|
Pictured Rove Beetle
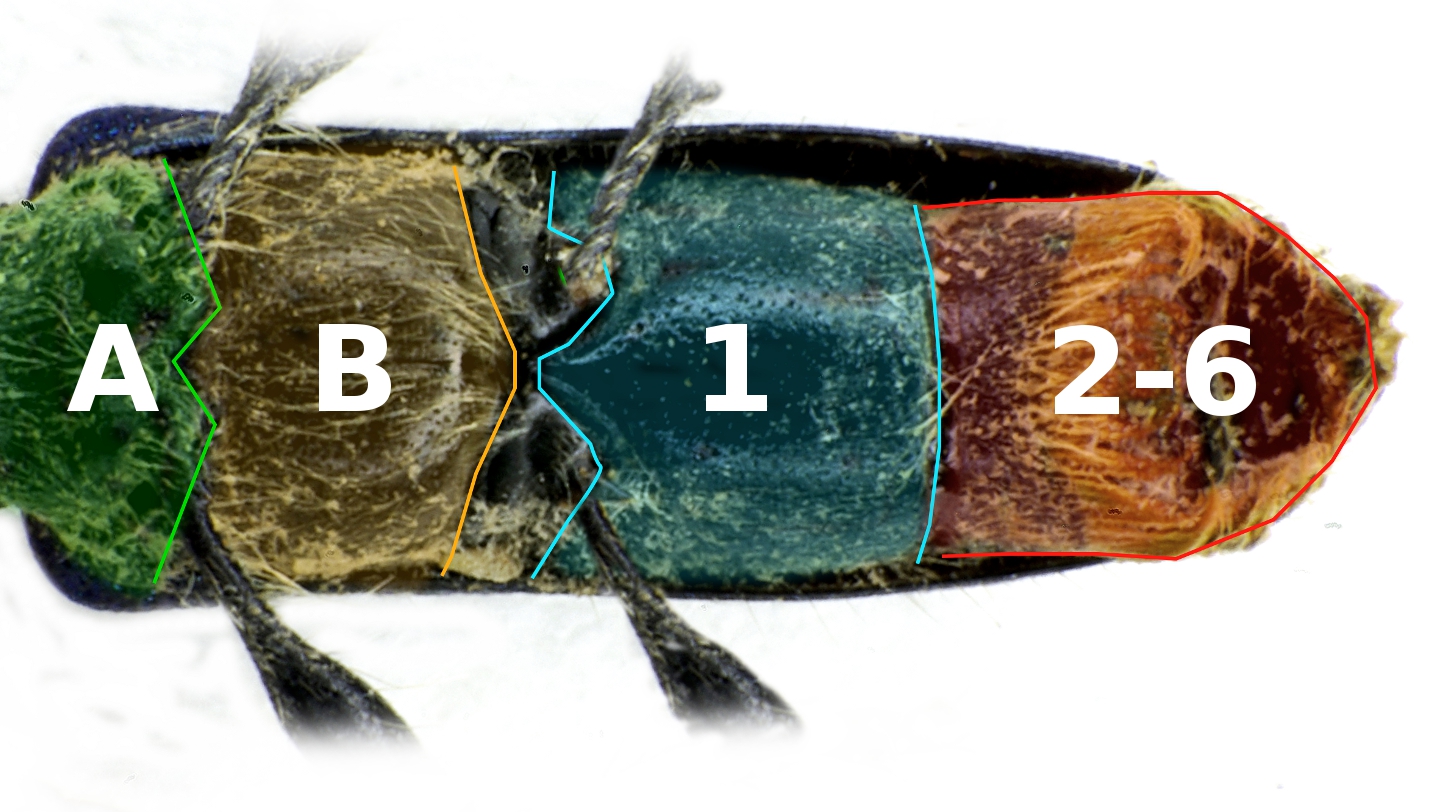
The pictured rove beetle (''Thinopinus pictus'') is a wingless rove beetle which lives on the sandy beaches of the West Coast of the United States from southern Alaska to Baja California. It is nocturnal, emerging at night from temporary sand burrows to feed on beach hoppers ('' Orchestoidea''). Identification Like other rove beetles, ''T. pictus'' has shortened elytra, so that most of its abdomen is exposed. Males average , females average . Males possess a cleft in the last abdominal sternite, which makes them readily discernible from females. Their cryptic coloration varies geographically in response to lighter colored sand in the southern part of their range. Populations north of central California tend to be darker in response to the dark volcanic sand, while those in the southern range are quite pale. Because of this variation, ''T. pictus'' was once thought to be made up of two subspecies. Ecology ''T. pictus'' inhabits the sandy intertidal zone; during the day, they hide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are motility, able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million extant taxon, living animal species have been species description, described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and biological interaction, interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternite
The sternum (: sterna) is the ventral portion of a segment of an arthropod thorax or abdomen. In insects, the sterna are usually single, large sclerites, and external. However, they can sometimes be divided in two or more, in which case the subunits are called sternites, and may also be modified on the terminal abdominal segments so as to form part of the functional genitalia, in which case they are frequently reduced in size and development, and may become internalized and/or membranous. For a detailed explanation of the terminology, see Kinorhynchs have tergal and sternal plates too, though seemingly not homologous with those of arthropods.Sørensen, M. V. et al. Phylogeny of Kinorhyncha based on morphology and two molecular loci. PLoS One 10, 1–33 (2015). Ventrites are externally visible sternites. Usually the first sternite is covered up, so that ventrite numbers do not correspond to sternite numbers. The term is also used in other arthropod groups such as crustaceans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wingless Beetles
In cellular biology, the Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt, pronounced "wint", is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling pathways use either nearby cell-cell communication (paracrine) or same-cell communication (autocrine). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans. Three Wnt signaling pathways have been characterized: the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway. All three pathways are activated by the binding of a Wnt-protein ligand to a Frizzled family receptor, which passes the biological signal to the Dishevelled protein inside the cell. The canonical Wnt pathway leads to regulation of gene transcription, and is thought to be negatively regulated in part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beetles Of North America
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Holometabola. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 described species, is the largest of all orders, constituting almost 40% of described arthropods and 25% of all known animal species; new species are discovered frequently, with estimates suggesting that there are between 0.9 and 2.1 million total species. However, the number of beetle species is challenged by the number of species in dipterans (flies) and hymenopterans (wasps). Found in almost every habitat except the sea and the polar regions, they interact with their ecosystems in several ways: beetles often feed on plants and fungi, break down animal and plant debris, and eat other invertebrates. Some species are serious agricultural pests, such as the Colorado potato beetle, while others such as Coccinellidae (ladybirds or ladybugs) eat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beetles Described In 1852
Beetles are insects that form the Taxonomic rank, order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Holometabola. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 described species, is the largest of all orders, constituting almost 40% of described arthropods and 25% of all known animal species; new species are discovered frequently, with estimates suggesting that there are between 0.9 and 2.1 million total species. However, the number of beetle species is challenged by the number of species in Fly, dipterans (flies) and hymenopterans (wasps). Found in almost every habitat except the sea and the polar regions, they interact with their ecosystems in several ways: beetles often feed on plants and fungi, break down animal and plant debris, and eat other invertebrates. Some species are serious agricultural pests, such as the Colorado potato beetle, while others such as Coccinellidae (ladybirds or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. A larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. In the case of smaller primitive arachnids, the larval stage differs by having three instead of four pairs of legs. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviposition
The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typically its form is adapted to functions such as preparing a place for the egg, transmitting the egg, and then placing it properly. For most insects, the organ is used merely to attach the egg to some surface, but for many parasitic species (primarily in wasps and other Hymenoptera), it is a piercing organ as well. Some ovipositors only retract partly when not in use, and the basal part that sticks out is known as the scape, or more specifically oviscape, the word ''scape'' deriving from the Latin word , meaning "stalk" or "shaft". In insects Grasshoppers use their ovipositors to force a burrow into the earth to receive the eggs. Cicadas pierce the wood of twigs with their ovipositors to insert the eggs. Sawflies slit the tissues of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Entomology
The Royal Entomological Society is a learned society devoted to the study of insects. It aims to disseminate information about insects and to improve communication between entomology, entomologists. The society was founded in 1833 as the Entomological Society of London. It had many antecedents beginning as the Society of Entomologists of London. History The foundation of the society began with a meeting of "gentlemen and friends of entomological science", held on 3 May 1833 in the British Museum convened by Nicholas Aylward Vigors with the presidency of John George Children. Those present were the Reverend Frederick William Hope, Cardale Babington, William Yarrell, John Edward Gray, James Francis Stephens, Thomas Horsfield, George Thomas Rudd and George Robert Gray. Letters of Adrian Hardy Haworth, George Bennett (naturalist), George Bennett and John Curtis (entomologist), John Curtis were read where they expressed their regrets to be unable to attend the meeting. They decid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopoda
Isopoda is an order of crustaceans. Members of this group are called isopods and include both aquatic species and terrestrial species such as woodlice. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, and five pairs of branching appendages on the abdomen that are used in respiration. Females brood their young in a pouch under their thorax called the marsupium. Isopods have various feeding methods: some eat dead or decaying plant and animal matter, others are grazers or filter feeders, a few are predators, and some are internal or external parasites, mostly of fish. Aquatic species mostly live on the seabed or the bottom of freshwater bodies of water, but some taxa can swim for short distance. Terrestrial forms move around by crawling and tend to be found in cool, moist places. Some species are able to roll themselves into a ball as a defense mechanism or to conserve moisture like species in the family Armadilli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Experimental Marine Biology And Ecology
The ''Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology'' is a peer-reviewed bimonthly journal which publishes work on the biochemistry, physiology, behaviour, and genetics of marine plants and animals in relation to their ecology. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2015 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 1.796. References English-language journals Academic journals established in 1967 Biology journals Ecology journals Bimonthly journals Elsevier academic journals Marine biology {{ecology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphipoda
Amphipoda () is an order (biology), order of malacostracan crustaceans with no carapace and generally with laterally compressed bodies. Amphipods () range in size from and are mostly detritivores or scavengers. There are more than 10,700 amphipod species currently recognized. They are mostly marine animals, but are found in almost all aquatic environments. Some 2,250 species live in fresh water, and the order also includes the terrestrial Talitridae, sandhoppers such as ''Talitrus saltator'' and ''Arcitalitrus sylvaticus''. Etymology and names The name ''Amphipoda'' comes, via Neo-Latin ', from the Greek language, Greek root (linguistics), roots 'on both/all sides' and 'foot'. This contrasts with the related Isopoda, which have a single kind of thoracic leg. Particularly among Angling, anglers, amphipods are known as ''freshwater shrimp'', ''scuds'', or ''sideswimmers''. Description Anatomy The body of an amphipod is divided into 13 segments, which can be tagmosis, grouped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oecologia
''Oecologia'' is an international peer-reviewed English-language journal published by Springer since 1968 (some articles were published in German or French until 1976). The journal publishes original research in a range of topics related to plant and animal ecology. ''Oecologia'' has an international focus and presents original papers, methods, reviews and special topics. Papers focus on population ecology, plant-animal interactions, ecosystem ecology, community ecology, global change ecology, conservation ecology, behavioral ecology and physiological ecology. ''Oecologia'' had an impact factor of 3.298 (2021) and is ranked 37 out of 136 in the subject category "ecology". Editorial Board As of December 2022, the journal has six editors in chief: * Carlos L. Ballaré (plant-microbe/plant-animal interactions), University of Buenos Aires, Argentina * Nina Farwig (terrestrial invertebrate ecology), University of Marburg, Germany * Indrikis Krams (terrestrial vertebrate ecology), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |