|
Piastów Avenue, Szczecin
Piastów is a town in central Poland in the Masovian Voivodship, within the Warsaw metropolitan area, with 23,331 inhabitants (2006 est). With 3963 persons/km², it is the second most densely populated township in Poland (after Świętochłowice). Geography History In the Middle Ages, the villages of Żdżary and Utrata existed in the place of today's Piastów. Following the joint German-Soviet invasion of Poland, which started World War II in September 1939, Piastów was occupied by Germany until January 1945. In early 1940, 100 expelled Poles from Poznań were deported to Piastów. The local branch of the Polish Red Cross looked after Polish displaced persons, treated the wounded, organised food parcels for local Poles held in German prisoner-of-war camps and conducted secret sanitary and rescue training. The last pre-war chief of the Piastów police station was murdered by the Russians in Tver in the Katyn massacre in 1940. During the Warsaw Uprising, in August 1944, Pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konotopa, Warsaw West County
Konotopa is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Ożarów Mazowiecki, within Warsaw West County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. It lies approximately south-east of Ożarów Mazowiecki and west of Warsaw Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at .... References Villages in Warsaw West County {{WarsawWest-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Resistance Movement In World War II
In Poland, the Resistance during World War II, resistance movement during World War II was led by the Home Army. The Polish resistance is notable among others for disrupting German supply lines to the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front (damaging or destroying 1/8 of all rail transports), and providing military intelligence, intelligence reports to the United Kingdom, British British intelligence agencies, intelligence agencies (providing 43% of all reports from German-occupied Europe, occupied Europe). It was a part of the Polish Underground State. Organizations The largest of all Polish resistance organizations was the Armia Krajowa (Home Army, AK), loyal to the Polish government in exile in London. The AK was formed in 1942 from the Union of Armed Struggle (''Związek Walki Zbrojnej'' or ZWZ, itself created in 1939) and would eventually incorporate most other Polish armed resistance groups (except for the communists and some far-right groups). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw Voivodeship (1975-1998)
{{Disambiguation ...
Warsaw Voivodeship may refer to: * Masovian Voivodeship (1526–1795) * Warsaw Voivodeship (1919–1939) * Warsaw Voivodeship (1944–1975) * Warsaw Voivodeship (1975–1998) * Masovian Voivodeship, created in 1999 See also *Voivodeships of Poland *Warsaw Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wola
Wola () is a district in western Warsaw, Poland. An industrial area with traditions reaching back to the early 19th century, it underwent a transformation into a major financial district, featuring various landmarks and some of the tallest office buildings in the city. History Village Wielka Wola was first mentioned in the 14th century. It became the site of the elections, from 1573 to 1764, of Polish kings by the szlachta (nobility) of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Wola district later became famous for the Polish Army's defence of Warsaw in 1794 during the Kościuszko Uprising and in 1831 during the November Uprising, when Józef Sowiński and Józef Bem defended the city against Tsarist forces. In the 17th century, the jurydyki of Wielopole, Leszno, Nowolipie and Grzybów were established, which were incorporated into Warsaw in 1791, and today are wholly or partly within the boundaries of the Wola district. In the 19th century, Wola developed as a factory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katyn Massacre
The Katyn massacre was a series of mass killings under Communist regimes, mass executions of nearly 22,000 Polish people, Polish military officer, military and police officers, border guards, and intelligentsia prisoners of war carried out by the Soviet Union, specifically the NKVD (the Soviet secret police), at Joseph Stalin's order in April and May 1940. Though the killings also occurred in the Tver#20th century, Kalinin and Kharkiv NKVD prisons and elsewhere, the massacre is named after the Katyn forest, where some of the mass graves were first discovered by Nazi German forces in 1943. The massacre is qualified as a Crimes against humanity, crime against humanity, Crime of aggression, crime against peace, war crime and (within the Polish Penal Code) a Communist crimes (Polish legal concept), Communist crime. According to a 2009 resolution of the Polish parliament's Sejm, it bears the hallmarks of a genocide. The order to execute captive members of the Polish officer corps wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tver
Tver (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative centre of Tver Oblast, Russia. It is situated at the confluence of the Volga and Tvertsa rivers. Tver is located northwest of Moscow. Population: The city is situated where three rivers meet, splitting the town into northern and southern parts by the Volga, and divided again into quarters by the Tvertsa River, which splits the left (northern) bank into east and west halves, and the Tmaka River which does the same along the southern bank. Tver was formerly the capital of a powerful medieval state and a model provincial town in the Russian Empire, with a population of 60,000 by 14 January 1913. The city was known as Kalinin () from 1931 to 1990. Etymology According to one hypothesis, the name of the city is of Finnic languages, Finnic origin, ''*Tiheverä''. History Medieval origins Tver's foundation year is officially accepted to be 1135.Charter of Tver, Article 1 Originally a minor se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Prisoner-of-war Camps In World War II
Nazi Germany operated around 1,000 prisoner-of-war camps () during World War II (1939-1945). The most common types of camps were Oflag, Oflags ("Officer camp") and Stalag, Stalags ("Base camp" – for enlisted personnel POW camps), although other less common types existed as well. Legal background German Reich, Germany signed the Third Geneva Convention of 1929, which established norms relating to the treatment of prisoners of war. * Article 10 required PoWs be lodged in adequately heated and lighted buildings where conditions were the same as for German troops. * Articles 27-32 detailed the conditions of labour. Enlisted ranks were required to perform whatever labour they were asked if able to do, so long as it was not dangerous and did not support the German war-effort. Senior non-commissioned officers (sergeants and above) were required to work only in a supervisory role. Commissioned officers were not required to work, although they could volunteer. The work performed was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Red Cross
Polish Red Cross (, abbr. PCK) is the Polish member of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement. Its 19th-century roots may be found in the Russian and Austrian Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. On regaining its independence in 1918 Poland's charitable institutions were able to reconvene and establish the Red Cross on its territory under the presidency of Paweł Sapieha, formerly President of the Red Cross in Galicia. The new society was recognized by the International Red Cross on 24 July 1919. During the Polish People's Republic (1947–1989) the Polish Red Cross lost its autonomy and all its assets to the state. Across its hundred year history it continues its humanitarian work at home and abroad. Its focus is on education, exhumations and missing persons. It continues to carry aid to refugees. History On 18 January 1919 the Polish Samaritan Society organized a meeting of all Polish charities that followed the Red Cross principles. With the supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
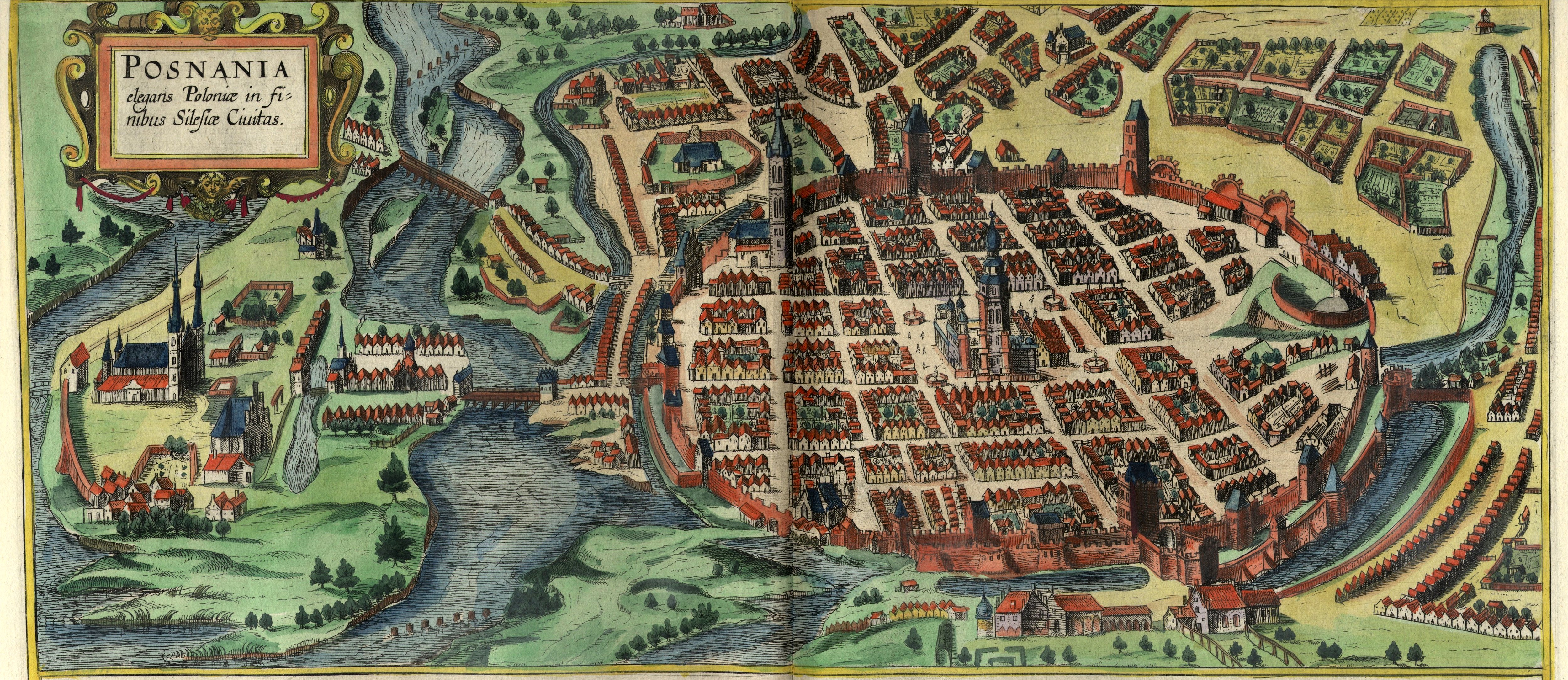
Poznań
Poznań ( ) is a city on the Warta, River Warta in west Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business center and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John's Fair, Poznań, Saint John's Fair (''Jarmark Świętojański''), traditional St. Martin's croissant, Saint Martin's croissants and a local dialect. Among its most important heritage sites are the Renaissance in Poland, Renaissance Old Town, Poznań Town Hall, Town Hall and Poznań Cathedral. Poznań is the fifth-largest List of cities and towns in Poland#Cities, city in Poland. As of 2023, the city's population is 540,146, while the Poznań metropolitan area (''Metropolia Poznań'') comprising Poznań County and several other communities is inhabited by over 1.029 million people. It is one of four historical capitals of medieval Poland and the ancient capital of the Greater Poland region, currently the administrative capital of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expulsion Of Poles By Nazi Germany
The Expulsion of Poles by Nazi Germany during World War II was a massive operation consisting of the forced resettlement of over 1.7 million Polish people, Poles from the territories of Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), German-occupied Poland, with the aim of their Germanisation in Poland (1939–1945), Germanization (see ''Lebensraum'') between 1939 and 1944. The German Government had plans for the extensive Settler colonialism, colonisation of territories of occupied Poland, which were annexed directly into Nazi Germany in 1939. Eventually these plans grew bigger to include parts of the General Government. The region was to become a "purely German area" within 15–20 years, as explained by Adolf Hitler in March 1941. By that time the General Government was to be cleared of 15 million Polish nationals, and resettled by 4–5 million ethnic Germans. The operation was the culmination of the expulsion of Poles by Germany carried out since the 19th century, when Poland was Parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
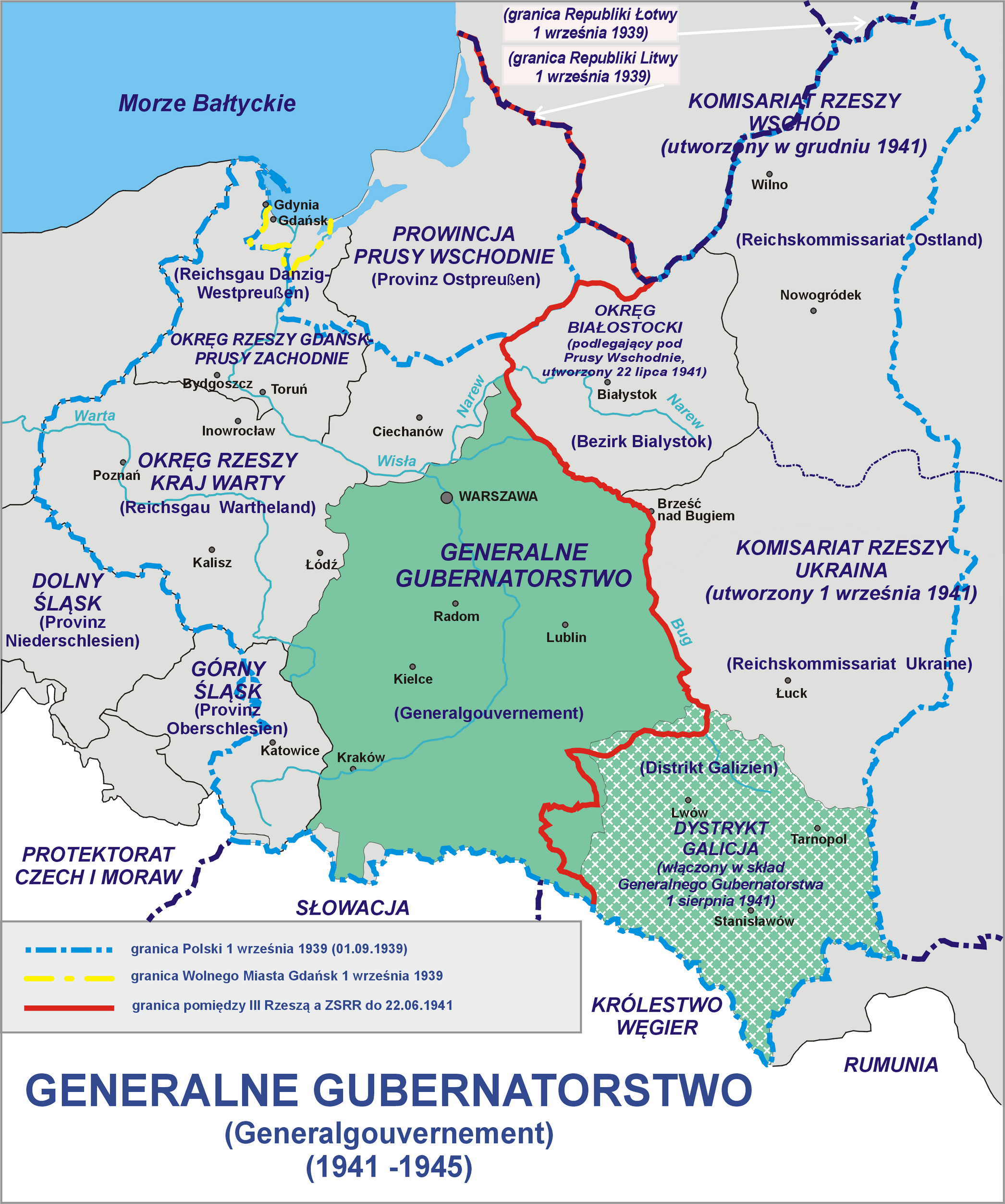
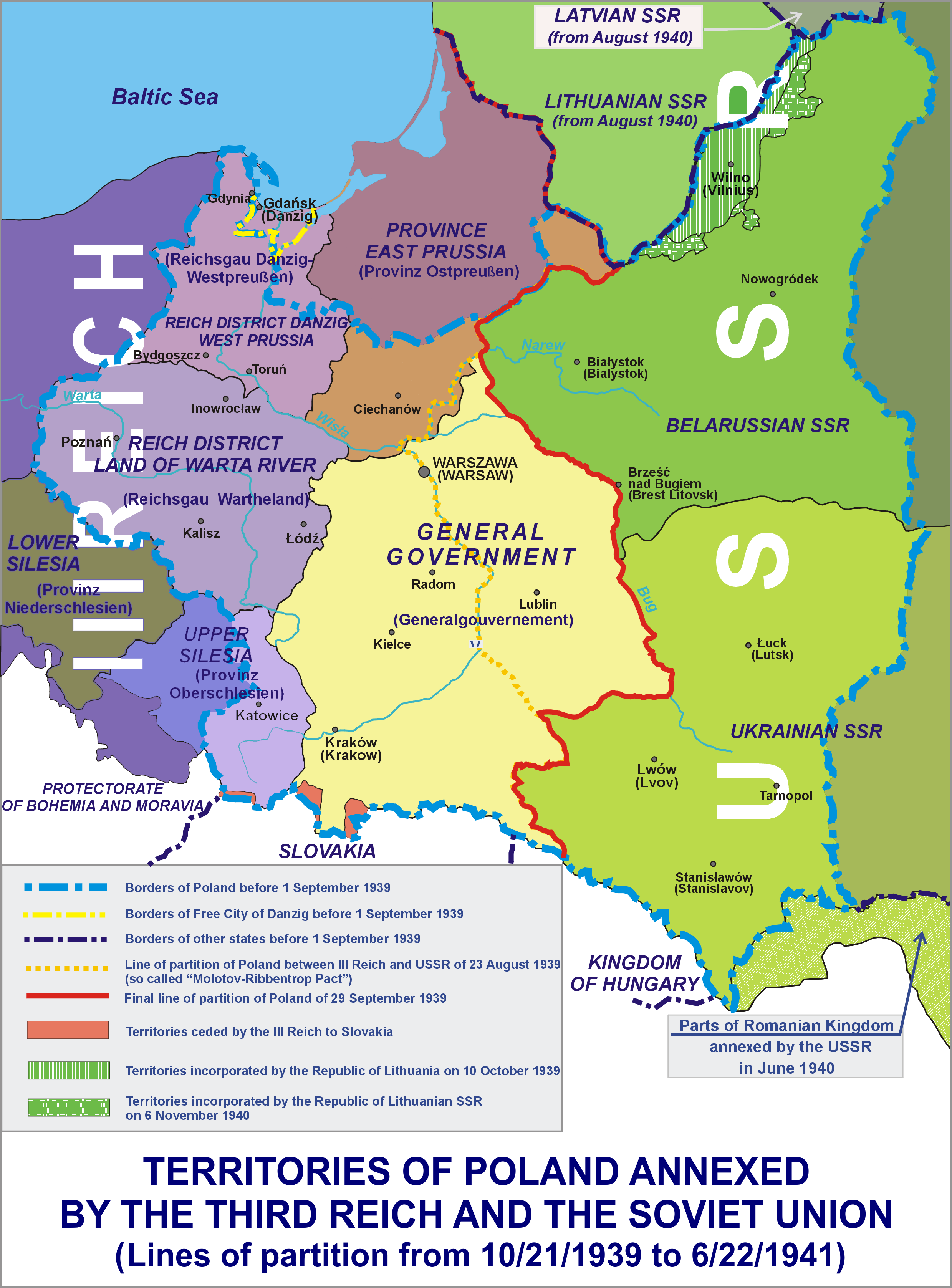
Occupation Of Poland (1939–1945)
During World War II, Poland was occupied by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union following the invasion in September 1939, and it was formally concluded with the defeat of Germany by the Allies in May 1945. Throughout the entire course of the occupation, the territory of Poland was divided between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union (USSR), both of which intended to eradicate Poland's culture and subjugate its people. In the summer-autumn of 1941, the lands which were annexed by the Soviets were overrun by Germany in the course of the initially successful German attack on the USSR. After a few years of fighting, the Red Army drove the German forces out of the USSR and crossed into Poland from the rest of Central and Eastern Europe. Sociologist Tadeusz Piotrowski argues that both occupying powers were hostile to the existence of Poland's sovereignty, people, and the culture and aimed to destroy them. Before Operation Barbarossa, Germany and the Soviet Union coordinated th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |