally perturb each other's orbits and collide, gradually coalescing into the dominant planets. The planetesimal hypothesis A planetesimal is an object formed from dust, rock, and other materials, measuring from meters to hundreds of kilometers in size. According to the Chamberlin–Moulton planetesimal hypothesis and the theories of Viktor Safronov, a protoplanetary disk of materials such as gas and dust would orbit a star early in the formation of a planetary system. The action of gravity on such materials form larger and larger chunks until some reach the size of planetesimals. It is thought that the collisions of planetesimals created a few hundred larger planetary embryos. Over the course of hundreds of millions of years, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoplanetary Disk
A protoplanetary disk is a rotating circumstellar disc of dense gas and dust surrounding a young newly formed star, a T Tauri star, or Herbig Ae/Be star. The protoplanetary disk may not be considered an accretion disk; while the two are similar, an accretion disk is hotter and spins much faster; it is also found on black holes, not stars. This process should not be confused with the accretion process thought to build up the planets themselves. Externally illuminated photo-evaporating protoplanetary disks are called proplyds. Formation Protostars form from molecular clouds consisting primarily of molecular hydrogen. When a portion of a molecular cloud reaches a critical size, mass, or density, it begins to collapse under its own gravity. As this collapsing cloud, called a solar nebula, becomes denser, random gas motions originally present in the cloud average out in favor of the direction of the nebula's net angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum causes the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation And Evolution Of The Solar System
There is evidence that the formation of the Solar System began about 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed. This model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, chemistry, geology, physics, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the Space Age in the 1950s and the discovery of exoplanets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations. The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetesimal
Planetesimals () are solid objects thought to exist in protoplanetary disks and debris disks. Believed to have formed in the Solar System about 4.6 billion years ago, they aid study of its formation. Formation A widely accepted theory of planet formation, the planetesimal hypothesis of Viktor Safronov, states that planets form from cosmic dust grains that collide and stick to form ever-larger bodies. Once a body reaches around a kilometer in size, its constituent grains can attract each other directly through mutual gravity, enormously aiding further growth into moon-sized protoplanets. Smaller bodies must instead rely on Brownian motion or turbulence to cause the collisions leading to sticking. The mechanics of collisions and mechanisms of sticking are intricate. Alternatively, planetesimals may form in a very dense layer of dust grains that undergoes a collective gravitational instability in the mid-plane of a protoplanetary disk—or via the concentration and gravitatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets by the most restrictive definition of the term: the terrestrial planets Mercury (planet), Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, and the giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a young protostar orbited by a protoplanetary disk. Planets grow in this disk by the gradual accumulation of material driven by gravity, a process called accretion (astrophysics), accretion. The word ''planet'' comes from the Greek () . In Classical antiquity, antiquity, this word referred to the Sun, Moon, and five points of light visible to the naked eye that moved across the background of the stars—namely, Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
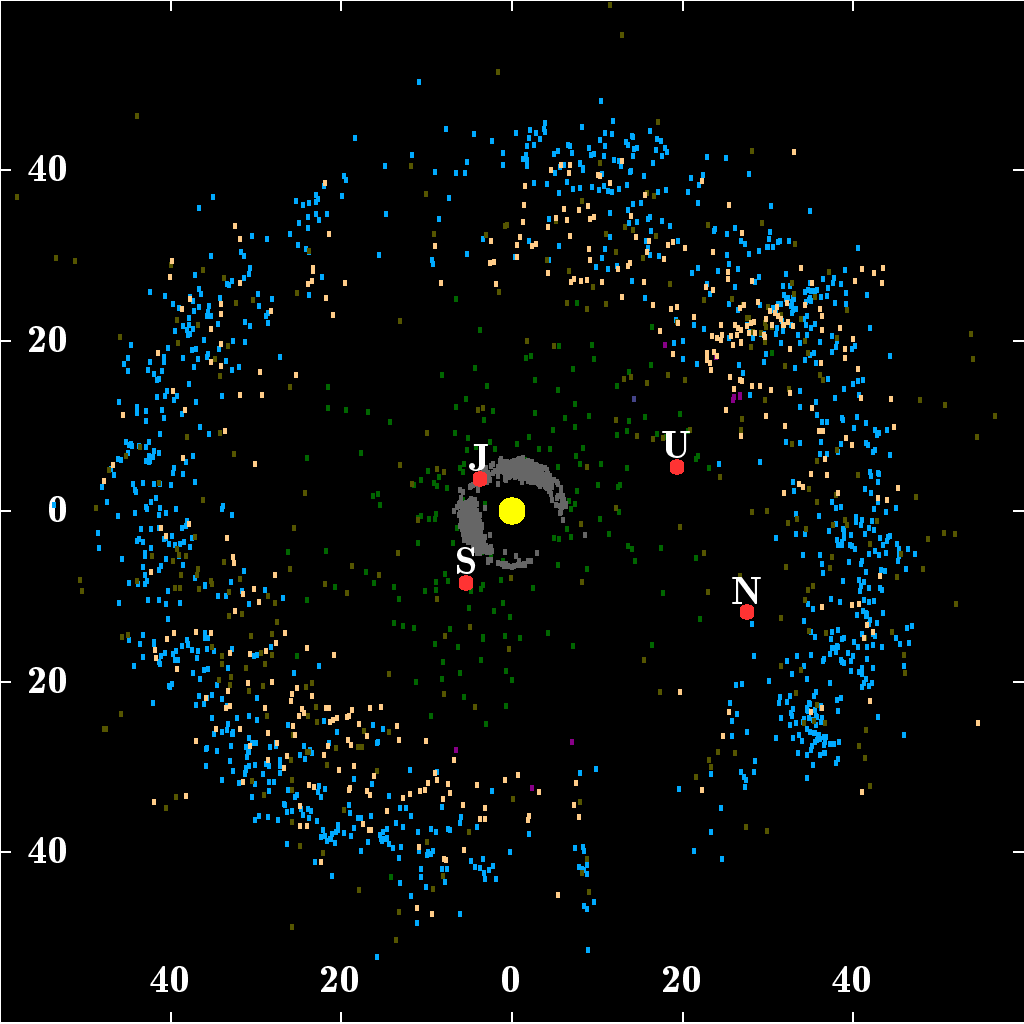
Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound Planetary system, system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It Formation and evolution of the Solar System, formed about 4.6 billion years ago when a dense region of a molecular cloud collapsed, forming the Sun and a protoplanetary disc. The Sun is a typical star that maintains a hydrostatic equilibrium, balanced equilibrium by the thermonuclear fusion, fusion of hydrogen into helium at its stellar core, core, releasing this energy from its outer photosphere. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2 Pallas
Pallas (minor-planet designation: 2 Pallas) is the List of largest asteroids, third-largest asteroid in the Solar System by volume and mass. It is the second asteroid to have been discovered, after 1 Ceres, Ceres, and is likely a remnant protoplanet. Like Ceres, it is believed to have a mineral composition similar to carbonaceous chondrite meteorites, though significantly less hydrated than Ceres. It is 79% the mass of 4 Vesta, Vesta and 22% the mass of Ceres, constituting an estimated 7% of the total mass of the asteroid belt. Its estimated volume is equivalent to a sphere in diameter, 90–95% the volume of Vesta. During the planetary formation era of the Solar System, objects grew in size through an accretion (astrophysics), accretion process to approximately the size of Pallas. Most of these protoplanets were incorporated into the growth of larger bodies, which became the planets, whereas others were ejected by the planets or destroyed in collisions with each other. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). Asteroids are rocky, metallic, or icy bodies with no atmosphere, and are broadly classified into C-type asteroid, C-type (carbonaceous), M-type asteroid, M-type (metallic), or S-type asteroid, S-type (silicaceous). The size and shape of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from small rubble piles under a kilometer across to Ceres (dwarf planet), Ceres, a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter. A body is classified as a comet, not an asteroid, if it shows a coma (tail) when warmed by solar radiation, although recent observations suggest a continuum between these types of bodies. Of the roughly one million known asteroids, the greatest number are located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, approximately 2 to 4 astronomical unit, AU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
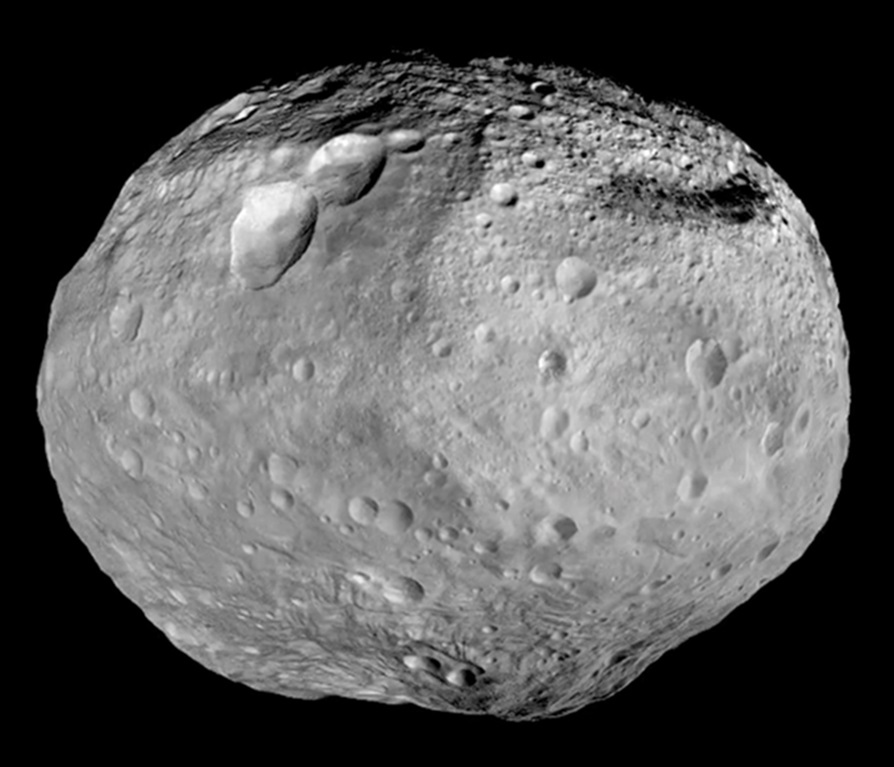
4 Vesta
Vesta (minor-planet designation: 4 Vesta) is one of the largest objects in the asteroid belt, with a mean diameter of . It was discovered by the German astronomer Heinrich Wilhelm Matthias Olbers on 29 March 1807 and is named after Vesta (mythology), Vesta, the virgin goddess of home and hearth from Roman mythology. Vesta is thought to be the second-largest asteroid, both by mass and by volume, after the dwarf planet Ceres (dwarf planet), Ceres. Measurements give it a nominal volume only slightly larger than that of 2 Pallas, Pallas (about 5% greater), but it is 25% to 30% more massive. It constitutes an estimated 9% of the mass of the asteroid belt. Vesta is the only known remaining rocky protoplanet of the kind that formed the terrestrial planets. Numerous fragments of Vesta were ejected by collisions one and two billion years ago that left two enormous craters occupying much of Vesta's southern hemisphere. Debris from these events has fallen to Earth as HED meteorite, howardi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceres (dwarf Planet)
Ceres (minor-planet designation: 1 Ceres) is a dwarf planet in the middle main asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It was the first known asteroid, discovered on 1 January 1801 by Giuseppe Piazzi at Palermo Astronomical Observatory in Sicily, and announced as a new planet. Ceres was later classified as an asteroid and then a dwarf planet, the only one not beyond Neptune's orbit. Ceres's diameter is about a quarter that of the Moon. Its small size means that even at its brightest it is too dim to be seen by the naked eye, except under extremely dark skies. Its apparent magnitude ranges from 6.7 to 9.3, peaking at opposition (planets), opposition (when it is closest to Earth) once every 15- to 16-month synodic period. As a result, its surface features are barely visible even with the most powerful telescopes, and little was known about it until the robotic NASA spacecraft Dawn (spacecraft), ''Dawn'' approached Ceres for its orbital mission in 2015. ''Dawn'' fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Differentiation
In planetary science, planetary differentiation is the process by which the chemical elements of a planetary body accumulate in different areas of that body, due to their physical or chemical behavior (e.g. density and chemical affinities). The process of planetary differentiation is mediated by partial melting with heat from radioactive isotope decay and planetary accretion. Planetary differentiation has occurred on planets, dwarf planets, the asteroid 4 Vesta, and natural satellites (such as the Moon). Physical differentiation Gravitational separation High- density materials tend to sink through lighter materials. This tendency is affected by the relative structural strengths, but such strength is reduced at temperatures where both materials are plastic or molten. Iron, the most common element that is likely to form a very dense molten metal phase, tends to congregate towards planetary interiors. With it, many siderophile elements (i.e. materials that readily alloy with iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuiper Belt
The Kuiper belt ( ) is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times as wide and 20–200 times as massive. Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small Solar System body, small bodies or remnants from when the Formation and evolution of the Solar System, Solar System formed. While many asteroids are composed primarily of rock (geology), rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen Volatile (astrogeology), volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane, ammonia, and water. The Kuiper belt is home to most of the objects that astronomers generally accept as dwarf planets: 90482 Orcus, Orcus, Pluto, Haumea, 50000 Quaoar, Quaoar, and Makemake. Some of the Solar System's natural satellite, moons, such as Neptune's Triton (moon), Triton and Saturn's Phoebe (moon), Phoebe, may ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Impact Hypothesis
The giant-impact hypothesis, sometimes called the Theia Impact, is an astrogeology hypothesis for the formation of the Moon first proposed in 1946 by Canadian geologist Reginald Daly. The hypothesis suggests that the Early Earth collided with a Mars-sized protoplanet of the same orbit approximately 4.5 billion years ago in the early Hadean eon (about 20 to 100 million years after the Solar System coalesced), and the ejecta of the impact event later accreted to form the Moon. The impactor planet is sometimes called Theia, named after the mythical Greek Titan who was the mother of Selene, the goddess of the Moon. Analysis of lunar rocks published in a 2016 report suggests that the impact might have been a direct hit, causing a fragmentation and thorough mixing of both parent bodies. The giant-impact hypothesis is currently the favored hypothesis for lunar formation among astronomers. Evidence that supports this hypothesis includes: * The Moon's orbit has a simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |