|
Pierre-François Flaugergues
Pierre-François Flaugergues (1767–1836) was a French lawyer who took an active part in national politics between January 1813 and September 1816. Biography Flaugergues was born on 14 January 1767 in Saint-Cyprien, Aveyron. He was a member of the National Assembly and the Chamber of Deputies representing: *Aveyron (6 January 1813 – 4 June 1814) — Sat with the opposition. *Aveyron (4 June 1814 – 20 March ) — Sat with the Royalists. *Aveyron (15 May 1815 – 13 July 1815) — Sat with the opposition. *Aveyron (22 August 1815 – 5 September 1816) — Sat with the moderates. He died on 31 October 1836 in Brie, Ariège. In December 1813 he was a member of the committee of three that prepared an address to Napoleon Bonaparte on the state of the nation. On 21 June 1815 shortly after the French defeat at the Battle of Waterloo and shortly before the abdication of Napoleon Boneparte as Emperor of the French, Flaugergues was on the commission of five members consisting of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Cyprien-sur-Dourdou
Saint-Cyprien-sur-Dourdou (, literally ''Saint-Cyprien on Dourdou de Conques, Dourdou''; ) is a former Communes of France, commune in the Aveyron Departments of France, department in southern France. On 1 January 2016, it was merged into the new commune of Conques-en-Rouergue. 19 November 2015 Population See also *Communes of the Aveyron departmentReferences Former communes of Aveyron Aveyron communes articles needing translation from French Wikipedia Populated places disestablished in 2016 {{Aveyron-geo-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brie, Ariège
Brie (; ) is a commune in the Ariège department of southwestern France. The commune is located on the slopes between the rivers Ariège and Lèze. It borders the department of Haute-Garonne. The mayor is Isabelle Peyrefitte. Population In 2017, the commune had 219 inhabitants, an increase of 31% compared to 2007. Inhabitants of Brie are called ''Briençais''. See also *Communes of the Ariège department The following is a list of the 325 communes of the Ariège department of France France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French ... References Communes of Ariège (department) Ariège communes articles needing translation from French Wikipedia {{Ariège-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career of Napoleon, a series of military campaigns across Europe during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars from 1796 to 1815. He led the French First Republic, French Republic as French Consulate, First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then ruled the First French Empire, French Empire as Emperor of the French from 1804 to 1814, and briefly again in 1815. He was King of Italy, King of Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Italy from 1805 to 1814 and Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine, Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine from 1806 to 1813. Born on the island of Corsica to a family of Italian origin, Napoleon moved to mainland France in 1779 and was commissioned as an officer in the French Royal Army in 1785. He supported the French Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (then in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium), marking the end of the Napoleonic Wars. The French Imperial Army (1804–1815), French Imperial Army under the command of Napoleon, Napoleon I was defeated by two armies of the Seventh Coalition. One was a United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British-led force with units from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom, the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Kingdom of Hanover, Hanover, Duchy of Brunswick, Brunswick, and Duchy of Nassau, Nassau, under the command of field marshal Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Arthur Wellesley, Duke of Wellington. The other comprised three corps of the Kingdom of Prussia, Prussian army under Field Marshal Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, Blücher. The battle was known contemporaneously as the ''Battle of Mont-Saint-Jean, Belgium, Mont Saint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
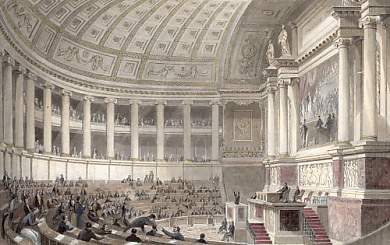
Chamber Of Deputies (France)
The Chamber of Deputies (, ) was the lower house of parliament in France at various times in the 19th and 20th centuries: * 1814–1848 during the Bourbon Restoration in France, Bourbon Restoration and the July Monarchy, the Chamber of Deputies was the lower house of the French Parliament, elected by census suffrage. * 1875–1940 during the French Third Republic, the Chamber of Deputies was the legislative assembly of the French Parliament, elected by two-round system with universal male suffrage. When reunited with the Senate (France), Senate in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, the French Parliament was called the National Assembly (France), National Assembly (''Assemblée nationale'') and carried out the election of the President of France, president of the French Republic. During the Bourbon Restoration Created by the Charter of 1814 and replacing the Corps législatif, which existed under the First French Empire, the Chamber of Deputies was composed of individuals electe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdication Of Napoleon, 1815
Napoleon abdicated on 22 June 1815, in favour of his son Napoleon II. On 24 June, the Provisional Government then proclaimed his abdication to France and the rest of the world. After his defeat at the Battle of Waterloo, Napoleon I returned to Paris, seeking to maintain political backing for his position as Emperor of the French. Assuming his political base to be secured, he aspired to continue the war. However, the parliament (formed according to the Charter of 1815) created a Provisional Government and demanded Napoleon's abdication. Napoleon initially considered a ''coup d'état'' similar to Eighteenth of Brumaire, but ultimately discarded this idea. On 25 June, after a stay at the Palace of Malmaison, Napoleon left Paris towards the coast, hoping to reach the United States of America. Meanwhile, the Provisional Government deposed his son and attempted negotiating a conditional surrender with the Coalition powers. As they failed obtaining concessions from the Coalition, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Provisional Government, 1815
The French Provisional Government or French Executive Commission of 1815 replaced the French government of the Hundred Days that had been formed by Napoleon after his return from exile on Elba. It was formed on 22 June 1815 after the abdication of Napoleon following his defeat at the Battle of Waterloo. The government acted under the nominal authority of Napoleon II, who had technically succeeded his father as Emperor after the abdication; however, this was a mere formality, since Napoleon II was a four-year-old child and was in Austria with his mother Marie Louise, and thus unable to actually exercise his powers. Following the second Bourbon Restoration, on 9 July 1815 the Provisional Government was replaced by the Ministry of Charles-Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord. Formation On 12 June 1815 Napoleon left Paris for modern day Belgium, where the two Coalition armies, an allied one commanded by the Duke of Wellington and a Prussian one under Prince Gebhard Leberecht von Blü ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Wellington
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ranked below grand dukes and above or below princes, depending on the country or specific title. The title comes from French ''duc'', itself from the Latin '' dux'', 'leader', a term used in republican Rome to refer to a military commander without an official rank (particularly one of Germanic or Celtic origin), and later coming to mean the leading military commander of a province. In most countries, the word ''duchess'' is the female equivalent. Following the reforms of the emperor Diocletian (which separated the civilian and military administrations of the Roman provinces), a ''dux'' became the military commander in each province. The title ''dux'', Hellenised to ''doux'', survived in the Eastern Roman Empire where it continued in se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Blücher
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". In a related sense, now not commonly used, all more or less sovereign rulers over a state, including kings, were "princes" in the language of international politics. They normally had another title, for example king or duke. Many of these were Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, ), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the ''princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus established the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventh Coalition
The Hundred Days ( ), also known as the War of the Seventh Coalition (), marked the period between Napoleon's return from eleven months of exile on the island of Elba to Paris on20 March 1815 and the second restoration of King Louis XVIII on 8 July 1815 (a period of 110 days). This period saw the War of the Seventh Coalition, and includes the Waterloo campaign and the Neapolitan War as well as several other minor campaigns. The phrase ''les Cent Jours'' (the Hundred Days) was first used by the prefect of Paris, Gaspard, comte de Chabrol, in his speech welcoming the king back to Paris on 8 July. Napoleon returned while the Congress of Vienna was sitting. On 13 March, seven days before Napoleon reached Paris, the powers at the Congress of Vienna declared him an outlaw, and on 25 March, Austria, Prussia, Russia and the United Kingdom, the four Great Powers and key members of the Seventh Coalition, bound themselves to put 150,000 men each into the field to end his rule. This s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1767 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – The first annual volume of ''The Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris'', produced by British Astronomer Royal Nevil Maskelyne at the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, gives navigators the means to find longitude at sea, using tables of lunar distance. * January 9 – William Tryon, governor of the Royal Colony of North Carolina, signs a contract with architect John Hawks to build Tryon Palace, a lavish Georgian style governor's mansion on the New Bern waterfront. * February 16 – On orders from head of state Pasquale Paoli of the newly independent Republic of Corsica, a contingent of about 200 Corsican soldiers begins an invasion of the small island of Capraia off of the coast of northern Italy and territory of the Republic of Genoa. By May 31, the island is conquered as its defenders surrender.George Renwick, ''Romantic Corsica: Wanderings in Napoleon's Isle'' (Charles Scribner's Sons, 1910) p230 * February 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1836 Deaths
Events January–March * January 1 — Hill Street Academy is named Colombo Academy and acquired by the Government, establishing the first public school in Sri Lanka. * January 1 – Queen Maria II of Portugal marries Prince Ferdinand Augustus Francis Anthony of Saxe-Coburg-Gotha. * January 5 – Former U.S. Representative Davy Crockett of Tennessee arrives in Texas to join the Texan fight for independence from Mexico. * January 12 ** , with Charles Darwin on board, reaches Sydney. ** Will County, Illinois, is formed. * February 8 – London and Greenwich Railway opens its first section, the first railway in London, England. * February 23 – Texas Revolution: The Battle of the Alamo begins, with an American settler army surrounded by the Mexican Army, under Santa Anna. * February 25 – Samuel Colt receives a United States patent for the Colt revolver, the first revolving barrel multishot firearm. * March 1 – Texas Revolution – Convention of 1836: Delegates from m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |