|
Platystacus
''Platystacus '' is a genus of banjo catfish in the family Aspredinidae. It is monotypic, being represented by the single species ''Platystacus cotylephorus'', commonly known as the banded banjo . The genus ''Platystacus'' is the sister group to a clade containing '' Aspredo'' and '' Aspredinichthys''. ''P. cotylephorus'' originates from coastal waters and lower portions of rivers of northern South America, from Venezuela to northern Brazil. This species grows up to about SL and is distinguished from all other aspredinids by having 4+5 caudal fin rays. They are further distinguished from its close relatives by the absence of accessory maxillary barbels and the presence of well developed rows of unculiferous tubercles. ''P. cotylephorus'' is usually found in brackish waters on the soft bottoms of shallow, turbid water near to the mouths of rivers. reportedly it migrates into freshwater, though spawning Spawn is the Egg cell, eggs and Spermatozoa, sperm released or deposit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banjo Catfish
The Aspredinidae are a small South American family of catfishes (order Siluriformes) also known as the banjo catfishes, with about 43 species. Distribution Aspredinids are found throughout the major tropical rivers of South America (e.g., Magdalena, Orinoco, Amazon, São Francisco, Paraguay- Paraná, and Uruguay). ''Bunocephalus'' is the only genus found in rivers west of the Andes including the Atrato, San Juan, and Patía Rivers. Taxonomy Of the 13 genera in the family Aspredinidae, a few genera have been described relatively recently, including ''Acanthobunocephalus'' in 1995, ''Micromyzon'' in 1996, and ''Pseudobunocephalus'' in 2008. These genera are categorized into three subfamilies. The Aspredinidae are often recognized as a part of the primarily Asian superfamily Sisoroidea as the sister group to the family Erethistidae. However, other authors find that they are sister to the superfamily Doradoidea, which includes Doradidae, Auchenipteridae, and perhaps Mochokid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspredinidae
The Aspredinidae are a small South American family (biology), family of catfishes (order (biology), order Siluriformes) also known as the banjo catfishes, with about 43 species. Distribution Aspredinids are found throughout the major tropical rivers of South America (e.g., Magdalena River, Magdalena, Orinoco, Amazon River, Amazon, São Francisco River, São Francisco, Paraguay River, Paraguay-Paraná River, Paraná, and Uruguay River, Uruguay). ''Bunocephalus'' is the only genus found in rivers west of the Andes including the Atrato River, Atrato, San Juan River (Colombia), San Juan, and Patía Rivers. Taxonomy Of the 13 genus, genera in the family Aspredinidae, a few genera have been described relatively recently, including ''Acanthobunocephalus'' in 1995, ''Micromyzon'' in 1996, and ''Pseudobunocephalus'' in 2008. These genera are categorized into three subfamilies. The Aspredinidae are often recognized as a part of the primarily Asian superfamily Sisoroidea as the cladistics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspredo
''Aspredo aspredo'' is the only species of banjo catfish (order Siluriformes) in the genus ''Aspredo''. This species originates from the lower portions of rivers from Venezuela to northern Brazil. It occurs in the Orinoco delta, through the Guianas, to the Amazon River to the island of Trinidad. ''A. aspredo'' is the largest species of aspredinid, reaching about 38.3 centimetres (15.1 in) SL. The maxillary barbels are attached to the head, the colouration is uniform without any pattern of dark saddles, and the unculiferous tubercles present in other aspredinids are highly reduced. ''A. aspredo'' is a benthic fish that is found on sandy-muddy bottoms in turbid waters in coastal river mouths where it can be found in brackish waters. However, it appears to enter further into fresh water Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salt (chemistry), salts and other total dissolved solids. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
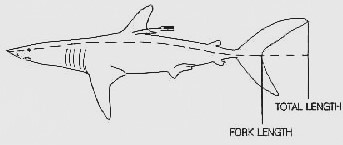
Fish Measurement
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the hypural plate. This measurement excludes the length of the caudal (tail) fin. Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes ( lampreys) and usually Elasmobranchii (shark Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Described In 1794
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fish wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |