|
Polonisation
Polonization or Polonisation ()In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэяй. Польскі рух на беларускіх і літоўскіх землях. 1864–1917 г. / Пад рэд. С. Куль-Сяльверставай. – Гродна: ГрДУ, 2001. – 322 с. (2004). Pp.24, 28.), an additional distinction between the Polonization () and self-Polonization () has been being made, however, most modern Polish researchers do not use the term ''polszczenie się''. is the acquisition or imposition of elements of Polish culture, in particular the Polish language. This happened in some historic periods among non-Polish populations in territories controlled by or substantially under the influence of Poland. Like other examples of cultural assimilation, Polonization could be either voluntary or forced. It was most vis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, German people, people, and German culture, culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In linguistics, Germanisation of non-German languages also occurs when they adopt many German words. Under the policies of states such as the State of the Teutonic Order, Teutonic Order, Federal State of Austria, Austria, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the German Empire, non-German minorities were often discouraged or even prohibited from using their native language, and had their traditions and culture suppressed in the name of linguistic imperialism. In addition, the Government also encouraged immigration from the Germanosphere to further upset the linguistic balance, but with varying degrees of success. In Nazi Germany, linguistic Germanisation was replaced by a policy of genocide against certain ethnic groups li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruthenian Nobility
The Ruthenian nobility (; ; ) originated in the territories of Kievan Rus' and Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, Galicia–Volhynia, which were incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and later the Russian Empire, Russian and Austrian Empires. The Ruthenian nobility became increasingly Polonized and later Russified, while retaining a separate cultural identity. The Ruthenian nobility, originally characterized as East Slavic languages, East Slavic-speaking and Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox, found itself ruled by the expanding Grand Duchy of Lithuania, where it rose from second class status to equal partners of the Lithuanian nobility. Following the Polish–Lithuanian union of the 14th century, the Ruthenian nobles became increasingly Polonized, adopting the Polish language and religion (which increasingly meant converting from the Orthodox faith to Roman Catholicism). Ruthenian nobility, however, retained a distinct identity within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. The territory has a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and a temperate climate. Poland is composed of Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 million people, and the List of European countries by area, fifth largest EU country by area, covering . The capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, and Gdańsk. Prehistory and protohistory of Poland, Prehistoric human activity on Polish soil dates to the Lower Paleolithic, with continuous settlement since the end of the Last Gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, History of Berlin, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. Prussia formed the German Empire when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by 1932 Prussian coup d'état, an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by Abolition of Prussia, an Allied decree in 1947. The name ''Prussia'' derives from the Old Prussians who were conquered by the Teutonic Knightsan organized Catholic medieval Military order (religious society), military order of Pru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian National Revival
The Lithuanian National Revival, alternatively the Lithuanian National Awakening or Lithuanian nationalism (), was a period of the history of Lithuania in the 19th century, when a major part of Lithuanian-inhabited areas belonged to the Russian Empire (the Russian partition of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth). It was expressed by the rise of self-determination of the Lithuanians that led to the formation of the modern Lithuanian nation and culminated in the re-establishment of an independent Lithuanian state. The most active participants of the national revival included Vincas Kudirka and Jonas Basanavičius. The period largely corresponded to the rise of romantic nationalism and other national revivals of 19th-century Europe. The revival was predated by a short period of the early 19th century known as the "Samogitian revival" led by students of Vilnius University, including Simonas Daukantas and Simonas Stanevičius. The most recent Lithuanian national revival may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Poland
The history of Poland spans over a thousand years, from Lechites, medieval tribes, Christianization of Poland, Christianization and Kingdom of Poland, monarchy; through Polish Golden Age, Poland's Golden Age, Polonization, expansionism and becoming one of the largest Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, European powers; to its Partitions of Poland, collapse and partitions, two world wars, Polish People's Republic, communism, and the restoration of democracy. The roots of Polish history can be traced to Ancient history, ancient times, when the territory of present-day Poland was inhabited by diverse ethnic groups, including Celts, Scythians, Sarmatians, Slavs, Balts and Germanic peoples. However, it was the West Slavs, West Slavic Lechites, the closest ancestors of ethnic Polish people, Poles, who established permanent settlements during the Early Middle Ages. The Lechitic Polans (western), Western Polans, a tribe whose name denotes "people living in open fields", dominated the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assimilation (sociology)
Cultural assimilation is the process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a society's majority group or fully adopts the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group. The melting pot model is based on this concept. A related term is cultural integration, which describes the process of becoming economically and socially integrated into another society while retaining elements of one’s original culture. This approach is also known as cultural pluralism, and it forms the basis of a cultural mosaic model that upholds the preservation of cultural rights. Another closely related concept is acculturation, which occurs through cultural diffusion and involves changes in the cultural patterns of one or both groups, while still maintaining distinct characteristics. There are various types of cultural assimilation, including full assimilation and forced assimilation. Full assimilation is common, as it occurs spontaneously. Assimilation can also involve what is call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russification
Russification (), Russianisation or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians adopt Russian culture and Russian language either voluntarily or as a result of a deliberate state policy. Russification was at times pursued by the governments of the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union, either as a goal in itself or as a consequence of policies aimed at centralisation and modernisation. The major areas of Russification are politics and culture. In politics, an element of Russification is assigning Russian nationals to lead administrative positions in national institutions. In culture, Russification primarily amounts to the hegemony of the Russian language in official business and the strong influence of the Russian language on national idioms. The shifts in demographics in favor of the ethnic Russian population are sometimes considered a form of Russification as well. Some researchers distinguish ''Russification'', as a process of changing one's ethn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
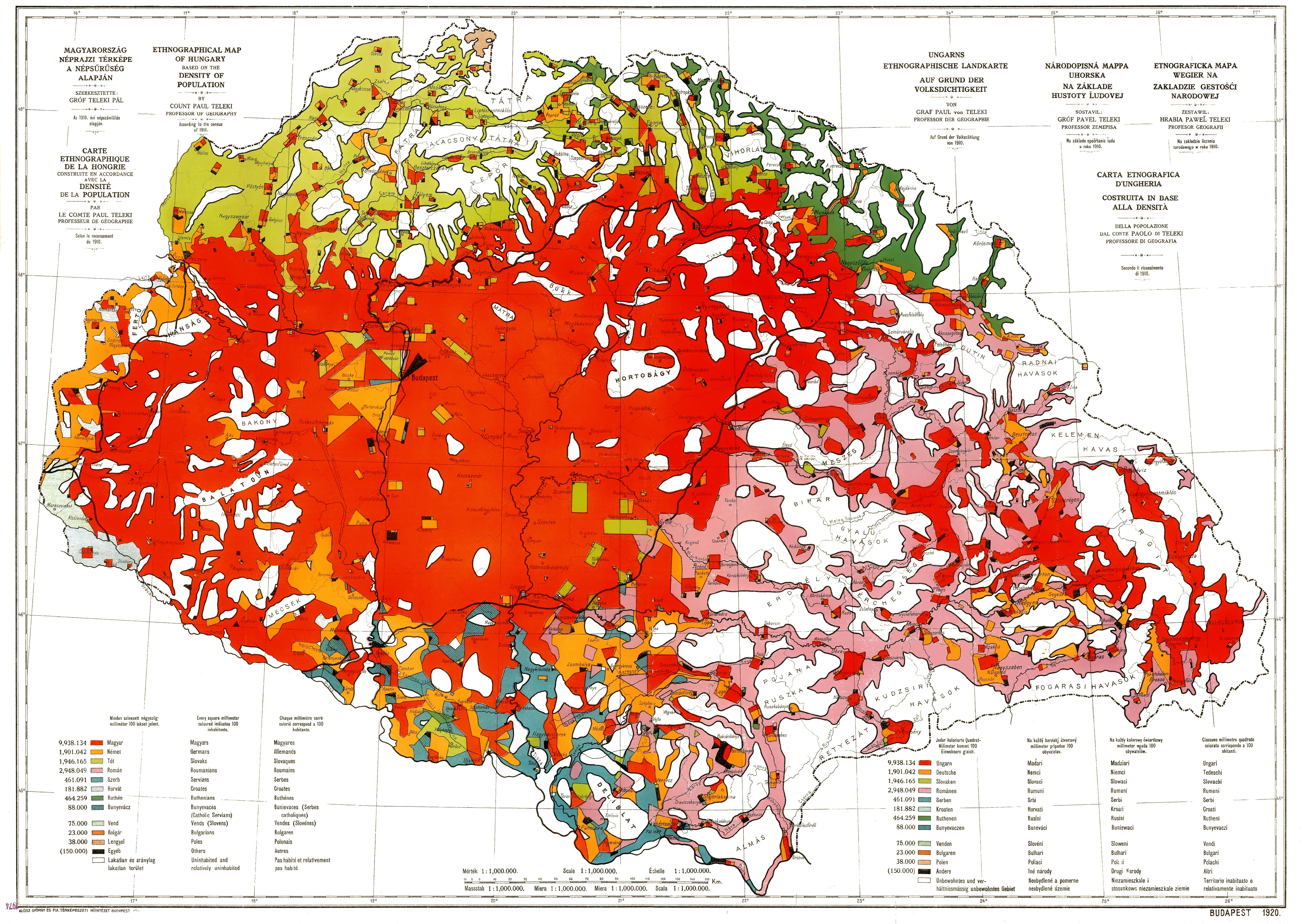
Magyarization
Magyarization ( , also Hungarianization; ), after "Magyar"—the Hungarian autonym—was an assimilation or acculturation process by which non-Hungarian nationals living in the Kingdom of Hungary, then part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, adopted the Hungarian national identity and language in the period between the Compromise of 1867 and Austria-Hungary's dissolution in 1918. Magyarization occurred both voluntarily and as a result of social pressure, and was mandated in certain respects by specific government policies. Before World War I, only three European countries declared ethnic minority rights, and enacted minority-protecting laws: the first was Hungary (1849 and 1868), the second was Austria (1867), and the third was Belgium (1898). In contrast, the legal systems of other pre-WW1 era European countries did not allow the use of European minority languages in primary schools, in cultural institutions, in offices of public administration and at the legal courts. Magyar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partitions Of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partition (politics), partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place between 1772 and 1795, toward the end of the 18th century. They ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 123 years. The partitions were conducted by the Habsburg monarchy, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Russian Empire, which divided up the Commonwealth lands among themselves progressively in the process of territorial seizures and annexations. The First Partition of Poland, First Partition was decided on August 5, 1772, after the Bar Confederation lost the war with Russia. The Second Partition of Poland, Second Partition occurred in the aftermath of the Polish–Russian War of 1792 and the Targowica Confederation when Russian and Prussian troops entered the Commonwealth and the partition treaty was signed during the Grodno Sejm on January 23, 1793 (without Austria). The Third Partition of Poland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanianization
Romanianization is the series of policies aimed toward ethnic assimilation implemented by the Romanian authorities during the 20th and 21st century. The most noteworthy policies were those aimed at the Hungarian minority in Romania, Jews and as well the Ukrainian minority in Bukovina and Bessarabia. Romanianization in Transylvania In the period between the two World Wars After the end of World War I, on 1 December 1918, the Romanian National Council (elected representatives of the Romanian population) and soon afterwards, the representatives of the German population had decided to unify with Romania. The decision was contested by the Hungarian minority. The Hungarian–Romanian War of 1918–1919 established Romanian control over Transylvania, while the Treaty of Trianon of 1920 determined the Romanian border with the new Hungarian state. However, Transylvania had a large Hungarian minority of 25.5%, according to the 1920 census. A portion of them fled to Hungary after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainization
Ukrainization or Ukrainisation ( ) is a policy or practice of increasing the usage and facilitating the development of the Ukrainian language and promoting other elements of Ukrainian culture in various spheres of public life such as education, publishing, government, and religion. The term is also used to describe a process by which non-Ukrainians or Russian-speaking Ukrainians are assimilated to Ukrainian culture and language, either by individual choices or as a result of social processes or policies. In Western historiography, the term ''Ukrainization'' refers also to a policy and resulting process of forcing ethnic minorities living on Ukrainian territories to abandon their ethnic identity by means of the enforced assimilation of Ukrainian culture and identity. During the aftermath of World War II, in the Ukrainian SSR this process had been preceded by the expulsion of some ethnic minoritiesNorman Davies, '' God's Playground, a History of Poland'', Columbia University Press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |