|
Progressive Political Parties (Japan)
Kakushin seitō , meaning reformist political parties or progressive political parties, is an umbrella term used in Japan to refer to a variety of left-leaning political parties generally viewed as "anti-conservative." In the postwar period, it has generally been applied to democratic socialist, social democratic and socially progressive parties that seek to uphold Article 9 of the Japanese Constitution. Japan's "progressive parties" are basically opposed to constitutional amendments led by right-wing conservatives, so they are partly in solidarity with moderate liberal parties. "Kakushin" parties have been considered progressive or radical-liberal forces. In general, while the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) has a strong conservative tendency, the Japanese Communist Party (JCP) has shown a strong progressive tendency in the Japanese political spectrum. In the 21st century, not only traditional democratic socialist parties but also some liberal parties began to be regarded as part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postwar Japan
Postwar Japan is the period in Japanese history beginning with the surrender of Japan to the Allies of World War II on 2 September 1945, and lasting at least until the end of the Shōwa era in 1989. Despite the massive devastation it suffered in the Second World War, Japan established itself as a global economic power at peace with the world after the Allied-occupation ended on 28 April 1952 by the Treaty of San Francisco. In terms of political power it was more reluctant, especially in the nonuse of military force. The post-war constitution of 1947 included Article 9, which restricted Japan from having a military force and engaging in war. However, it has operated military forces in the stationing of the United States Forces Japan based on the U.S.-Japan Security Treaty after the Allied occupation and the form of the Japanese Self-Defense Forces since 1954. Over the years, the meaning of Article 9 has been interpreted differently, because the United States now encour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Socialist Party
The was a major socialist and progressive political party in Japan which existed from 1945 to 1996. The party was the primary representative of the Japanese left and main opponent of the right-wing Liberal Democratic Party for most of its existence. The JSP was founded in 1945 by members of pre-war proletarian parties, including the Shakai Taishūtō. In the 1947 election, the JSP became the largest party in the National Diet and formed a government under Tetsu Katayama until 1948. From 1951 to 1955, the JSP was split into the Left Socialist Party and the Right Socialist Party, and in 1960 some of its members broke away to form the rival Democratic Socialist Party. In 1955, Japan's two major conservative parties merged to form the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP), which has held power near-continuously since. The JSP was the largest opposition party for the next 40 years, but was incapable of forming a government. Nonetheless, it managed to hold about one third of the sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Media In Japan
The mass media in Japan include numerous television and radio networks as well as newspapers and magazines in Japan. For the most part, television networks were established based on capital investments by existing radio networks. Variety shows, serial dramas, and news constitute a large percentage of Japanese evening shows. Western movies are also shown, many with a subchannel for English. There are all-English television channels on cable and satellite (with Japanese subtitles). Television networks There are 6 nationwide television networks, as follows: * NHK is a public service broadcaster. The company is financed through "viewer fees," similar to the licence fee system used in the UK to fund the BBC. NHK deliberately maintains neutral reporting as a public broadcast station, even refusing to mention commodity brand names. NHK has 2 terrestrial TV channels, unlike the other TV networks (in the Tokyo region—channel 1 (NHK General TV) and channel 3 (NHK Educational TV)). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomiichi Murayama
is a Japanese politician who served as Prime Minister of Japan from 1994 to 1996. He was the country's first socialist premier since Tetsu Katayama in 1948, and is best remembered for the Murayama Statement on the 50th anniversary of the end of World War II, in which he officially apologized for Japan's past colonial wars and aggression. Born in Ōita Prefecture, Murayama graduated from Meiji University in 1946, and became a labor union official in his home prefecture. He was elected to the Ōita City Council in 1955 as a member of the Japan Socialist Party; he was then elected to the Ōita Prefectural Assembly in 1963 and to the National Diet in 1972. After the JSP joined the government following the 1993 election, he became its leader, then became prime minister in 1994 as the head of a new coalition of the JSP, Liberal Democratic Party, and New Party Sakigake. Murayama reversed his party's long-standing opposition to the U.S.–Japan Security Treaty, and his government w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reiwa Shinsengumi
is a Progressivism, progressive and left-wing populist List of political parties in Japan, political party in Japan founded by actor-turned-politician Taro Yamamoto in April 2019. The party was formed by left-wing members of the Liberal Party (Japan, 2016), Liberal Party who opposed its merger with the Democratic Party for the People. The party won more than 4% of the vote after contesting the 2019 Japanese House of Councillors election, House of Councilors election in July 2019, gaining two seats only about three and a half months after the formation of the party. History Founding Taro Yamamoto, a member of the House of Councillors (Japan), House of Councillors for Tokyo at-large district, Tokyo, founded the party on 1 April 2019. This was with the intent of standing multiple candidates, including himself, in the upcoming House of Councillors election later in the year. On 10 April, Yamamoto held a press conference and announced the party's platform. 2019 House of Councillors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberal Party (Japan, 2016)
The was a political party in Japan that merged with the Democratic Party For the People on 26 April 2019. It had 2 out of the 475 seats in the House of Representatives, and 3 in the 242-member House of Councillors prior to merging. Formed as the in December 2012, it changed its name to in December 2014. The party adopted the name Liberal Party in October 2016 in preparation for an expected general election in early 2017. History Foundation The party's foundation lay in the wake of the December 2012 general election, in which the Tomorrow Party of Japan's membership in the 480-seat House of Representatives was reduced from 61 members to just 9. Tension between President Yukiko Kada and former People's Life First party leader Ichirō Ozawa increased to the point that on 26 December 2012 the party's remaining Diet members that were aligned with Ozawa held a meeting in spite of Kada's instruction not to do so. Members aligned with Kada announced their intention to leave the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Democratic Party Of Japan
The is a Liberalism, liberal List of political parties in Japan, political party in Japan. It is the primary centre-left politics, centre-left party in Japan, and as of 2024 is the second largest party in the National Diet behind the ruling Liberal Democratic Party (Japan), Liberal Democratic Party (LDP). It was founded in October 2017 as a split from the Democratic Party (Japan, 2016), Democratic Party ahead of the 2017 Japanese general election, 2017 general election. In late 2020, the party was re-founded following a merger with majorities of the Democratic Party For the People and the Social Democratic Party (Japan), Social Democratic Party as well as some independent lawmakers. The party's platform supports raising the minimum wage, expanded welfare spending, welfare policies, the legalization of same-sex marriage, increased gender equality, renewable energy policies, decentralization, a multilateralism, multilateral foreign policy, the revision of the U.S.–Japan Statu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
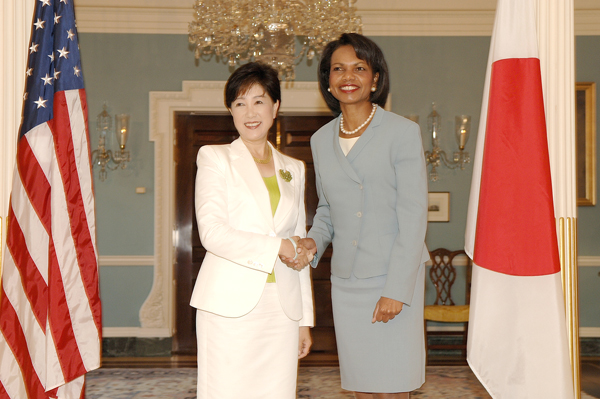
Yuriko Koike
Yuriko Koike (小池 百合子, Koike Yuriko; born 15 July 1952) is a Japanese politician who has served as the Governor of Tokyo since 2016. Previously, she was also served as a member of the House of Councillors from 1992 to 1993, a member of the House of Representatives from 1993 to 2016, Minister of the Environment under from 2003 to 2006, and Minister of Defense in between July and August 2007. Born and raised in Ashiya, a wealthy, small, and popular city near Kobe in Hyōgo Prefecture, Koike graduated from Cairo University in Cairo, Egypt in 1976, and served as a member of the House of Representatives of Japan from 1993 until 2016, when she resigned to run for Governor of Tokyo. Previously, she also served as the Minister of the Environment under Junichiro Koizumi's cabinet from 2003 to 2006 and briefly as Minister of Defense under the first cabinet of Shinzo Abe in between July and August 2007. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kibō No Tō
was a Conservatism, conservative List of political parties in Japan, political party in Japan founded by Governor of Tokyo, Tokyo Governor Yuriko Koike. The party was founded just before the call of the 2017 Japanese general election, 2017 general election. The party's ideology was mainly Japanese conservatism and Japanese nationalism, nationalism. Kibō no Tō merged with the Democratic Party (Japan, 2016), Democratic Party to form the Democratic Party For the People on 7 May 2018. However, some right-wing populist members decided to form a new party with the same name. In October 2021, the party disbanded a second time. History In 2016's 2016 Tokyo gubernatorial election, gubernatorial election, Governor Koike was elected as the Governor with membership of the Liberal Democratic Party (Japan), Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) even though she was not the official candidate of the party.The official candidate was Hiroya Masuda. Then, she formed a regional party: Tomin First no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Party (Japan, 2016)
The was a political party in Japan. It was the largest opposition political party in Japan from 2016 until its marginalization in the House of Representatives in 2017.民進英語名、略称DPに Yomiuri Shimbun The party was founded on 27 March 2016 from the merger of the and the . The majority of the party split on 28 September 2017, before the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Democratic Party (Japan)
The is a political party in Japan that was established in 1996. Since its reformation and name change in 1996, it has advocated pacifism and defined itself as a social-democratic party. It was previously known as the . The party was re-founded in January 1996 by the majority of legislators of the former Japan Socialist Party, which was the largest opposition party in the 1955 System. However, most of those legislators joined the Democratic Party of Japan after that. Five leftist legislators who did not join the SDP formed the New Socialist Party, which lost all its seats in the following election. The SDP enjoyed a short period of government participation from 1993 to 1994 as part of the Hosokawa Cabinet and later formed a coalition government with the Liberal Democratic Party under 81st Prime Minister Tomiichi Murayama of the JSP from 1994 to January 1996. The SDP was part of ruling coalitions between January and November 1996 ( First Hashimoto Cabinet) and from 2009 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |