|
Process Calculi
In computer science, the process calculi (or process algebras) are a diverse family of related approaches for formally modelling concurrent systems. Process calculi provide a tool for the high-level description of interactions, communications, and synchronizations between a collection of independent agents or processes. They also provide algebraic laws that allow process descriptions to be manipulated and analyzed, and permit formal reasoning about equivalences between processes (e.g., using bisimulation). Leading examples of process calculi include CSP, CCS, ACP, and LOTOS. More recent additions to the family include the π-calculus, the ambient calculus, PEPA, the fusion calculus and the join-calculus. Essential features While the variety of existing process calculi is very large (including variants that incorporate stochastic behaviour, timing information, and specializations for studying molecular interactions), there are several features that all process calculi have i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, automation, and information. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, information theory, and automation) to practical disciplines (including the design and implementation of hardware and software). Computer science is generally considered an area of academic research and distinct from computer programming. Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and for preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of repositories ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
π-calculus
In theoretical computer science, the -calculus (or pi-calculus) is a process calculus. The -calculus allows channel names to be communicated along the channels themselves, and in this way it is able to describe concurrent computations whose network configuration may change during the computation. The -calculus has few terms and is a small, yet expressive language (see ). Functional programs can be encoded into the -calculus, and the encoding emphasises the dialogue nature of computation, drawing connections with game semantics. Extensions of the -calculus, such as the spi calculus and applied , have been successful in reasoning about cryptographic protocols. Beside the original use in describing concurrent systems, the -calculus has also been used to reason about business processesOMG Specification (2011)"Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) Version 2.0" ''Object Management Group''. p.21 and molecular biology. Informal definition The -calculus belongs to the family of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Bergstra
Johannes Aldert "Jan" Bergstra (born 1951) is a Dutch computer scientist. His work has focussed on logic and the theoretical foundations of software engineering, especially on formal methods for system design. He is best known as an expert on algebraic methods for the specification of data and computational processes in general. Biography Jan Bergstra was born in 1951 in Rotterdam, the son of Tjeerd Bergstra and Johanna Bisschop.Jan A. Bergstra (2009)Curriculum Vitae Jan Aldert Bergstra at ''uva.nl''. October 20, 2009. Accessed August 30, 2013 He was educated at the Montessori Lyceum Rotterdam (gymnasium beta) and then studied mathematics at Utrecht University, starting in 1969. After an MSc he wrote a PhD thesis, defended in 1976, on recursion theory in higher types, under the supervision of Dirk van Dalen. Bergstra held posts at the Institute of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science of the University of Leiden (1976–82), and the Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica (CWI) in Ams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robin Milner
Arthur John Robin Gorell Milner (13 January 1934 – 20 March 2010), known as Robin Milner or A. J. R. G. Milner, was a British computer scientist, and a Turing Award winner.Obituary – Professor Robin Milner: computer scientist '''', 31 March 2010. Life, education and career Milner was born in Yealmpton, near , |
Actor Model
The actor model in computer science is a mathematical model of concurrent computation that treats ''actor'' as the universal primitive of concurrent computation. In response to a message it receives, an actor can: make local decisions, create more actors, send more messages, and determine how to respond to the next message received. Actors may modify their own private state, but can only affect each other indirectly through messaging (removing the need for lock-based synchronization). The actor model originated in 1973. It has been used both as a framework for a theoretical understanding of computation and as the theoretical basis for several practical implementations of concurrent systems. The relationship of the model to other work is discussed in actor model and process calculi. History According to Carl Hewitt, unlike previous models of computation, the actor model was inspired by physics, including general relativity and quantum mechanics. It was also influenced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
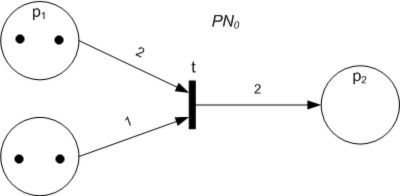
Petri Net A Petri net, also known as a place/transition (PT) net, is one of several mathematical modeling languages for the description of distributed systems. It is a class of discrete event dynamic system. A Petri net is a directed bipartite graph that has two types of elements, places and transitions. Place elements are depicted as white circles and transition elements are depicted as rectangles. A place can contain any number of tokens, depicted as black circles. A transition is enabled if all places connected to it as inputs contain at least one token. Some sources state that Petri nets were invented in August 1939 by Carl Adam Petri—at the age of 13—for the purpose of describing chemical processes. Like industry standards such as UML activity diagrams, Business Process Model and Notation, and event-driven process chains, Petri nets offer a graphical notation for stepwise processes that include choice, iteration, and concurrent execution. Unlike these standards, Petri nets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] < |