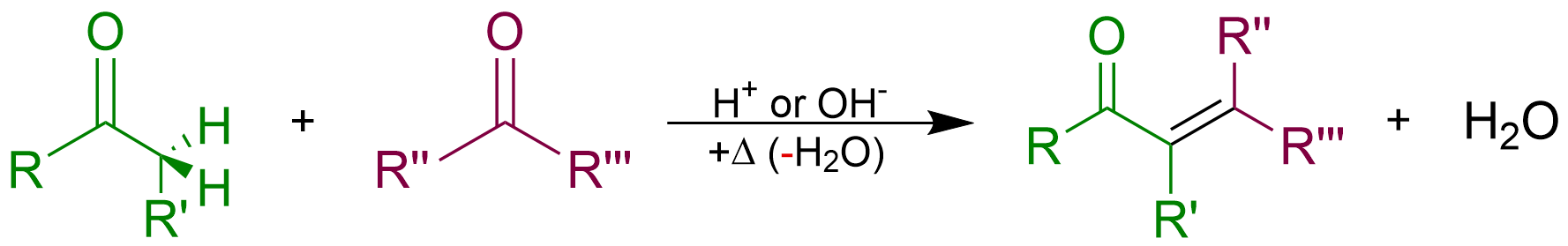|
Pomeranz–Fritsch Reaction
The Pomeranz–Fritsch reaction, also named Pomeranz–Fritsch cyclization, is a named reaction in organic chemistry. It is named after Paul Fritsch (chemist), Paul Fritsch (1859–1913) and Cäsar Pomeranz (1860–1926). In general it is a synthesis of isoquinoline. General reaction scheme The reaction below shows the acid-promoted synthesis of isoquinoline from benzaldehyde and a 2,2-dialkoxyethylamine. Various alkyl, alkyl groups, e.g. methyl and ethyl group, ethyl groups, can be used as substituent R. In the archetypical reaction sulfuric acid was used as proton donor, but Lewis acids such as trifluoroacetic anhydride and lanthanide triflates have been used occasionally. Later, a wide range of diverse isoquinolines were successfully prepared. Reaction mechanism A possible mechanism is depicted below: First the benzalaminoacetal 1 is built by the condensation reaction, condensation of benzaldehyde and a 2,2-dialkoxyethylamine. After the condensation a hydrogen-atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Fritsch (chemist)
Paul Fritsch (25 February 1901 – 22 September 1970) was a French featherweight professional boxing, boxer who competed in the early 1920s. In 1920 he became the first French boxer to win an Olympic title, defeating teammate Jean Gachet in the final, despite losing to Gachet at the national championships before the Olympics. After more than 300 amateur bouts, Fritsch turned professional in 1921. He fought approximately 100 more bouts, but never won a major title. He retired from boxing in 1929 due to a retinal detachment and became a car salesman. 1920 Olympic results Below is the record of Paul Fritsch, a French featherweight boxer who competed at the 1920 Antwerp Olympics: * Round of 32: bye * Round of 16: defeated George Etcell (USA) * Quarterfinal: defeated Paul Erdal (Norway) * Semifinal: defeated Edoardo Garzena (Italy) * Final: defeated Jean Gachet (France) Note: In 1920 a country could have more than one boxer per weight classification References 1901 birth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the chemical formula, formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocycle Forming Reactions
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on organic unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained organic 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of organic heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of pyridin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Heterocycle Forming Reactions
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colourless and odourless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant chemical species in air. Because of the volatility of nitrogen compounds, nitrogen is relatively rare in the solid parts of the Earth. It was first discovered and isolated by Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford in 1772 and independently by Carl Wilhelm Scheele and Henry Cavendish at about the same time. The name was suggested by French chemist Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal in 1790 when it was found that nitrogen was present in nitric acid and nitrates. Antoine Lavoisier suggested instead the nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pictet–Spengler Reaction
The Pictet–Spengler reaction is a chemical reaction in which a β-arylethylamine undergoes Condensation reaction, condensation with an aldehyde or ketone followed by ring closure. The reaction was first discovered in 1911 by Amé Pictet and Theodor Spengler (22 February 1886 – 18 August 1965). Traditionally, an Acid catalysis, acidic catalyst in protic solvent was employed with heating; however, the reaction has been shown to work in Aprotic solvent, aprotic media in superior yields and sometimes without acid catalysis. The Pictet–Spengler reaction can be considered a special case of the Mannich reaction, which follows a similar reaction pathway. The driving force for this reaction is the electrophilicity of the iminium ion generated from the condensation of the aldehyde and amine under acid conditions. This explains the need for an acid catalyst in most cases, as the imine is not electrophilic enough for ring closure but the Iminium, iminium ion is capable of undergoing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bischler–Napieralski Reaction
The Bischler–Napieralski reaction is an intramolecular electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction that allows for the cyclization of β-arylethylamides or β-arylethylcarbamates. It was first discovered in 1893 by August Bischler and , in affiliation with Basel Chemical Works and the University of Zurich. The reaction is most notably used in the synthesis of dihydroisoquinolines, which can be subsequently organic redox reaction, oxidized to isoquinolines. Mechanisms Two types of mechanisms have appeared in the literature for the Bischler–Napieralski reaction. Mechanism I involves a dichlorophosphoryl imine-ester intermediate, while Mechanism II involves a nitrilium ion intermediate (both shown in brackets). This mechanistic variance stems from the ambiguity over the timing for the elimination reaction, elimination of the carbonyl oxygen in the starting amide. In Mechanism I, the elimination occurs with imine formation ''after'' cyclization; while in Mechanism II, the elimi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papaverine
Papaverine (Latin '' papaver'', "poppy") is an opium alkaloid antispasmodic drug, used primarily in the treatment of visceral spasms and vasospasms (especially those involving the intestines, heart, or brain), occasionally in the treatment of erectile dysfunction and acute mesenteric ischemia. While it is found in the opium poppy, papaverine differs in both structure and pharmacological action from the analgesic morphine and its derivatives (such as codeine). In addition to opium, papaverine is purported to be present in high concentrations in star gooseberry. History Papaverine was discovered in 1848 by Georg Merck (1825–1873). Merck was a student of the German chemists Justus von Liebig and August Hofmann, and he was the son of Emanuel Merck (1794–1855), founder of the Merck corporation, a major German chemical and pharmaceutical company. Uses Papaverine is approved to treat spasms of the gastrointestinal tract, bile ducts and ureter and for use as a ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinisocaine
Quinisocaine (INN) or dimethisoquin ( BAN and USAN) is a topical anesthetic used as an antipruritic Antipruritics, abirritants, or anti-itch drugs, are medications that inhibit itching (Latin: ''pruritus''). Itching is often associated with sunburns, allergic reactions, eczema, psoriasis, chickenpox, Fungal infection in animals, fungal infections .... Synthesis The Henry reaction between phthalaldehydic acid (2-Formylbenzoic acid) 19-67-5(1) and 1-nitropentane 28-05-7occurs by a mechanism that involves a hydroxy acid (2). Expulsion of water then gives (3). Reduction of the nitro group via catalytic hydrogenation leads to the amineCID:158569430(4). Treatment of that amine with sodium hydroxide leads to ring opening of the lactone ring to the intermediary amino acid (5). This cyclises spontaneously to the lactam so that the product isolated from the reaction mixture is in fact the isoquinoline derivativeCID:154188092(7). Dehydration by means of strong acid gives 3-Butylisocarbos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
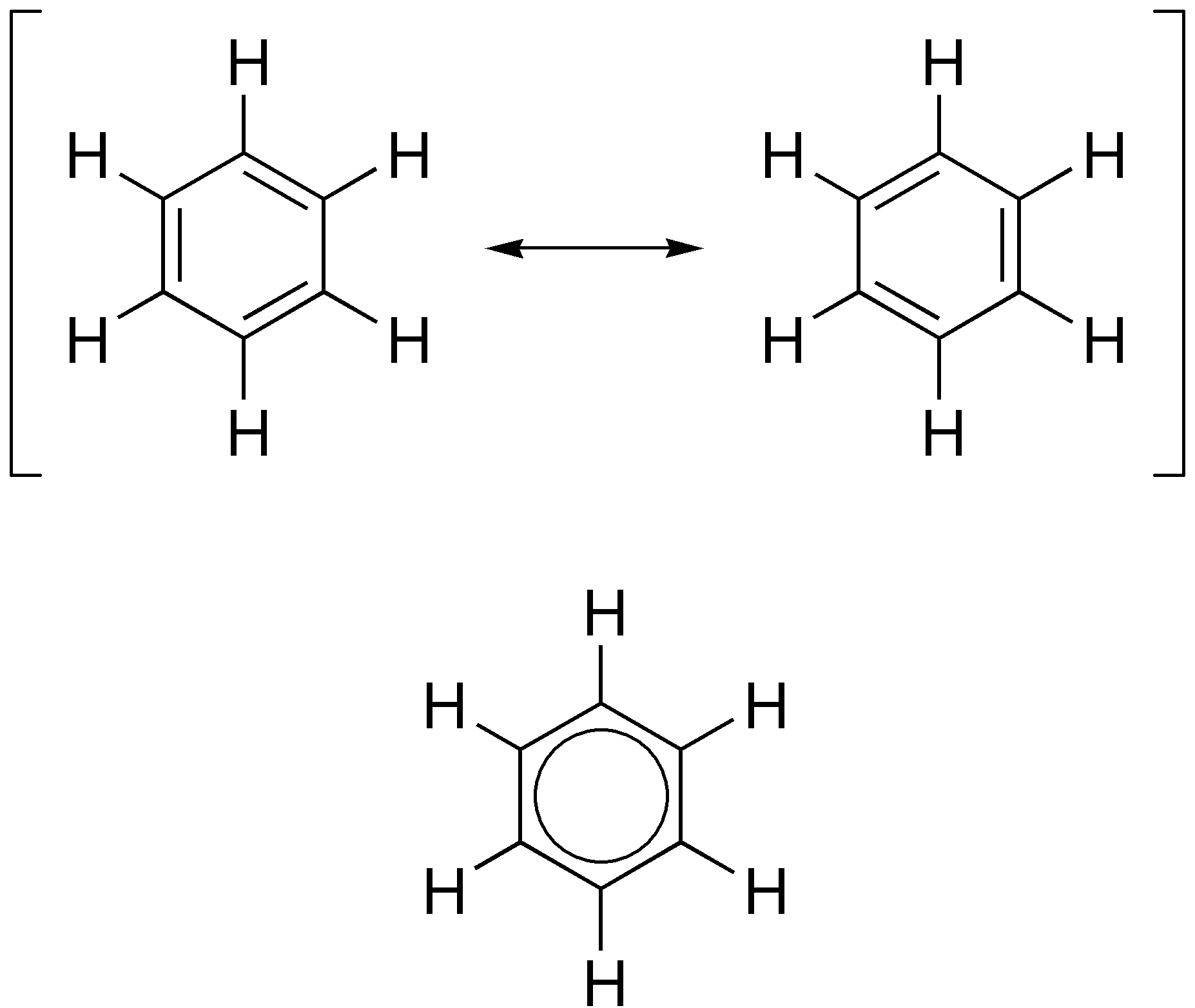
Aromatic
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated system, conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. There is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfaction, olfactory properties of such compounds. Aromaticity can also be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of Resonance (chemistry), resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double-covalent bond, bonded to one another. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by Friedrich August Kekulé ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |