|
Proprioceptor
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position. Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of proprioceptors, which detect distinct kinesthetic parameters, such as joint position, movement, and load. Although all mobile animals possess proprioceptors, the structure of the sensory organs can vary across species. Proprioceptive signals are transmitted to the central nervous system, where they are integrated with information from other sensory systems, such as the visual system and the vestibular system, to create an overall representation of body position, movement, and acceleration. In many animals, sensory feedback from proprioceptors is essential for stabilizing body posture and coordinating body movement. System overview In vertebrates, limb movement and velocity (muscle length and the rate of change) are encoded by one group of se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hair Plate
Hair plates are a type of Proprioception, proprioceptor found in the folds of insect joints. They consist of a cluster of hairs, in which each hair is innervated by a single Mechanosensation, mechanosensory neuron. Functionally, hair plates operate as "limit-detectors" by signaling the extremes of joint movement, which then drives reflexive leg movement. Hair plate location and anatomy Hair plates consist of a field of cuticular hairs, in which each hair is innervated by a single mechanosensory neuron (Figure 1). Hair plates are positioned within folds of cuticle at joints, and the associated hairs are deflected during joint movement. The number of hairs across and within hair plates can vary and hair plates are found on different body parts, including the legs, neck, and antennae. On the legs of insects, hair plates are found at the proximal joints (i.e. thorax-coxa, coxa-trochanter, and trochanter-femur joints) across the front, middle, and hind legs. Hair plate neurons projec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campaniform Sensilla
Campaniform sensilla are a class of mechanoreceptors found in insects, which respond to local stress and strain within the animal's cuticle. Campaniform sensilla function as Proprioception, proprioceptors that detect mechanical load as resistance to muscle contraction, similar to mammalian Golgi tendon organs. Sensory feedback from campaniform sensilla is integrated in the control of posture and locomotion. Structure Each campaniform sensillum consists of a flexible dome, which is embedded in a spongy socket within the cuticle and innervated by the dendrites of a single bipolar sensory neuron (see schematic cross-section). Campaniform sensilla are often oval-shaped with long axes of about 5-10 μm (see SEM). Campaniform sensilla are distributed across the body surface of many insects. The fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'', for example, has over 680 sensilla. Campaniform sensilla are located in regions where stress is likely to be high, including on the legs, antennae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Ia Sensory Fiber
A type Ia sensory fiber, or a primary afferent fiber, is a type of afferent nerve fiber. It is the sensory fiber of a stretch receptor called the muscle spindle found in muscles, which constantly monitors the rate at which a muscle stretch changes. The information carried by type Ia fibers contributes to the sense of proprioception. Function of muscle spindles For the body to keep moving properly and with finesse, the nervous system has to have a constant input of sensory data coming from areas such as the muscles and joints. In order to receive a continuous stream of sensory data, the body has developed special sensory receptors called proprioceptors. Muscle spindles are a type of proprioceptor, and they are found inside the muscle itself. They lie parallel with the contractile fibers. This gives them the ability to monitor muscle length with precision. Types of sensory fibers This change in length of the spindle is transduced (transformed into electric membrane potentials) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golgi Tendon Organ
The Golgi tendon organ (GTO) (also called Golgi organ, tendon organ, neurotendinous organ or neurotendinous spindle) is a proprioceptor – a type of sensory receptor that senses changes in muscle tension. It lies at the interface between a muscle and its tendon known as the musculotendinous junction also known as the myotendinous junction. It provides the sensory component of the Golgi tendon reflex. The Golgi tendon organ is one of several eponymous terms named after the Italian physician Camillo Golgi. Structure The body of the Golgi tendon organ is made up of braided strands of collagen (intrafusal fasciculi) that are less compact than elsewhere in the tendon and are encapsulated. The capsule is connected in series (along a single path) with a group of muscle fibers () at one end, and merge into the tendon proper at the other. Each capsule is about long, has a diameter of about , and is perforated by one or more afferent type Ib sensory nerve fibers ( Aɑ fiber), whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
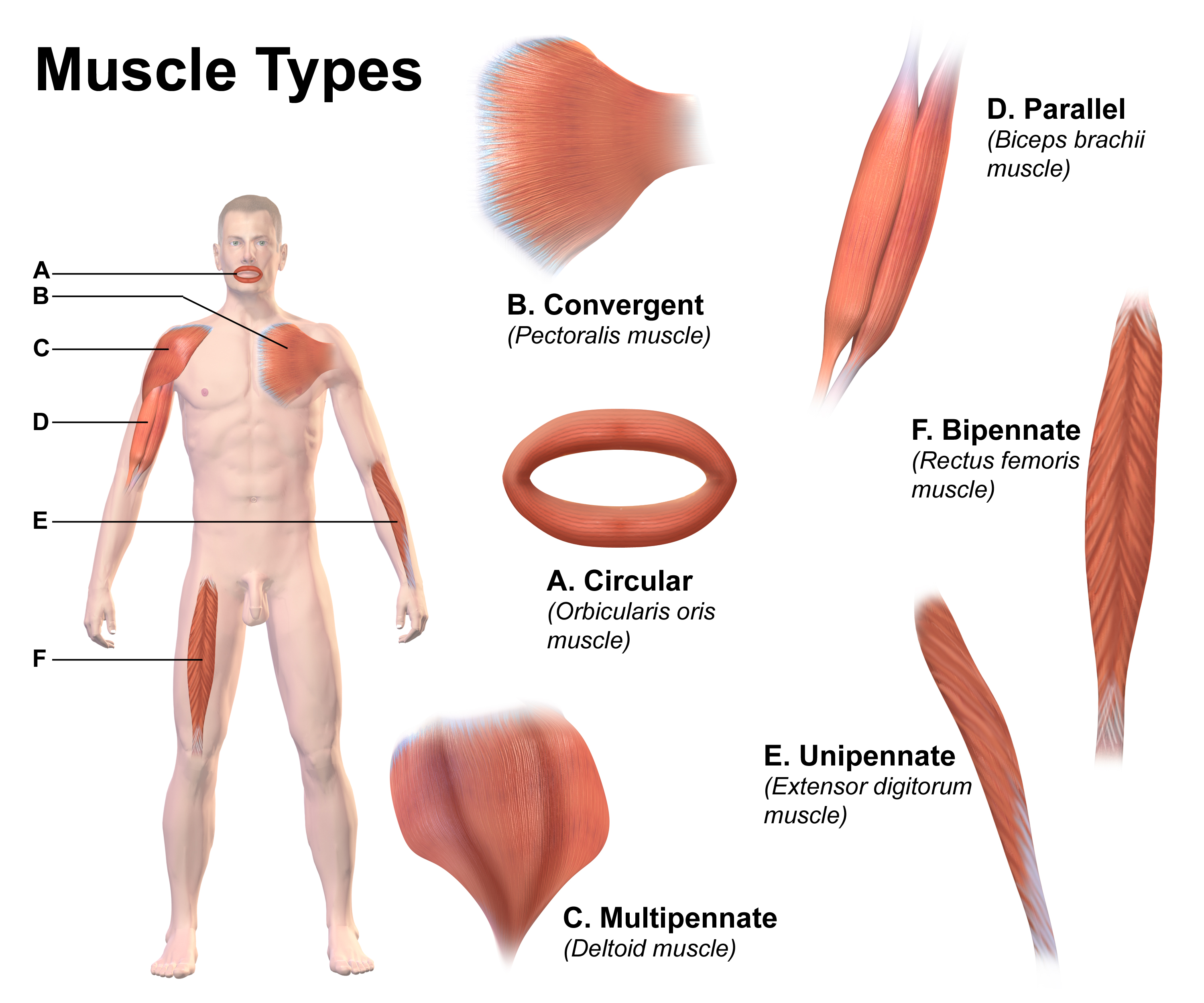
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral Spinocerebellar Tract
The spinocerebellar tracts are nerve tracts originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side ( ipsilateral) of the cerebellum. The two main tracts are the dorsal spinocerebellar tract, and the ventral spinocerebellar tract. Both of these tracts are located in the peripheral region of the lateral funiculi (white matter columns). Other tracts are the rostral spinocerebellar tract, and the cuneocerebellar tract (posterior external arcuate fibers). They carry proprioceptive, and cutaneous information to the cerebellum, where movement can be coordinated. Origins of proprioceptive information Proprioceptive information is obtained by Golgi tendon organs and muscle spindles. * Golgi tendon organs consist of a fibrous capsule enclosing tendon fascicles and bare nerve endings that respond to tension in the tendon by causing action potentials in type Ib afferents. These fibers are relatively large, myelinated, and quickly conducting. * Muscle spindles monitor the le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordotonal Organ
Chordotonal organs are stretch receptor organs found only in insects and crustaceans. They are located at most joints and are made up of clusters of scolopidia that either directly or indirectly connect two joints and sense their movements relative to one another. They can have both Exteroception, extero- and Proprioception, proprioceptive functions, for example sensing auditory stimuli or leg movement. The word was coined by Vitus Graber in 1882, though he interpreted them as being stretched between two points like a string, sensing vibrations through resonance. Structure Chordotonal organs can be composed of a single Scolopidia, scolopidium with only a single sensory, bipolar neuron (such as the Tympanal organ, tympanal ear of a notodontid moth), or up to several thousand scolopidia, each equipped with up to four sensory neurons (as in the mosquito Johnston's organ). The bipolar sensory neurons each have an apical dendritic structure with a cilium densely packed with microtubu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the surroundings through the detection of Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. Although, in some cultures, five human senses were traditionally identified as such (namely Visual perception, sight, Olfaction, smell, Somatosensory system, touch, taste, and hearing), many more are now recognized. Senses used by non-human organisms are even greater in variety and number. During sensation, sense organs collect various stimuli (such as a sound or smell) for Transduction (physiology), transduction, meaning transformation into a form that can be understood by the brain. Sensation and perception are fundamental to nearly every aspect of an organism's cognition, behavior and thought. In organisms, a sensory organ consists of a group of interrelated Sensory neuron, sensory cells that respond to a specific type of physical stimulus. Via Cranial nerves, cranial and spinal nerves (nerves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Righting Reflex
The righting reflex, also known as the labyrinthine righting reflex, or the Cervico-collic reflex; is a reflex that corrects the orientation of the body when it is taken out of its normal upright position. It is initiated by the vestibular system, which detects that the body is not erect and causes the head to move back into position as the rest of the body follows. The perception of head movement involves the body sensing linear acceleration or the force of gravity through the otoliths, and angular acceleration through the semicircular canals. The reflex uses a combination of visual system inputs, vestibular inputs, and somatosensory inputs to make postural adjustments when the body becomes displaced from its normal vertical position. These inputs are used to create what is called an efference copy. This means that the brain makes comparisons in the cerebellum between expected posture and perceived posture, and corrects for the difference. The reflex takes 6 or 7 weeks to perfect, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |