|
Policía Federal Argentina
The Argentine Federal Police ( or PFA) is the national civil police force of the Argentine federal government. The PFA has detachments throughout the country. Until January 1, 2017, it also acted as the local law enforcement agency in the capital, Buenos Aires. History The history of this police force can be traced to 1580, when the founder of Buenos Aires, Captain Juan de Garay, established a local militia for defense against potential Native American raids. The ''Policía de Buenos Aires'' (Buenos Aires Police) operated for the first three hundred years up to 1880, when the Federalization of Buenos Aires resulted in the creation of the ''Policía de la Capital'' (Police of the Capital). Incidents of social unrest in subsequent years helped prompt the Fraga Law in 1904, which provided for the inclusion of neighborhood representatives as commissioners in their respective precincts. The failed Revolution of 1905, by which the UCR sought to bring about reforms to the undemocr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
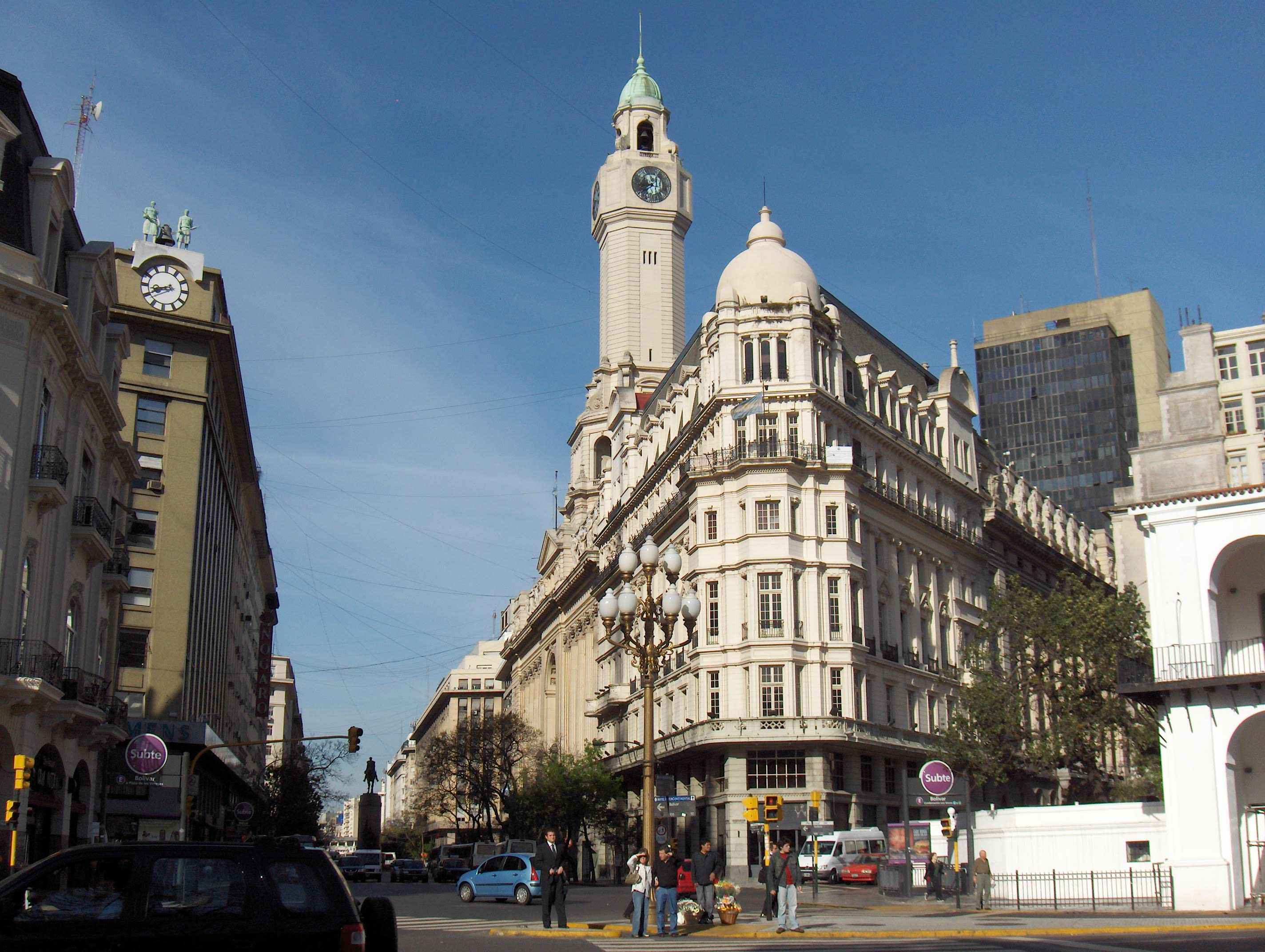
Montserrat, Buenos Aires
Monserrat or Montserrat () is a neighbourhood in the east of the Buenos Aires central business district, Buenos Aires CBD. The district features some of the most important public buildings in Buenos Aires, including city hall, the city legislature, Casa Rosada, the Colegio Nacional de Buenos Aires and the Libertador Building (Argentine Armed Forces, Ministry of Defense), among others. Avenida de Mayo runs through the Monserrat district, connecting Plaza de Mayo and the Plaza de los Dos Congresos (Congressional Plaza). A block, or two, south of the Plaza de Mayo, the older section of Monserrat begins. This is Buenos Aires' oldest neighborhood and even today, very little of the cityscape there is less than a hundred years old (except along Avenida Belgrano, Belgrano Avenue), thereby making a nearly seamless transition to the likewise historic San Telmo district, to the south. History The Monserrat area traces its origins to the foundation of Buenos Aires itself, when, in 158 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Perón
Juan Domingo Perón (, , ; 8 October 1895 – 1 July 1974) was an Argentine military officer and Statesman (politician), statesman who served as the History of Argentina (1946-1955), 29th president of Argentina from 1946 to Revolución Libertadora, his overthrow in 1955 and again as the 40th president from 1973 to his death in 1974. He is the only Argentine president elected three times and holds the September 1973 Argentine presidential election, highest percentage of votes in clean elections with universal suffrage. Perón is arguably the most important and controversial Argentine politician of the 20th century and his influence extends to the present day. Perón's ideas, policies and movement are known as Peronism, which continues to be one of the major forces in Argentine politics. On 1 March 1911, Perón entered military college, graduating on 13 December 1913. Over the years, he rose through the military ranks. In 1930, Perón supported the coup against President Hipólito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Argentina
The government of Argentina, within the framework of a federal system, is a presidential system, presidential Representative democracy, representative democratic republic. The president of Argentina is both head of state and head of government. Executive power is exercised by the president. Legislative power is vested in the Argentine National Congress, National Congress. The Judiciary is independent from the Executive and from the Legislature, and is vested in the Supreme Court of Argentina, Supreme Court and the lower national tribunals. From the own government is also called Presidency of the Nation (). Executive branch The current composition of the executive branch includes solely the President of Argentina, president, who is the head of state and is formally given the power over the administration to follow through with the interests of the nation. The president is also the chief of the Argentine Armed Forces. The president and the List of vice presidents of Argentina, v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonio Cafiero
Antonio Francisco Cafiero (12 September 1922 – 13 October 2014) was an Argentine Justicialist Party politician. Cafiero held a number of important posts throughout his career, including, most notably, the governorship of Buenos Aires Province from 1987 to 1991, the Cabinet Chief's Office under interim president Eduardo Camaño from 2001 to 2002, and a seat in the Senate of the Nation from 1993 to 2005. Early and personal life Cafiero was born in Buenos Aires. He joined Catholic Action in 1938, and enrolled at the University of Buenos Aires, becoming President of the Students' Association. He graduated as an accountant in 1944, and earned a Doctor in Economic Sciences in 1948, teaching in the discipline as a professor from 1952 to 1984. Cafiero became a militant Peronist from the 17 October 1945 mass demonstrations in support of populist leader Juan Perón, and entered public service in 1952 as Minister of Foreign Trade in the latter's administration, serving until 1954. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentine Senate
The Honorable Senate of the Argentine Nation () is the upper house of the National Congress of Argentina. Overview The National Senate was established by the Argentine Confederation on July 29, 1854, pursuant to Articles 46 to 54 of the 1853 Constitution. There are 72 members: three for each province and three for the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires. The number of senators per province was raised from two to three following the 1994 amendment of the Argentine Constitution as well as the addition of the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires' senators. Those changes took effect following the May 14, 1995, general elections. Senators are elected to six-year terms by direct election on a provincial basis, with the party with the most votes being awarded two of the province's senate seats and the second-place party receiving the third seat. Historically, senators were indirectly elected to nine-year terms by each provincial legislature. These provisions were abolished in the 1994 co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peronist
Peronism, also known as justicialism, is an Argentine ideology and movement based on the ideas, doctrine and legacy of Juan Perón (1895–1974). It has been an influential movement in 20th- and 21st-century Argentine politics. Since 1946, Peronists have won 10 out of the 14 presidential elections in which they have been allowed to run. Peronism is defined through its three flags: "economic independence" (an economy that does not depend on other countries, by developing its national industry), "social justice" (the fight against socioeconomic inequalities) and " political sovereignty" (the non-interference of foreign powers in domestic affairs). Peronism as an ideology is described as a social form of nationalism, as it pushes for a sense of national pride among Argentines. However, it promotes an inclusive form of nationalism that embraces all ethnicities and races as integral parts of the nation, distinguishing it from racial or chauvinistic ethno-nationalism that priori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buenos Aires City Legislature
The Buenos Aires City Legislature (, commonly known as the ) is the legislative power of the government of the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires, Argentina. It is housed in the Buenos Aires City Legislature Palace, Legislature Palace (), an architectural landmark in the of Montserrat, Buenos Aires, Montserrat. History The internecine warfare between those who favored a united Argentina with a strong Centralism, central government (''Unitarian Party, Unitarios'') and Buenos Aires Province leaders who favored an independent nation of their own (''Federales (Argentina), Federales'') dominated local political life in the decades following the Argentine War of Independence, Wars of Independence and led to the 1880 Federalization of Buenos Aires. Pursuant to this new policy, in 1882 President Julio Roca signed National Law 1260, which created the presidential prerogative of the appointment of the Mayor of Buenos Aires, as well as a city council by way of compromise towards the put-upon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1994 Reform Of The Argentine Constitution
The 1994 amendment to the Constitution of Argentina was approved on 22 August 1994 by a Constitutional Assembly that met in the twin cities of Santa Fe and Paraná. The calling for elections for the Constitutional Convention and the main issues to be decided were agreed in 1993 between President Carlos Menem, and former president and leader of the opposition, Raúl Alfonsín. Constitutional Assembly election On April 10, 1994 the conventional constituent elections were held. The Justicialist Party led by President Menem won the elections with 38.50% of the votes. Radical Civic Union came second with 19.74% votes, while two newly born forces each obtained 13%: the progressive peronist Broad Front, led by Carlos Álvarez, and the rightist Movement for Dignity and Independence, led by the carapintada military man Aldo Rico. Out of a total of 305 constituents, the Justicialist Party obtained 137 representatives, Radical Civic Union 74, Broad Front 31, Movement for Dignity a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raúl Alfonsín
Raúl Ricardo Alfonsín (; 12 March 1927 – 31 March 2009) was an Argentine lawyer and statesman who served as President of Argentina from 10 December 1983 to 8 July 1989. He was the first democratically elected president after the 7-years National Reorganization Process. Ideologically, he identified as a Radicalism (historical), radical and a social democrat, serving as the leader of the Radical Civic Union from 1983 to 1991, 1993 to 1995, 1999 to 2001, with his political approach being known as "Alfonsinism". Born in Chascomús, Buenos Aires Province, Alfonsín began his studies of law at the National University of La Plata and was a graduate of the University of Buenos Aires. He was affiliated with the Radical Civic Union (UCR), joining the faction of Ricardo Balbín after the party split. He was elected a deputy in the legislature of the Buenos Aires province in 1958, during the presidency of Arturo Frondizi, and a national deputy during the presidency of Arturo Umber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlos Menem
Carlos Saúl Menem (2 July 1930 – 14 February 2021) served as the 50th president of Argentina for ten years, from 1989 to 1999. He identified as Peronism, Peronist, serving as President of the Justicialist Party for 13 years (from 1990 to 2001 and again from 2001 to 2003), and his political approach became known as Menemism. Born in Anillaco, La Rioja Province, Argentina, La Rioja, to a Syrian Argentines, Syrian family, Menem was raised as a Muslim,"Carlos Menem" ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' but later converted to Catholic Church, Roman Catholicism to pursue a political career. Menem became a Peronist during a visit to Buenos Aires. He was elected governor of La Rioja in 1973, deposed and detained following the 1976 Argentine coup d'état, and re-elected in 1983. He defeated the Buenos Aires governor Antonio Cafiero in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivos Pact
The Olivos Pact () refers to a series of documents signed on 17 November 1993, between the governing President of Argentina, Carlos Menem, and former President and leader of the opposition UCR, Raúl Alfonsín, that formed the basis of the constitutional reform of 1994. These memoranda of understanding were signed in the official presidential residence, the Quinta de Olivos. Context Raúl Alfonsín was the president of Argentina for the Radical Civic Union (UCR) from 1983 to 1989, and resigned during an economic crisis. Carlos Menem, from the Justicialist Party (PJ), was elected in 1989. The Convertibility plan ended the economic crisis and increased his popularity, allowing the PJ to win the 1991 and 1993 midterm elections. The presidential term of office was of six years, with no reelection. Menem sought to change that with an amendment to the Constitution of Argentina. For this he would require a supermajority of two thirds of both houses of the Argentine Congress. Althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March 1976 Coup
March is the third month of the year in both the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Its length is 31 days. In the Northern Hemisphere, the meteorological beginning of spring occurs on the first day of March. The March equinox on the 20 or 21 marks the astronomical beginning of spring in the Northern Hemisphere and the beginning of autumn in the Southern Hemisphere, where September is the seasonal equivalent of the Northern Hemisphere's March. History The name of March comes from '' Martius'', the first month of the earliest Roman calendar. It was named after Mars, the Roman god of war, and an ancestor of the Roman people through his sons Romulus and Remus. His month ''Martius'' was the beginning of the season for warfare, and the festivals held in his honor during the month were mirrored by others in October, when the season for these activities came to a close. ''Martius'' remained the first month of the Roman calendar year perhaps as late as 153 BC, and several religious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |