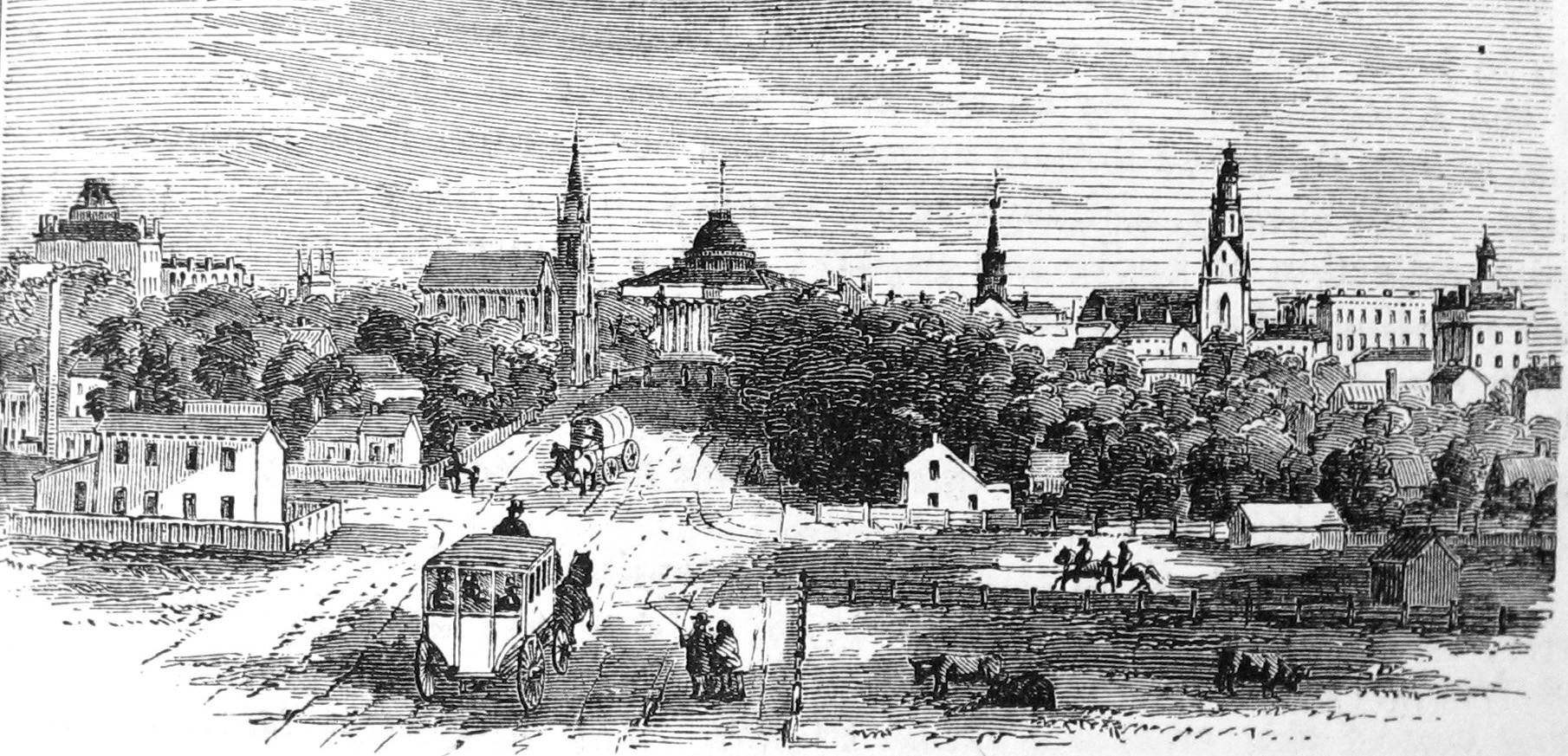|
Polish Studies Program At The University Of Wisconsin–Madison
Polish Studies Program at the University of Wisconsin–Madison (UW–Madison) is the oldest academic program in existence with the focus on the study and teaching of the Polish language, literature, and culture in the United States. Polish language instruction began in the fall semester of 1936 and has been offered at the University of Wisconsin–Madison ever since. The Polish program is offered by the UW–Madison Department of German, Nordic, and Slavic+. As a result, with the foundation of the Department of Polish at the University of Wisconsin-Madison in 1936, the teaching of Slavic languages and literatures started. History The Polish Studies Program at the University of Wisconsin–Madison traces its history back to 1935, when the combined effort of the local Polish American community and state legislators led to the establishment of the Department of Polish (1936), the first academic program devoted to the teaching of the Polish language, literature, and culture in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (, , or simply , ) is a West Slavic languages, West Slavic language of the Lechitic languages, Lechitic subgroup, within the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is written in the Latin script. It is primarily spoken in Poland and serves as the official language of the country, as well as the language of the Polish diaspora around the world. In 2024, there were over 39.7 million Polish native speakers. It ranks as the sixth-most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional Dialects of Polish, dialects. It maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, Honorifics (linguistics), honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (, , , , , , , , ) to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet. The traditional set compri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian ( / ), also known as Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS), is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. It is a pluricentric language with four mutually intelligible Standard language, standard varieties, namely Serbian language, Serbian, Croatian language, Croatian, Bosnian language, Bosnian, and Montenegrin language, Montenegrin. South Slavic languages historically formed a dialect continuum. The region's turbulent history, particularly due to the expansion of the Ottoman Empire, led to a complex dialectal and religious mosaic. Due to population migrations, Shtokavian became the most widespread supradialect in the western Balkans, encroaching westward into the area previously dominated by Chakavian and Kajkavian. Bosniaks, Croats, and Serbs differ in religion and were historically often part of different cultural spheres, although large portions of these populations lived side by side und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maiden Vows
Maiden Vows (Polish original title: :pl:Śluby panieńskie (film), Śluby Panieńskie and USA title: War of Love) is a 2010 Poland, Polish historical drama directed by Filip Bajon. The film is an adaptation of Aleksander Fredro's play of the same title from 1832. The film is set in the Austrian Partition and was shot in Kotuń and Nowa Sucha from August 26 to September 30, 2010. The film is set in the nineteenth century, but the film has anachronism, anachronistic contemporary inserts (e.g. car, cell phones, modern press). Plot 1825, a small manor house in the south of Poland. Majętny Radost (Robert Więckiewicz) intends to get his nephew Gustaw (Maciej Stuhr) with the beautiful Aniela (Anna Cieślak) - the daughter of Dobrójska (Edyta Olszówka) living next door. The parties quickly agree on the marriage contract. The problem is that Gucio spends the nights at the "Under the Golden Parrot" tavern, seduces women, drinks, dances and never marries. Also, Aniela, who is influenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filip Bajon
Filip Michał Bajon (born 25 August 1947) is a Polish people, Polish film director and screenwriter. Selected filmography References External links * 1947 births Living people Film people from Poznań Polish film directors Polish screenwriters {{Poland-film-director-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madison, Wisconsin
Madison is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of Wisconsin. It is the List of municipalities in Wisconsin by population, second-most populous city in the state, with a population of 269,840 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Madison metropolitan area had 680,796 residents. Centrally located on an isthmus between Lakes Lake Mendota, Mendota and Lake Monona, Monona, the vicinity also encompass Lakes Lake Wingra, Wingra, Lake Kegonsa, Kegonsa and Lake Waubesa, Waubesa. Madison was founded in 1836 and is named after American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and President James Madison. It is the county seat of Dane County. As the state capital, Madison is home to government chambers including the Wisconsin State Capitol building. It is also home to the University of Wisconsin–Madison, the flagship campus of the University of Wisconsin System. Major companies in the area include American Family Insurance, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lists Of Polish Films
List of films produced in the Cinema of Poland. For an A-Z list of films currently covered on Wikipedia see Polish films. 1902–1929 * List of Polish films before 1930 Interwar * List of films made in Poland in the Interwar Period 1930s * List of Polish films of the 1930s 1940s * List of Polish films of the 1940s 1950s * List of Polish films of the 1950s 1960s * List of Polish films of the 1960s 1970s * List of Polish films of the 1970s 1980s * List of Polish films of the 1980s 1990s * List of Polish films of the 1990s 2000s * List of Polish films of the 2000s 2010s * List of Polish films of the 2010s * List of Polish films of 2014 * List of Polish films of 2015 * List of Polish films of 2016 * List of Polish films of 2017 * List of Polish films of 2018 * List of Polish films of 2019 2020s * List of Polish films of the 2020s * List of Polish films of 2020 * List of Polish films of 2021 * List of Polish films of 2022 See also *List of years in Poland * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinema Of Poland
The history of cinema in Poland is almost as long as the history of cinematography, and it has universally recognized achievements, even though Polish films tend to be less commercially available than films from several other European nations. After World War II, the communist government built an auteur-based national cinema, trained hundreds of new directors and empowered them to make films. Filmmakers like Roman Polański, Krzysztof Kieślowski, Agnieszka Holland, Andrzej Wajda, Andrzej Żuławski, Andrzej Munk, and Jerzy Skolimowski impacted the development of Polish film-making. In more recent years, the industry has been producer-led with finance being the key to a film being made. History Early history The first cinema was founded in Łódź in 1899, several years after the invention of the Cinematograph. Initially dubbed ''Living Pictures Theatre'', it gained much popularity and by the end of the next decade there were cinemas in almost every major town in Poland. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Culture And National Heritage (Poland)
The Ministry of Culture and National Heritage () is a ministry within Polish government led by the Minister of Culture and National Heritage responsible for national heritage preservation and Polish culture promotion. Ministry oversees state or partially state cultural institutions and implements the law regarding art and cultural property. Ministry headquarters are located at Potocki Palace, 15 Krakowskie Przedmieście Street in Warsaw. Incumbent minister has been Hanna Wróblewska member of the Cabinet) since May 2024 History It was formed on 31 October 2005, from transformation of ''Ministry of Culture of the Republic of Poland''. The ministry can trace its history back to 1918 when the Ministry of Art and Culture was established. It was suppressed in 1922 due to rationalization of public expense and structural reform of the government. It was reestablished within the temporary communist government in 1944 and has existed continuously henceforth until the merger w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Science And Higher Education (Poland)
The Ministry of Science and Higher Education () in Poland was opened on 5 May 2006 by the Minister of Science and Higher Education, in replacement of several parts of the Ministry of Education and Science. The Minister of Science and Higher Education administers governmental activities in science and higher education and has a budget for scientific research provided by State funds. The Rada Nauki (Science Council) acts together with the Minister, in replacement of the Komitet Badań Naukowych (Science Research Council) which was closed in 2005. The headquarters of the ministry are located at ulica Wspólna 1/3, Warsaw. , the current Minister of Science and Higher Education is Marcin Kulasek. List of ministers Ministers of Education and Science {, class="wikitable" , + ! !Portrait !Name !Party ! colspan="2" , Term of Office !Cabinet (Prime minister) , - ! style="background:; , , , Michał Seweryński , Law and Justice (Poland), Law and Justice , 31 October 2005 , 5 May 2006 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a Warsaw metropolitan area, greater metropolitan area of 3.27 million residents, which makes Warsaw the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 6th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures and comprises List of districts and neighbourhoods of Warsaw, 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers . Warsaw is classified as an Globalization and World Cities Research Network#Alpha 2, alpha global city, a major political, economic and cultural hub, and the country's seat of government. It is also the capital of the Masovian Voivodeship. Warsaw traces its origins to a small fishing town in Masovia. The city rose to prominence in the late 16th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uzbek Language
Uzbek is a Karluk Turkic language spoken by Uzbeks. It is the official and national language of Uzbekistan and formally succeeded Chagatai, an earlier Karluk language endonymically called or , as the literary language of Uzbekistan in the 1920s. According to the Joshua Project, Southern Uzbek and Standard Uzbek are spoken as a native language by more than 34 million people around the world, making Uzbek the second-most widely spoken Turkic language after Turkish. There are about 36 million Uzbeks around the world, and the reason why the number of speakers of the Uzbek language is greater than that of ethnic Uzbeks themselves is because many other ethnic groups such as Tajiks, Kazakhs, Russians who live in Uzbekistan speak Uzbek as their second language. There are two major variants of the Uzbek language: Northern Uzbek, or simply "Uzbek", spoken in Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and China; and Southern Uzbek, spoken in Afghanistan and Paki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |