|
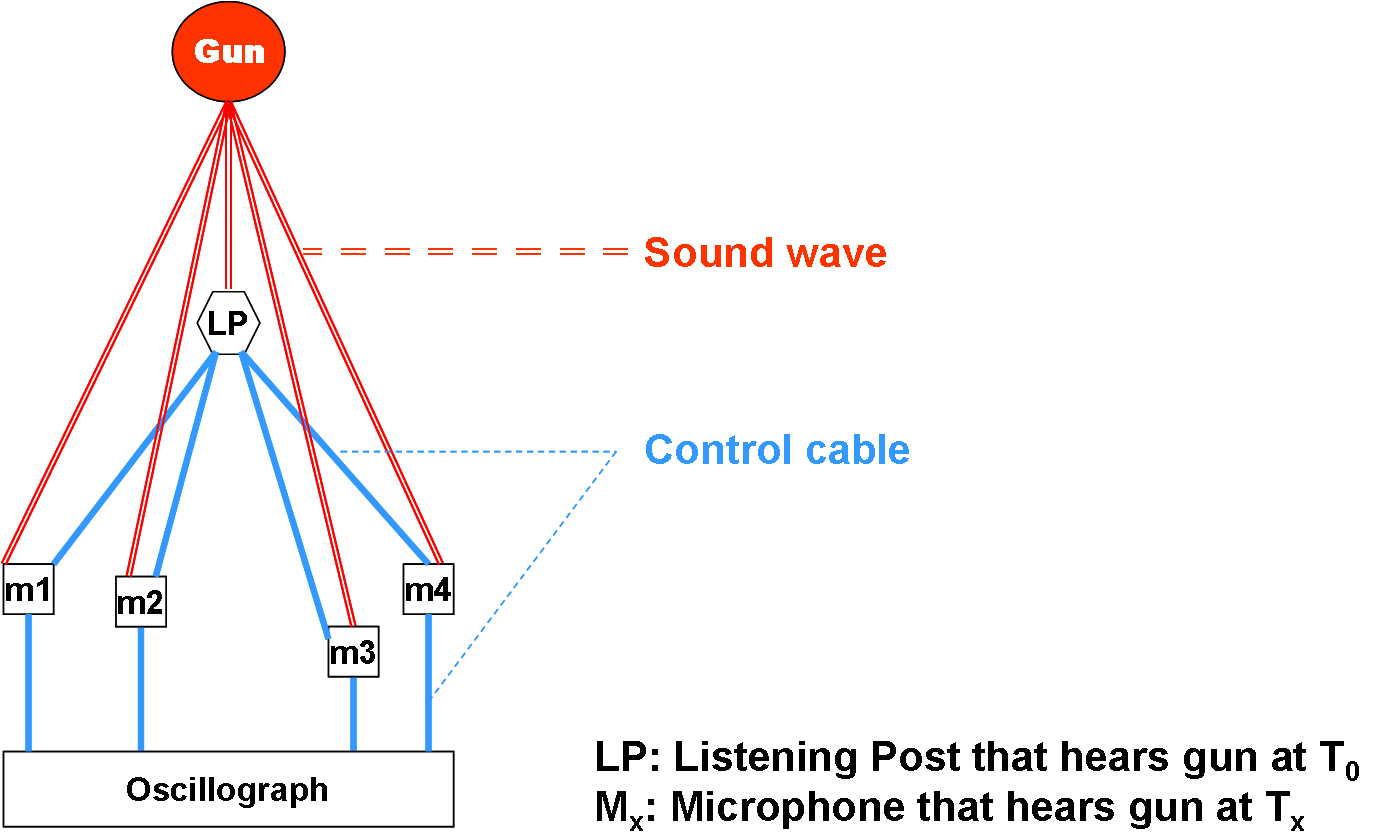
Project Mogul
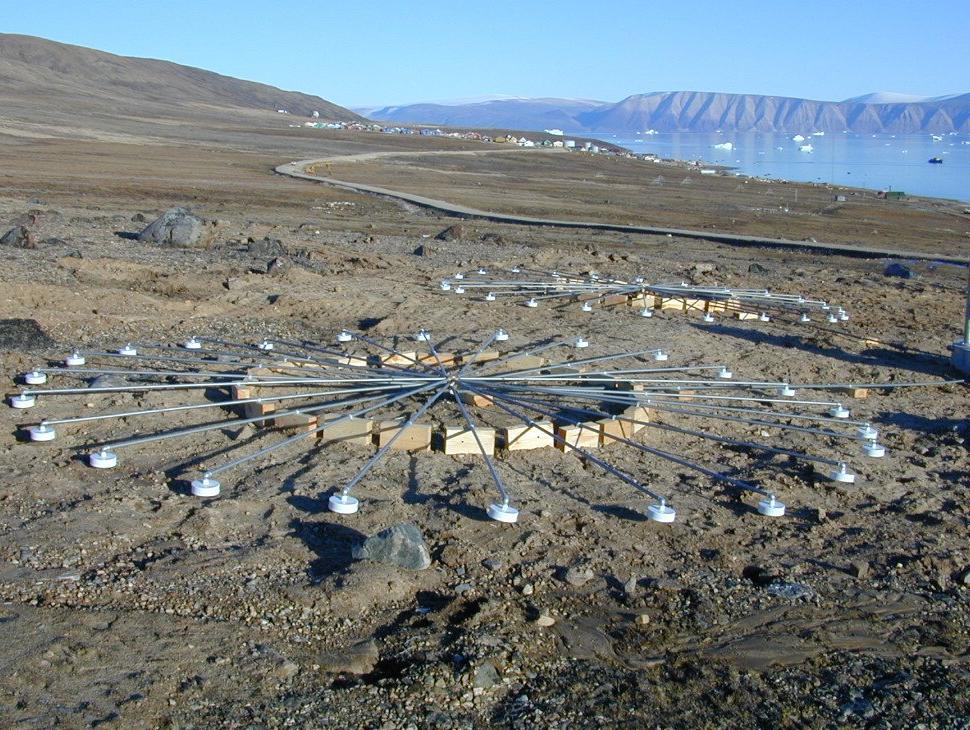
Project Mogul (sometimes referred to as Operation Mogul) was a top secret project by the US Army Air Forces involving microphones flown on high-altitude balloons, whose primary purpose was long-distance detection of sound waves generated by Soviet atomic bomb tests. The project was carried out from 1947 until early 1949. It was a classified portion of an unclassified project by New York University (NYU) atmospheric researchers. The project was moderately successful, but was very expensive and was superseded by a network of seismic detectors and air sampling for fallout, which were cheaper, more reliable, and easier to deploy and operate. Project Mogul was conceived by Maurice Ewing who had earlier researched the deep sound channel in the oceans and theorized that a similar sound channel existed in the upper atmosphere: a certain height where the air pressure and temperature result in minimal speed of sound, so that sound waves would propagate and stay in that channel due to refrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classified Information
Classified information is material that a government body deems to be sensitive information that must be protected. Access is restricted by law or regulation to particular groups of people with the necessary security clearance and need to know, and mishandling of the material can incur criminal penalties. A formal security clearance is required to view or handle classified material. The clearance process requires a satisfactory background investigation. Documents and other information must be properly marked "by the author" with one of several (hierarchical) levels of sensitivity—e.g. restricted, confidential, secret, and top secret. The choice of level is based on an impact assessment; governments have their own criteria, including how to determine the classification of an information asset and rules on how to protect information classified at each level. This process often includes security clearances for personnel handling the information. Some corporations and non-go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling and melting point are the lowest among all the elements. It is the second lightest and second most abundant element in the observable universe (hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant). It is present at about 24% of the total elemental mass, which is more than 12 times the mass of all the heavier elements combined. Its abundance is similar to this in both the Sun and in Jupiter, due to the very high nuclear binding energy (per nucleon) of helium-4, with respect to the next three elements after helium. This helium-4 binding energy also accounts for why it is a product of both nuclear fusion and radioactive decay. The most common isotope of helium in the universe is helium-4, the vast majority of which was formed during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysical MASINT
Geophysical MASINT is a branch of Measurement and Signature Intelligence (MASINT) that involves phenomena transmitted through the earth (ground, water, atmosphere) and manmade structures including emitted or reflected sounds, pressure waves, vibrations, and magnetic field or ionosphere disturbances. According to the United States Department of Defense, MASINT has technically derived intelligence (excluding traditional imagery IMINT and signals intelligence Signals intelligence, SIGINT) that – when collected, processed, and analyzed by dedicated MASINT systems – results in intelligence that detects, tracks, identifies or describes the signatures (distinctive characteristics) of fixed or dynamic target sources. MASINT was recognized as a formal intelligence discipline in 1986. Another way to describe MASINT is a "non-literal" discipline. It feeds on a target's unintended emissive by-products, the "trails" - the spectral, chemical or RF that an object leaves behind. These trails f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrasound
Infrasound, sometimes referred to as low status sound, describes sound waves with a frequency below the lower limit of human audibility (generally 20 Hz). Hearing becomes gradually less sensitive as frequency decreases, so for humans to perceive infrasound, the sound pressure must be sufficiently high. The ear is the primary organ for sensing low sound, but at higher intensities it is possible to feel infrasound vibrations in various parts of the body. The study of such sound waves is sometimes referred to as infrasonics, covering sounds beneath 20 Hz down to 0.1 Hz (and rarely to 0.001 Hz). People use this frequency range for monitoring earthquakes and volcanoes, charting rock and petroleum formations below the earth, and also in ballistocardiography and seismocardiography to study the mechanics of the heart. Infrasound is characterized by an ability to get around obstacles with little dissipation. In music, acoustic waveguide methods, such as a large pipe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national "newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roswell, New Mexico
Roswell () is a city in, and the seat of, Chaves County in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Chaves County forms the entirety of the Roswell micropolitan area. As of the 2020 census it had a population of 48,422, making it the fifth-largest city in New Mexico. It is home of the New Mexico Military Institute (NMMI), founded in 1891. The city is also the location of an Eastern New Mexico University campus. Bitter Lake National Wildlife Refuge is located a few miles northeast of the city on the Pecos River. Bottomless Lakes State Park is located east of Roswell on US 380. The Roswell incident was named after the town, though the crash site of the alleged UFO was some from Roswell and closer to Corona. The investigation and debris recovery was handled by the local Roswell Army Air Field. On the 50th anniversary of the Roswell UFO incident the UFO Festival was started. In the 1930s, Roswell was a site for much of Robert H. Goddard's early rocketry work. The Roswell Museu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
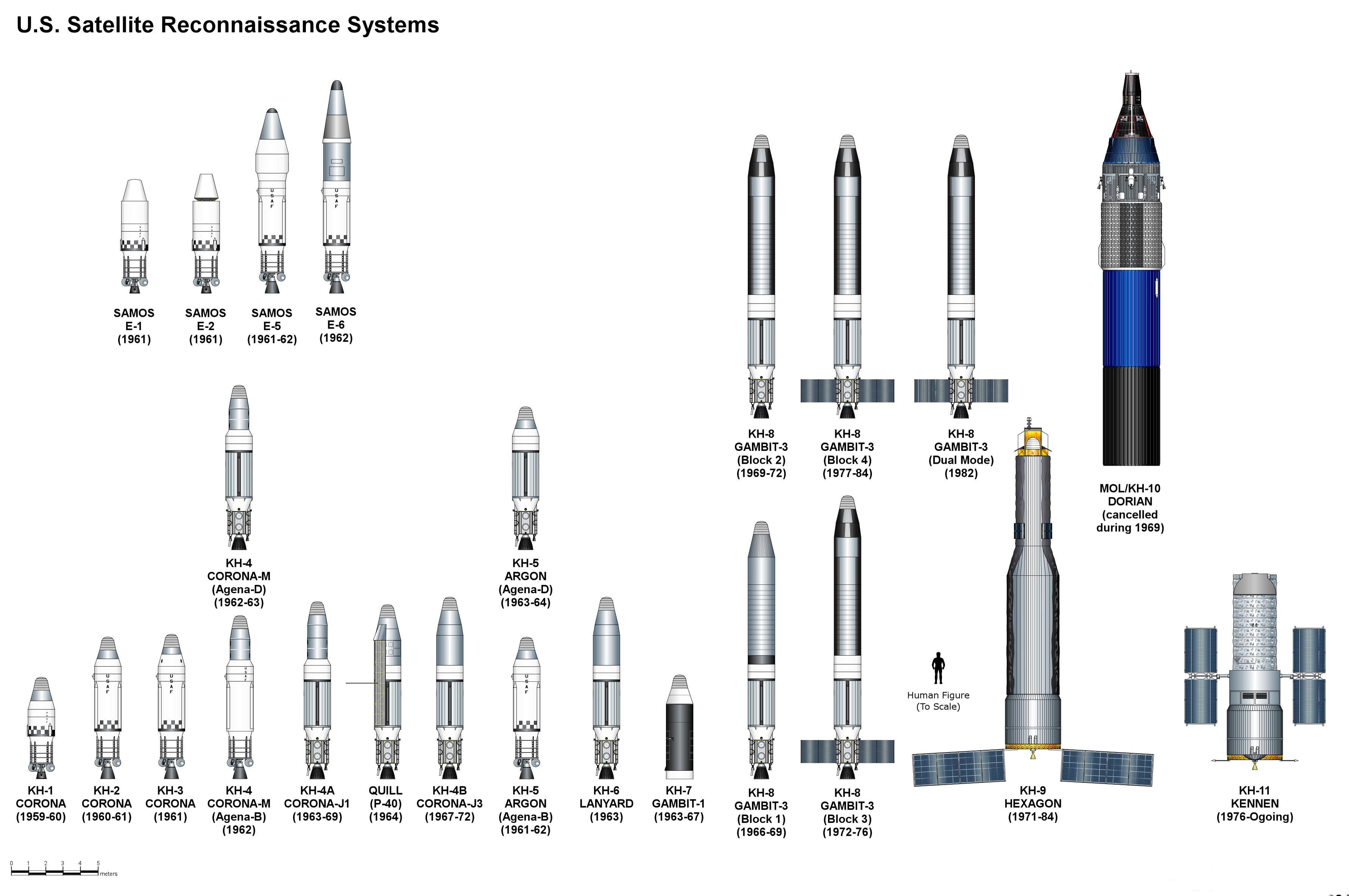
Reconnaissance Satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The first generation type (i.e., Corona and Zenit) took photographs, then ejected canisters of photographic film which would descend back down into Earth's atmosphere. Corona capsules were retrieved in mid-air as they floated down on parachutes. Later, spacecraft had digital imaging systems and downloaded the images via encrypted radio links. In the United States, most information available about reconnaissance satellites is on programs that existed up to 1972, as this information has been declassified due to its age. Some information about programs before that time is still classified information, and a small amount of information is available on subsequent missions. A few up-to-date reconnaissance satellite images have been declassif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
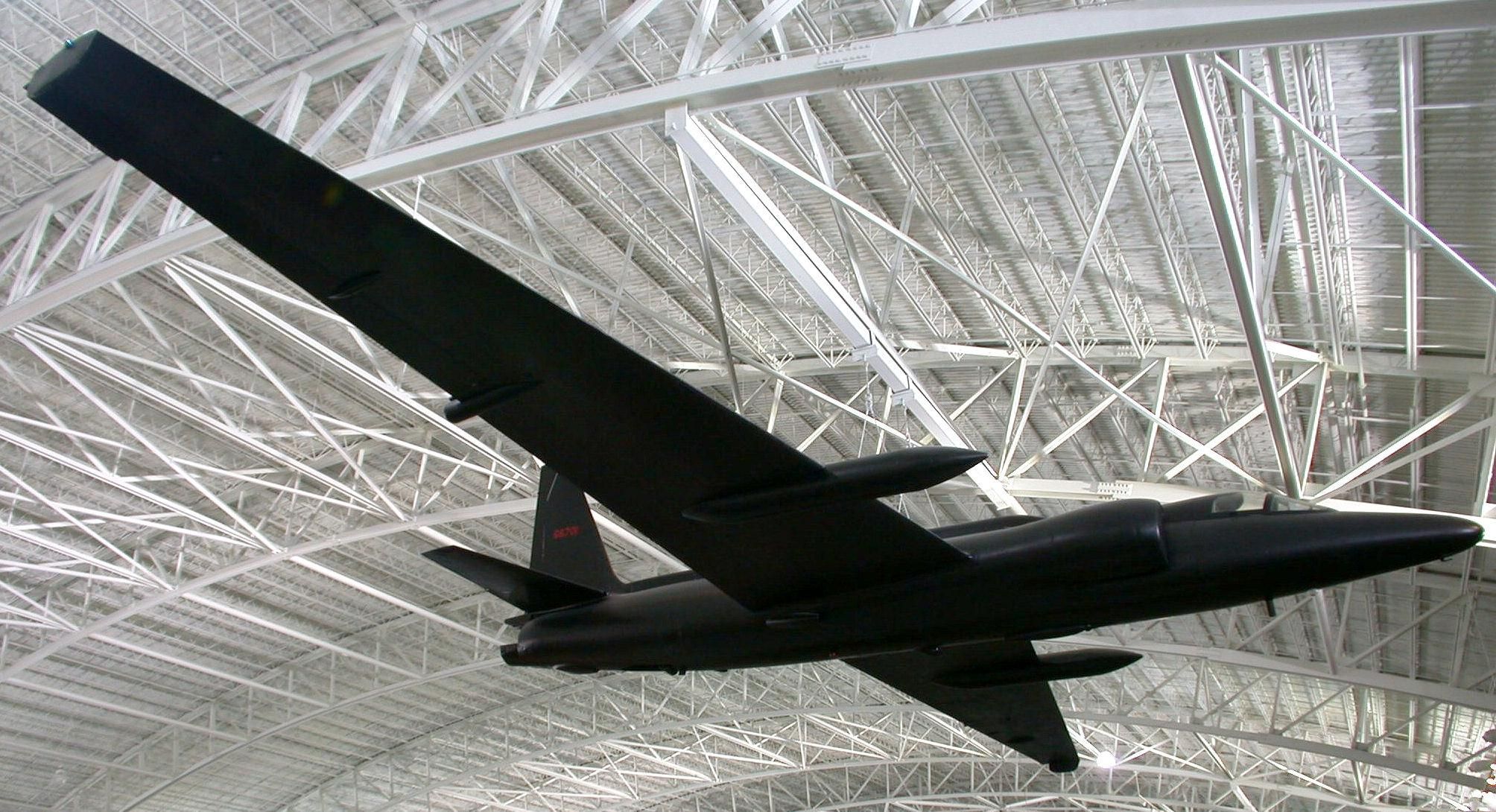
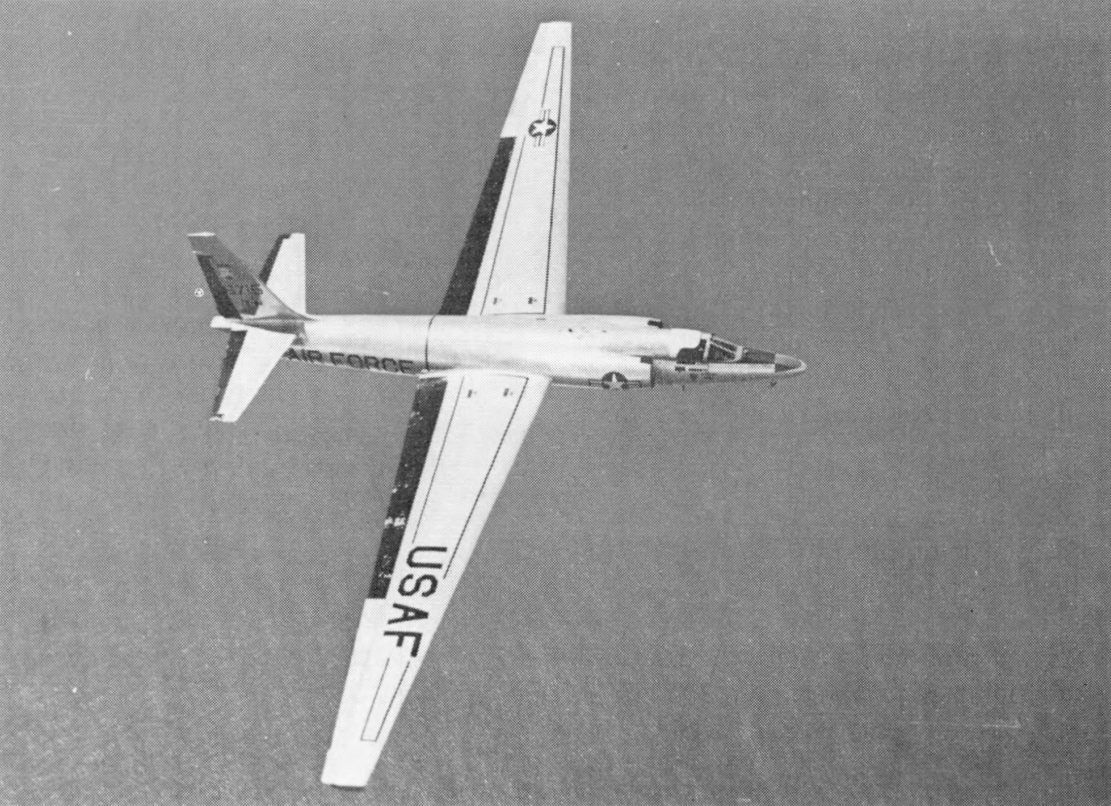
1960 U-2 Incident
On 1 May 1960, a United States U-2 spy plane was shot down by the Soviet Air Defence Forces while conducting photographic aerial reconnaissance deep inside Soviet territory. The single-seat aircraft, flown by American pilot Francis Gary Powers, had taken off from Peshawar, Pakistan, and crashed near Sverdlovsk (present-day Yekaterinburg), after being hit by an S-75 Dvina (SA-2 Guideline) surface-to-air missile. Powers parachuted to the ground safely and was captured. Initially, American authorities acknowledged the incident as the loss of a civilian weather research aircraft operated by NASA, but were forced to admit the mission's true purpose a few days later after the Soviet government produced the captured pilot and parts of the U-2's surveillance equipment, including photographs of Soviet military bases. The incident occurred during the tenures of American president Dwight D. Eisenhower and Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev, around two weeks before the scheduled o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Aerial Reconnaissance Of The Soviet Union
Between 1946 and 1960, the United States Air Force conducted aerial reconnaissance flights over the Soviet Union in order to determine the size, composition, and disposition of Soviet forces. Aircraft used included the Boeing B-47 Stratojet bomber and—from 1956—the Lockheed U-2 spy plane specifically designed for high-altitude reconnaissance flight. The overflight program was ended following the 1960 U-2 incident. Background After the second world war, the Iron Curtain made it hard for the United States to gather information in regards to the Soviet Union. The information gathered before the start of the reconnaissance flights were hugely limited and failed to satisfy what the U.S. intelligence sector wanted. Reconnaissance flights with fixed-wing jet aircraft began in 1946 along the borders of the Soviet Union and other Eastern Bloc states. The necessity of peacetime overflights was reinforced after the escalation of the Cold War in the late 1940s, and in particular after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Detonation Detection System
A nuclear detonation detection system (NDDS) is a device or a series of devices that are able to indicate, and pinpoint a nuclear explosion has occurred as well as the direction of the explosion. The main purpose of these devices or systems was to verify compliance of countries that signed nuclear treaties such as the Partial Test Ban treaty of 1963 (PTBT) and the Treaty of Tlatelolco. There are many different ways to detect a nuclear detonation, these include seismic, hydroacoustic, and infrasound detection, air sampling, and satellites. They have their own weaknesses and strengths, as well as different utilities. Each has been used separately, but at present the best results occur when data is used in tandem, since the energy caused by an explosion will transfer over to different mediums. Seismic Seismic networks are one of the possibilities of detonation detection. During an above ground nuclear explosion, there will be a blooming mushroom in the sky, but there will also be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface, although the bulk is deflected off into space by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere. Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics. Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are used on satellites and space probes for research into cosmic rays. Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013) have been interpreted as evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Genetrix
Project Genetrix, also known as WS-119L, was a United States Air Force program designed to launch General Mills manufactured surveillance balloons over Communist China, Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union to take aerial photographs and collect intelligence. The Genetrix balloons reached altitudes of 50,000–100,000 feet (15–30 km), well above any contemporary fighter plane. In 1955 a number of AN/DMQ-1 gondolas were launched from Lowry Air Force Base in Colorado as a test of the system. One was recovered years later in New Brunswick. Between 10 January and 6 February 1956, a total of 516 high-altitude vehicles were launched from the five different launch sites Gardermoen, Norway; Evanton, Scotland; Oberpfaffenhofen and Giebelstadt, West Germany; and Incirlik, Turkey; 54 were recovered and only 31 provided usable photographs. Numerous balloons were shot down or blown off course, and the flights led to many diplomatic protests from the target countries. MiG fighter pilo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)