|
Plaza De España (Pontevedra)
The Plaza de España is a 19th century pedestrian square located in the city centre of Pontevedra (Spain), on the edge of the old town and the Alameda de Pontevedra. Origin of the name The square owes its name to the fact that it is the seat of the city's most important political institutions and its central hub. History The Plaza de España was developed at the end of the 19th century following the line of the old medieval wall with the construction of the new City Hall as a transitional space between the historic centre and the Alameda de Pontevedra, which had been the former orchard of the Dominican convent and which the Dominicans transformed into a promenade in 1648 and which, in 1847, was closed off by stone walls. It was with the urban expansion at the end of the 19th century, which made the architect Alejandro Sesmero effective, that the process of forming the Alameda, and thus the Plaza de España, took shape within the framework of the city's bourgeois expansio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontevedra
Pontevedra (, ) is a city in the autonomous community of Galicia (Spain), Galicia, in northwestern Spain. It is the capital of both the ''Pontevedra (comarca), Comarca'' and Province of Pontevedra, and the capital of the Rías Baixas. It is also the capital of its own municipality which is often considered an extension of the actual city. The city is best known for its urban planning, pedestrianisation and the charm of its Old town of Pontevedra, old town. Between 2013 and 2020, the city received numerous awards for its urban planning, like the international European Intermodes Urban Mobility Award in 2013, the 2014 Dubai International Best Practices Award for Sustainable Development awarded by UN-Habitat in partnership with Dubai Municipality and the Excellence Award of the center for Active Design in New York City in 2015, among others. The city also won the European Commission's first prize for urban safety in 2020. Surrounded by hills, the city is located on the edge of a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
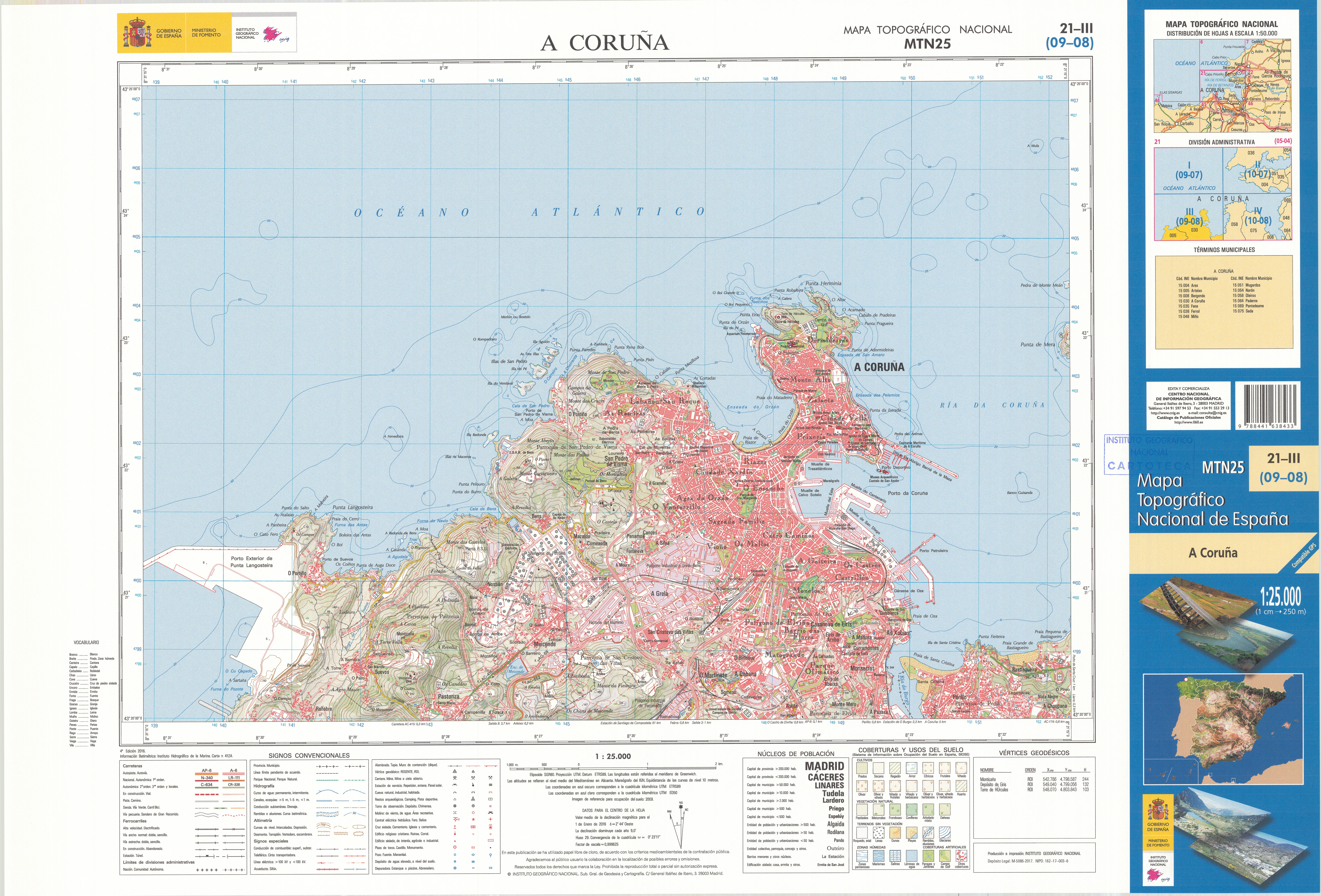
A Coruña
A Coruña (; ; also informally called just Coruña; historical English: Corunna or The Groyne) is a city and municipality in Galicia, Spain. It is Galicia's second largest city, behind Vigo. The city is the provincial capital of the province of A Coruña, having also served as political capital of the Kingdom of Galicia from the 16th to the 19th centuries, and as a regional administrative centre between 1833 and 1982. A Coruña is located on a promontory in the Golfo Ártabro, a large gulf on the Atlantic Ocean. It is the main industrial and financial centre of northern Galicia, and holds the headquarters of the Universidade da Coruña. A Coruña is the Spanish city featuring the tallest mean-height of buildings, also featuring a population density of of built land area. Name Origin There is no clear evidence as to what the name derives from. It seems to be from ''Crunia'', of unknown origin and meaning, documented for the first time at the time of Ferdinand II of Leó ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full achievement (heraldry), heraldic achievement, which in its whole consists of a shield, supporters, a crest (heraldry), crest, and a motto. A coat of arms is traditionally unique to the armiger (e.g. an individual person, family, state, organization, school or corporation). The term "coat of arms" itself, describing in modern times just the heraldic design, originates from the description of the entire medieval chainmail "surcoat" garment used in combat or preparation for the latter. Roll of arms, Rolls of arms are collections of many coats of arms, and since the early Modern Age centuries, they have been a source of information for public showing and tracing the membership of a nobility, noble family, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinthian Order
The Corinthian order (, ''Korinthiakós rythmós''; ) is the last developed and most ornate of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Ancient Roman architecture, Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order, which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. In Ancient Greek architecture, the Corinthian order follows the Ionic in almost all respects, other than the capitals of the columns, though this changed in Roman architecture. A Corinthian capital may be seen as an enriched development of the Ionic capital, though one may have to look closely at a Corinthian capital to see the Ionic volutes ("helices"), at the corners, perhaps reduced in size and importance, scrolling out above the two ranks of Acanthus (ornament), stylized acanthus leaves and stalks ("cauliculi" or ''caulicoles''), eight in all, and to notice that smaller volutes scroll inwards to meet each other on each side. The leaves may be quite stiff, schematic and dry, or t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic classical order, orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric order, Doric and the Corinthian order, Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan order, Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital (architecture), capital, which have been the subject of mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruins Of San Domingos
The ruins of San Domingos (Galician language, Galician: ''Ruínas de San Domingos'', Spanish language, Spanish ''Ruinas de Santo Domingo'') was a convent located in Pontevedra, Galicia (Spain), Galicia (Spain). It was declared ''Bien de Interés Cultural'' in 1895. History Early years This is the oldest of all Pontevedra Museum’s buildings. The only sections of the original buildings that have been conserved are the main apse, formed by five apses, exceptional in Galician gothic architecture, and part of the south wall of the church and the entrance to the chapter of the Santo Domingo convent, founded in around 1282, although the work on the conserved temple did not begin until 1383, continuing through the 15th century. 1836-1880 Following the introduction of the exclaustration law, the convent was closed on 8 December 1836 and handed over to the "Junta de Enajenación de Edificios y Efectos de los Conventos Suprimidos de la Provincia de Pontevedra" (body entrusted wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gobierno Civil De Pontevedra
The Gobierno Civil de Pontevedra, currently Subdelegación del Gobierno de Pontevedra, is an official building located in Pontevedra, Galicia (Spain). It has served since its construction as the government delegation office representing the Spanish state in the province of Pontevedra. Location The building is located in the centre of the city's political power, in the northwest corner of the Alameda de Pontevedra, next to the Plaza de España, very close to other institutional buildings such as the Pontevedra City Hall, the Valle-Inclán High School, the Faculty of Fine Arts and the Pontevedra Provincial Council Palace. History In 1833, the Spanish government appointed as the first provincial authority a State representative in each of the capitals of the Spanish provinces and in Pontevedra, his seat was until 1891 the convent of San Francisco. Until 1997, the name of this representative was "Civil Governor", when it was renamed " Sub-delegate of the Government". Such an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calle Marqués De Riestra
Calle may refer to: Places *Calle-Calle River, southern Chile Film and television *''Calle 7'', a Chilean TV Show *''Calle 54'' (2000), a documentary film Music *Calle 13 (band), a Puerto Rican hip hop band *"Calle Ocho" (2009), a hip hop song by Pitbull Other uses *Calle (name)Calle (brand)A SLC-based street soccer brand helping to build street soccer courts across America. *Calle (Venice), a typical Venetian street, located between two continuous rows of buildings See also *Cable (other) *Cale (other) *Call (other) *Calla (other) *Caller (other) Caller may refer to: * Caller (telecommunications), a party that originates a call * "gentlement callers", a term in courtship * Caller (dancing), a person that calls dance figures in round dances and square dances * Caller, the Catalan equival ... * Callie (other) * Cally (other) * Calpe (other) * Celle (other) {{disambiguation, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gran Vía De Montero Ríos
The Gran Vía de Montero Ríos is an avenue in Pontevedra (Spain) located in the Ensanche de Pontevedra, city centre, in the 19th century bourgeois area. It is one of the most emblematic avenues in Pontevedra. Origin of the name The avenue was called Gran Vía (major thoroughfare) because it was the widest in the city when it was created. After his death in 1914, the avenue was dedicated to Eugenio Montero Ríos, for his great political activity in favour of Pontevedra. History The Gran Vía de Montero Ríos, originally known as the Gran Vía, was designed in the 1870s to connect the Alameda de Pontevedra with the grounds of the Palm Trees Park, old fairground. Its design was included in the project commissioned by the City Council of Pontevedra, City Council in 1880 by the architect Alejandro Sesmero for the planning and development of the Alameda de Pontevedra, Alameda. In 1884, the Provincial Council of Pontevedra bought from the City Council of Pontevedra the land where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calle Michelena
The Calle Michelena is a street in Pontevedra (Spain) located in the city centre, on the edge of the old town. It is one of the main streets of Pontevedra and one of the most commercial streets of the city. Origin of the name Since 1858, the street has been dedicated to José María de Michelena, who was appointed Civil Governor of Pontevedra and President of the Provincial Council of Pontevedra on 11 November 1851 and who left his post on 6 May 1853. His great initiatives and activity, as well as his excellent conditions as governor, earned him a street in the city. He was responsible for the design of the access to the Church of St. Francis with its iron balustrade and flowerbed in the square in front of the church. History The present Michelena Street was a narrow path outside the perimeter of the walls of Pontevedra, with a beaten earth floor where water accumulated, known as Poza das Rans. In 1852, the walls of Pontevedra began to be demolished through the Trabancas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monument To The Heroes Of Puente Sampayo
The Monument to the Heroes of Puente Sampayo is a memorial and sculptural group created by the Spanish sculptor Julio González Pola, in Pontevedra, Spain. It is in the gardens of the Plaza de España and was inaugurated on 27 August 1911. The monument commemorates the courage of the people of Pontevedra led by the officer Pablo Morillo and their triumph over the Napoleonic troops of Marshal Michel Ney, liberating Pontevedra from the occupation of the French army on 7 and 8 June 1809. History The Galician parliamentarian Eduardo Vincenti Reguera and the Galician Centre in Madrid were the main actors in the creation of the monument. On 9 February 1909, the Pontevedra City Council agreed to grant a subsidy of 500 pesetas and, later, authorised the contribution of the granite stone that supports the figures. This initiative was also supported by Javier Puig Llamas, mayor of Pontevedra at the time, and Eugenio Montero Ríos, president of the Senate. All these authorities made s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgo Bridge
The Burgo Bridge ''(Puente del Burgo)'' is a medieval bridge, built over an older bridge of Roman origin, which crosses the Lérez River in the city of Pontevedra, Spain. It is on the route of the Portuguese Way to the north of the old town of Pontevedra, historic centre of Pontevedra and to the south of the O Burgo (Pontevedra), Burgo neighbourhood. Between the arches above the pillars are carved the famous stone pilgrim's Scallop Shell, shells. History The present medieval bridge is the heir to the first Roman bridge over which the Roman road XIX passed according to Antonine Itinerary. This bridge still existed in the 12th century but was in ruins. It remained for a very long time the only crossing point of the Lérez River on the Portuguese Way. The first references to the current bridge date back to 1165, when King Ferdinand the Catholic of León and King Afonso I of Portugal signed the Peace of Lérez in the ''super flumen Lerice in vetula ponte'', designating the old Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |