|
Port Wine, Queensland
Port Wine is a former rural locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , Port Wine had a population of 27 people. On 22 November 2019 the Queensland Government decided to amalgamate the localities in the Barcaldine Region, resulting in five expanded localities based on the larger towns: Alpha, Aramac, Barcaldine, Jericho and Muttaburra. Port Wine was incorporated into Alpha. Geography The Central Western railway line forms the northern boundary of the locality. The Capricorn Highway also traverses the north of the locality from east to west but diverges south from the railway line unlike other localities in which the railway and highway are adjacent. The western branch of the Belyando River enters the locality from the south-west (Sedgeford) while the eastern branch rises in the south of the locality. The two branches merge within the locality and then flow north to exit the locality to the north-west (Beaufort). The Beylando River is a tributary to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AEST
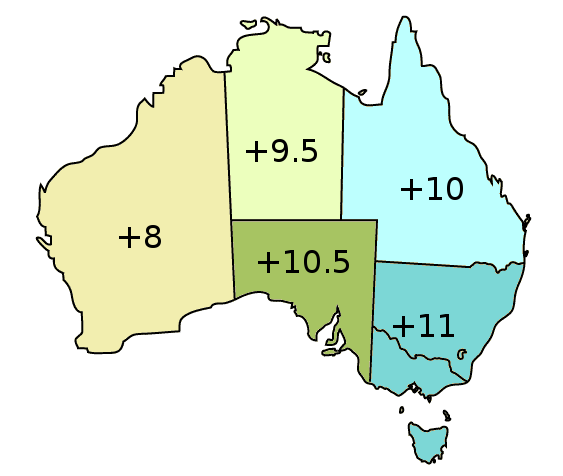
Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Western Standard Time (AWST; UTC+08:00), Australian Central Standard Time (ACST; UTC+09:30), and Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST; UTC+10:00). Time is regulated by the individual state governments, some of which observe daylight saving time (DST). Australia's external territories observe different time zones. Standard time was introduced in the 1890s when all of the Australian colonies adopted it. Before the switch to standard time zones, each local city or town was free to determine its local time, called local mean time. Now, Western Australia uses Western Standard Time; South Australia and the Northern Territory use Central Standard Time; while New South Wales, Queensland, Tasmania, Victoria, Jervis Bay Territory, and the Australian Capital Territory use Eastern Standard Time. Daylight saving time (+1 hour) is used in jurisdictions in the south and south-east: South Australia, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramac, Queensland
Aramac is a rural town and locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , Aramac had a population of 299 people. Geography Aramac is located north of Barcaldine, and by road from the state capital, Brisbane. It is situated on Aramac Creek, which flows into the Thomson River west of town. The predominant industry is grazing. The town water for Aramac is supplied from two bores connecting into the Great Artesian Basin. History Aramac lay on the traditional tribal lands of the Iningai. Iningai (also known as Yiningay, Muttaburra, Tateburra, Yinangay, Yinangi) is an Australian Aboriginal language spoken by the Iningai people. The Iningai language region includes the landscape within the local government boundaries of the Longreach Region and Barcaldine Region, particularly the towns of Longreach, Barcaldine, Muttaburra and Aramac as well as the properties of Bowen Downs and catchments of Cornish Creek and Alice River. In the 1850s, pastoralist an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogantungan
Bogantungan is a rural town in the locality of Willows in the Central Highlands Region, Queensland, Australia. Geography The town is north west of the state capital Brisbane and west of the regional city of Rockhampton. The Central Western railway line passes through the town which was once served by the Bogantungan railway station. The small number of houses in the town are located around the railway station. The Capricorn Highway once passed through the town but now bypasses it to the north. History The name ''Bogantungan'' derives from Aboriginal words "''bogan''" meaning "''grass''" and "''tungan''" meaning "''tree''". The Central Western railway was built in sections, beginning at Rockhampton and then heading west. Each section involved establishing a temporary settlement to accommodate the workers while they were building the railway. After that section was complete, the workers moved further west were a new settlement was established. Although intended as temporary, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland National Bank
The Queensland National Bank is a former bank in Queensland, Australia. History In 1872, the bank was established in Brisbane. In December 1914, the bank had its head office in Brisbane with branches throughout Queensland at Allora, Aramac, Ayr, Barcaldine, Beaudesert, Biggenden, Blackall, Boonah, Bundaberg, Burketown, Cairns (with a receiving office at Gordonvale), Charleville, Charters Towers, Childers (with a receiving office at Cordalba), Clifton, Cloncurry, Cooktown, Crows Nest, Cunnamulla, Dalby (with receiving offices at Bell and Tara), Esk, Forest Hill, Fortitude Valley, Gatton (with receiving office at Grantham), Gladstone, Goombungee, Goondiwindi, Greenmount, Gympie, Halifax, Herberton, Hughenden, Ingham, Innsifail, Ipswich, Invinebank, Jandowae, Kandanga, Killarney, Kingaroy, Laidley, Longreach, Mackay, Marburg, Mareeba, Maryborough, Millmerran, Mitchell (with receiving office at Mungallala), Mount Morgan, Murgon, Muttaburra, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morning Bulletin
''The Morning Bulletin'' is an online newspaper servicing the city of Rockhampton and the surrounding areas of Central Queensland, Australia. From 1861 to 2020, ''The Morning Bulletin'' was published as a print edition, before then becoming an exclusively online newspaper. The final print edition was published on 27 June 2020. History The first issue of ''The Bulletin'' was launched on 9 July 1861. It is the second oldest business in Rockhampton, the oldest being the Criterion Hotel which was established in October 1860. The founder and original owner, William Hitchcock Buzacott (1831–1880, brother of Charles Hardie Buzacott), brought the press and equipment from Sydney in 1861 where he operated a small weekly paper. At the time the paper was called the Rockhampton Bulletin and was eagerly read by the town's 698 residents. The newspaper was published as ''The Rockhampton Bulletin and Central Queensland Advertiser'' from July 1861 to 14 January 1871. Then as ''The Rockh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Queenslander
''The Queenslander'' was the weekly summary and literary edition of the '' Brisbane Courier'', the leading journal in the colony—and later, federal state—of Queensland since the 1850s. ''The Queenslander'' was launched by the Brisbane Newspaper Company in 1866, and discontinued in 1939. History ''The Queenslander'' was first published on 3 February 1866 in Brisbane by Thomas Blacket Stephens. The last edition was printed on 22 February 1939. In a country the size of Australia, a daily newspaper of some prominence could only reach the bush and outlying districts if it also published a weekly edition. Yet ''The Queenslander'', under the managing editorship of Gresley Lukin—managing editor from November 1873 until December 1880—also came to find additional use as a literary magazine. In September 1919, a series of aerial photographs of Brisbane and its surrounding suburbs were published under the title, ''Brisbane By Air''. The photographs were taken by the newspape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastoralism
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as " livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands ( pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The animal species involved include cattle, camels, goats, yaks, llamas, reindeer, horses and sheep. Pastoralism occurs in many variations throughout the world, generally where environmental characteristics such as aridity, poor soils, cold or hot temperatures, and lack of water make crop-growing difficult or impossible. Operating in more extreme environments with more marginal lands means that pastoral communities are very vulnerable to the effects of global warming. Pastoralism remains a way of life in many geographic areas, including Africa, the Tibetan plateau, the Eurasian steppes, the Andes, Patagonia, the Pampas, Australia and many other places. , between 200 million and 500 million people globally practised pastora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North East Coast Drainage Basin
The north-east coast drainage division or north-east coast basin is the area of Queensland between the Great Dividing Range and the Pacific Ocean. It lies between Torres Strait and an arbitrary line drawn along the Queensland - New South Wales border. In the north it meets the Gulf of Carpentaria basin to its west while further south lies the Lake Eyre Basin and the Murray-Darling Basin. In the south the Australian south-east coast drainage division continues to the east of the Great Divide. The basin covers 450,705 km2 across 46 river catchments. It is the seventh largest out of twelve separate drainage divisions covering Mainland Australia. Just under one half of all Australian freshwater species are found in the north east coast division. See also * Southwest corner of Western Australia * Indian Ocean drainage division: see Pilbara region of Western Australia * Timor Sea drainage division: see Top End and Kimberley region of Western Australia * South Australian gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burdekin River
The Burdekin River is a river located in North and Far North Queensland, Australia. The river rises on the northern slopes of Boulder Mountain at Valley of Lagoons, part of the western slope of the Seaview Range, and flows into the Coral Sea at Upstart Bay over to the southeast of the source, with a catchment area of approximately . The Burdekin River is Australia's largest river by (peak) discharge volume. The river was first encountered by Europeans during the expedition led by Ludwig Leichhardt in 1845 and named in honour of Thomas Burdekin, one of the sponsors of the expedition. Course and features The Burdekin River rises on the western slopes of the Seaview Range, part of the Great Dividing Range, west of . In the river's upper catchment, from its source the river generally flows west and then south out of the Girringun National Park, part of the UNESCO Wet Tropics World Heritage Area. This area, now part of Basalt was the location of one of the earliest inland sett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suttor River
The Suttor River is a river in Central Queensland, Australia. The Belyando River is its main tributary. The river has its origins in the Leichhardt Range, north west of Glenden. It flows into Lake Dalrymple, becoming a tributary of the Burdekin River. Geography A DIWA wetlands can be found along the course of the river. The wetland known as the Scartwater Aggregation is a floodplain upstream from Lake Dalrymple where the river is split into two major channels by Scartwater Hill, a sandstone outcrop, the channels contain two large permanent waterholes. History Jangga, also known as Yangga, is a language of Central Queensland. The Jangga language region includes the landscape within the local government boundaries of the Etheridge Shire Council. The river was named after William Henry Suttor on 7 March 1845 by explorer Ludwig Leichhardt on his expedition from Moreton Bay to Port Essington. Suttor had given Leichhardt some bullocks for his expedition. The Suttor R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belyando River
The Belyando River, including the Belyando River (Western Branch), is a river system located in Central Queensland, Australia. At in length and with a catchment area of , the Belyando River system is one of the longest rivers in Queensland. It is pronounced Bel-yando. Course and features Comprising a mix of anabranches from source to mouth, the Belyando River and the Belyando River (Western Branch) rise below Mount Narounyah in the Drummond Range, part of the Great Dividing Range in the area southeast of . The river flows generally in a northerly direction, joined by twenty-nine tributaries including the Carmichael River. The Belyando River flows through a series of waterholes and lagoons including Grays Lagoon, Bakoolama Waterhole, Ten Mile Waterhole, Boadles Waterhole, Georges Waterhole, Broadna Waterhole, Alinya Waterhole, Sandy Camp Waterhole, Bygana Waterhole, Dunjarrobina Waterhole and Yarmina Waterhole. The river reaches its confluence with the Suttor River before fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capricorn Highway
The Capricorn Highway is located in Central Queensland, Australia, and links the city of Rockhampton with western Queensland. The highway is long, and joins the Landsborough Highway at Barcaldine. Formerly National Route 66, Queensland began to convert to the alphanumeric system much of Australia had adopted in the early-2000s and is now designated as A4. The highway runs parallel with the Tropic of Capricorn, hence its name. Other towns situated along the highway include (from east to west): Gracemere, Kabra, Stanwell, Westwood, Gogango, Duaringa, Dingo, Bluff, Blackwater, Comet, Emerald, Bogantungan, Alpha and Jericho. Running virtually east/west, the highway traverses the area known as the Central Highlands, and crosses the Great Dividing Range between Alpha and Jericho. File:Capricorn Highway 1312.svg, Capricorn Highway (green on black) Northern Australia Roads Program upgrade The Northern Australia Roads Program announced in 2016 included the following proj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
