|
Polymorphida
Polymorphida are an order of thorny-headed worms (phylum Acanthocephala). The adults of these parasitic platyzoans feed mainly on fish and aquatic birds. This order contains 5 families:Huston, D. C., Cribb, T. H., & Smales, L. R. (2020). Molecular characterisation of acanthocephalans from Australian marine teleosts: proposal of a new family, synonymy of another and transfer of taxa between orders. Systematic Parasitology, 1-23. * Centrorhynchidae Van Cleave, 1916 * Isthomosacanthidae Smales, 2012 * Plagiorhynchidae Meyer, 1931 * Pyriprobosicidae *Polymorphidae The thorny-headed worm family Polymorphidae contains endoparasites which as adults feed mainly in fish and aquatic birds. When this taxon was erected by Meyer in 1931, a subfamily Polymorphinae was established in it. As the Polymorphidae as prese ... Meyer, 1931 References Palaeacanthocephala {{acanthocephalan-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymorphidae
The thorny-headed worm family Polymorphidae contains endoparasites which as adults feed mainly in fish and aquatic birds. When this taxon was erected by Meyer in 1931, a subfamily Polymorphinae was established in it. As the Polymorphidae as presently understood would then be monotypic, with no basal genera outside the Polymorphinae, the proposed subfamily is redundant for the time being and therefore most modern treatments simply omit it. '' Polymorphus minutus'' is an economically significant parasite in goose and duck farming. Species Polymorphidae contains the following species: ''Andracantha'' Schmidt, 1975 *''Andracantha baylisi'' (Zdzitowiecki, 1986) Zdzitowiecki, 1989 *''Andracantha clavata'' (Goss, 1940) ''Andracantha gravida'' (Alegret, 1941) Schmidt, 1975 *''Andracantha mergi'' Lundström, 1942 *''Andracantha phalacrocoracis'' (Yamaguti, 1939) *''Andracantha tandemtesticulata'' Monteiro, Amato & Amato, 2006 *''Andracantha tunitae'' (Weiss, 1914) ''Ardeirhynchus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymorphida
Polymorphida are an order of thorny-headed worms (phylum Acanthocephala). The adults of these parasitic platyzoans feed mainly on fish and aquatic birds. This order contains 5 families:Huston, D. C., Cribb, T. H., & Smales, L. R. (2020). Molecular characterisation of acanthocephalans from Australian marine teleosts: proposal of a new family, synonymy of another and transfer of taxa between orders. Systematic Parasitology, 1-23. * Centrorhynchidae Van Cleave, 1916 * Isthomosacanthidae Smales, 2012 * Plagiorhynchidae Meyer, 1931 * Pyriprobosicidae *Polymorphidae The thorny-headed worm family Polymorphidae contains endoparasites which as adults feed mainly in fish and aquatic birds. When this taxon was erected by Meyer in 1931, a subfamily Polymorphinae was established in it. As the Polymorphidae as prese ... Meyer, 1931 References Palaeacanthocephala {{acanthocephalan-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
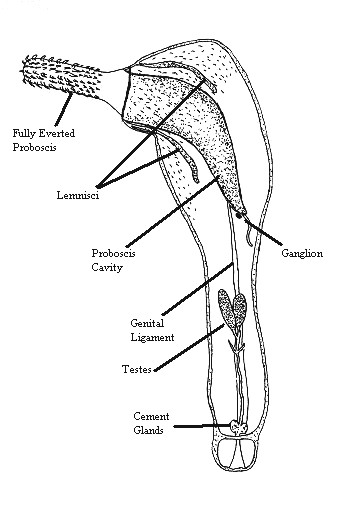
Corynosoma Wegeneri
''Corynosoma'' is a genus of parasitic worms belonging to the family Polymorphidae. The genus has almost cosmopolitan distribution. Species: *''Corynosoma alaskensis'' *''Corynosoma australe'' *''Corynosoma beaglense'' *''Corynosoma bullosum'' *''Corynosoma cameroni'' *''Corynosoma caspicum'' *''Corynosoma cetaceum'' *''Corynosoma curilense'' *''Corynosoma enhydri'' *''Corynosoma erignathi'' *''Corynosoma evae'' *''Corynosoma falcatum'' *''Corynosoma gibsoni'' *'' Corynosoma hamanni'' *''Corynosoma hannae'' *''Corynosoma magdaleni'' *''Corynosoma pseudohamanni'' *'' Corynosoma rauschi'' *'' Corynosoma reductum'' *'' Corynosoma semerme'' *'' Corynosoma septentrionale'' *'' Corynosoma shackletoni'' *'' Corynosoma simile'' *'' Corynosoma stanleyi'' *'' Corynosoma strumosum'' *'' Corynosoma validum'' *'' Corynosoma ventronudum'' *''Corynosoma villosum ''Corynosoma'' is a genus of parasitic worms belonging to the family Polymorphidae. The genus has al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrorhynchidae
''Centrorhynchidae'' is a family of parasitic worms. Three species of these thorny-headed worms in the genus Centrorhynchus were found to parasitize birds of prey and owls Slovakia. These hosts include '' Buteo buteo'', ''Buteo rufinus'', ''Falco tinnunculus'', ''Asio otus'', '' Strix aluco'', '' Strix uralensis'' and ''Tyto alba''. Species Centrorhynchidae contains the following species: ''Centrorhynchus'' Lühe, 1911 * ''Centrorhynchus acanthotrias'' (von Linstow, 1883) * ''Centrorhynchus albensis'' Rengaraju and Das, 1975 * ''Centrorhynchus albidus'' Meyer, 1932 * ''Centrorhynchus aluconis'' (Mueller, 1780) The complete mitochondrial genome of ''C. aluconis'' has been sequenced. * ''Centrorhynchus amini'' Khan, Muti-ur-Rahman, Bilqees and Khatoon, 2010 * ''Centrorhynchus amphibius'' Das, 1950 * ''Centrorhynchus appendiculatus'' (Westrumb, 1821) * ''Centrorhynchus asturinus'' (Johnston, 1912) * ''Centrorhynchus atheni'' Gupta and Fatma, 1983 * ''Centrorhynchus bancrofti'' (J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isthomosacanthidae
''Isthomosacanthidae'' is a family of parasitic spiny-headed (or thorny-headed) worms.Huston, D. C., Cribb, T. H., & Smales, L. R. (2020). Molecular characterisation of acanthocephalans from Australian marine teleosts: proposal of a new family, synonymy of another and transfer of taxa between orders. Systematic Parasitology, 1-23. Species ''Isthomosacanthidae'' contains the following genera and species: ''Golvanorhynchus'' Noronha, Fabio & Pinto, 1978 * ''Golvanorhynchus golvani'' Noronha, Fabio & Magalhaes, 1978 ''G. golvani'' was found parasitizing the Atlantic chub mackerel (''Scomber colias'').Pichelin, S. & Cribb, T. (2001). The status of the Diplosentidae (Acanthocephala: Palaeacanthocephala) and a new family of acanthocephalans from Australian wrasses (Pisces: Labridae). ''Folia Parasitologica'', 48(4), 289–303. ''Gorgorhynchoides'' Cable and Linderoth, 1963 *''Gorgorhynchoides bullocki'' Cable and Mafarachisi, 1970 *''Gorgorhynchoides cablei'' (Gupta and Fatma, 1987) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plagiorhynchidae
Plagiorhynchidae is a family of parasitic Acanthocephalan worms. Species Genera in Plagiorhynchidae are divided into three subfamilies: Plagiorhynchinae, Porrorchinae, and Sphaerechinorhynchinae. Plagiorhynchinae Meyer, 1931 ''Paralueheia'' Saxena & Gupta, 2008 *''Paralueheia guptai'' Saxena & Gupta, 2008 Species in '' Plagiorhynchus'' are divided into two subgenera: ''Plagiorhynchus'' and ''Prosthorhynchus''. ''Plagiorhynchus'' Lühe, 1911 * '' Plagiorhynchus allisonae'' Smales, 2002 * '' Plagiorhynchus aznari'' ''P. aznari'' was found infesting a long-billed curlew'' (Numenius americanus'') from northern Mexico. * '' Plagiorhynchus charadrii'' Yamaguti, 1939) * '' Plagiorhynchus charadriicola'' Dollfus, 1953) * '' Plagiorhynchus crassicollis'' Villot, 1875) * '' Plagiorhynchus freitasi'' Vicente, 1977 * '' Plagiorhynchus karachiensis'' Muti-ur-Rahman, Khan, Khatoon and Bilqees, 2008 * '' Plagiorhynchus lemnisalis'' Belopolskaya, 1958 * '' Plagiorhynchus linearis'' Westrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order ( la, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. For some groups of organisms, their orders may follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
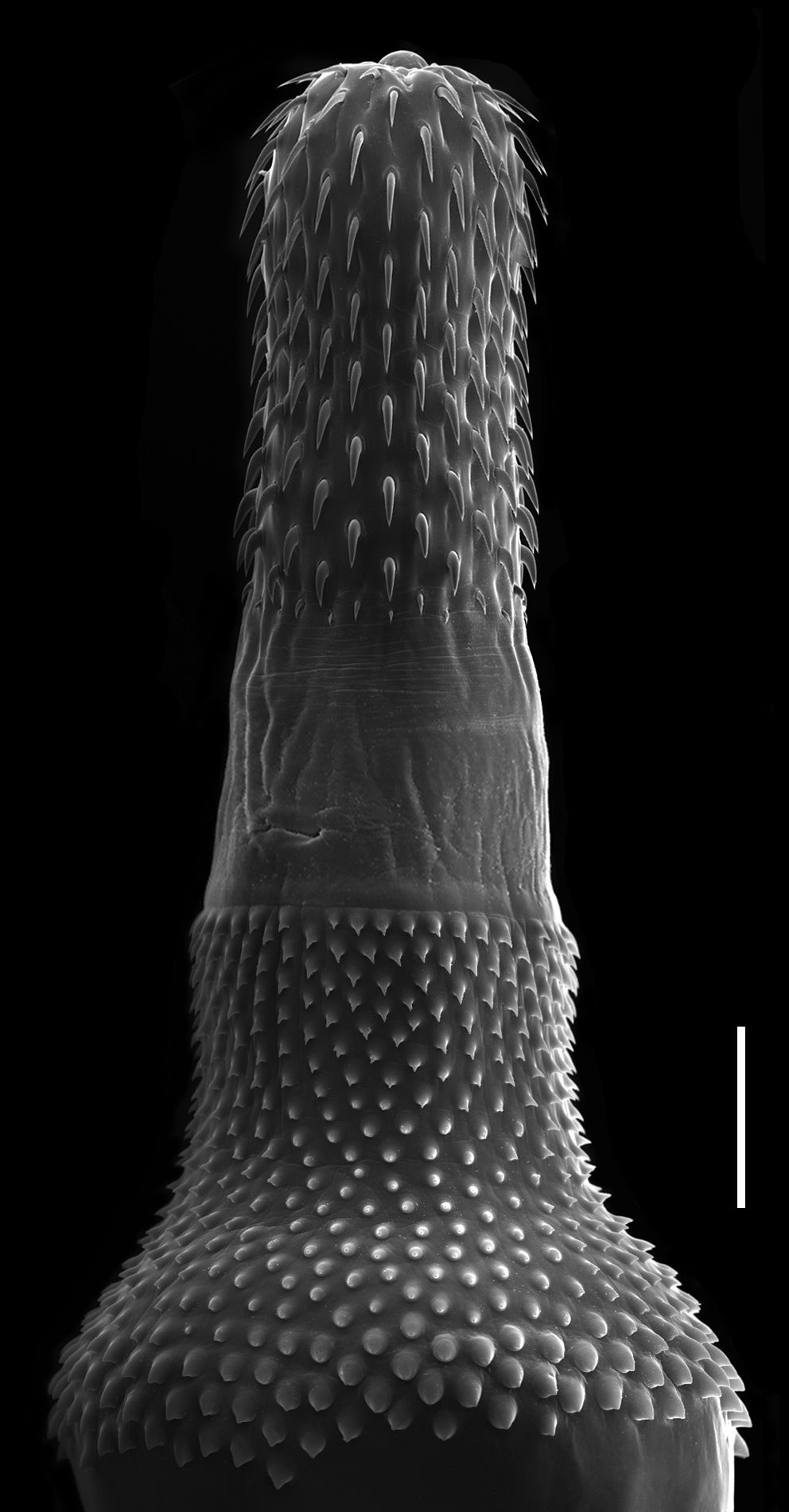
Thorny-headed Worm
Acanthocephala (Greek , ', thorn + , ', head) is a phylum of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and hold the gut wall of its host. Acanthocephalans have complex life cycles, involving at least two hosts, which may include invertebrates, fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 1420 species have been described. The Acanthocephala were thought to be a discrete phylum. Recent genome analysis has shown that they are descended from, and should be considered as, highly modified rotifers. This unified taxon is known as Syndermata. History The earliest recognisable description of Acanthocephala – a worm with a proboscis armed with hooks – was made by Italian author Francesco Redi (1684).Crompton 1985, p. 27 In 1771, Joseph Koelreuter proposed the name Acanthocephala. Philipp Ludwig Statius Müller independently called th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants accepts the terms as equivalent. Depending on definitions, the animal kingdom Animalia contains about 31 phyla, the plant kingdom Plantae contains about 14 phyla, and the fungus kingdom Fungi contains about 8 phyla. Current research in phylogenetics is uncovering the relationships between phyla, which are contained in larger clades, like Ecdysozoa and Embryophyta. General description The term phylum was coined in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel from the Greek (, "race, stock"), related to (, "tribe, clan"). Haeckel noted that species constantly evolved into new species that seemed to retain few consistent features among themselves and therefore few features that distinguished them as a group ("a self-contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparasite lives inside the host's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platyzoa
The paraphyletic "Platyzoa" are a group of protostome unsegmented animals proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 1998. Cavalier-Smith included in Platyzoa the phylum Platyhelminthes (or flatworms), and a new phylum, the Acanthognatha, into which he gathered several previously described phyla of microscopic animals. Later it has been described as paraphyletic, containing the Rouphozoa and the Gnathifera. Phyla One scheme placed the following phyla in Platyzoa: * Rouphozoa ** Platyhelminthes ** Gastrotricha * Gnathifera ** Syndermata *** Rotifera *** Seisonida ** Acanthocephala ** Gnathostomulida ** Micrognathozoa ** Cycliophora Characteristics None of the Platyzoa groups have a respiration or circulation system because of their small size, flat body or parasitic lifestyle. The Platyhelminthes and Gastrotricha are acoelomate. The other phyla have a pseudocoel, and share characteristics such as the structure of their jaws and pharynx, although these have been secondarily l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |