|
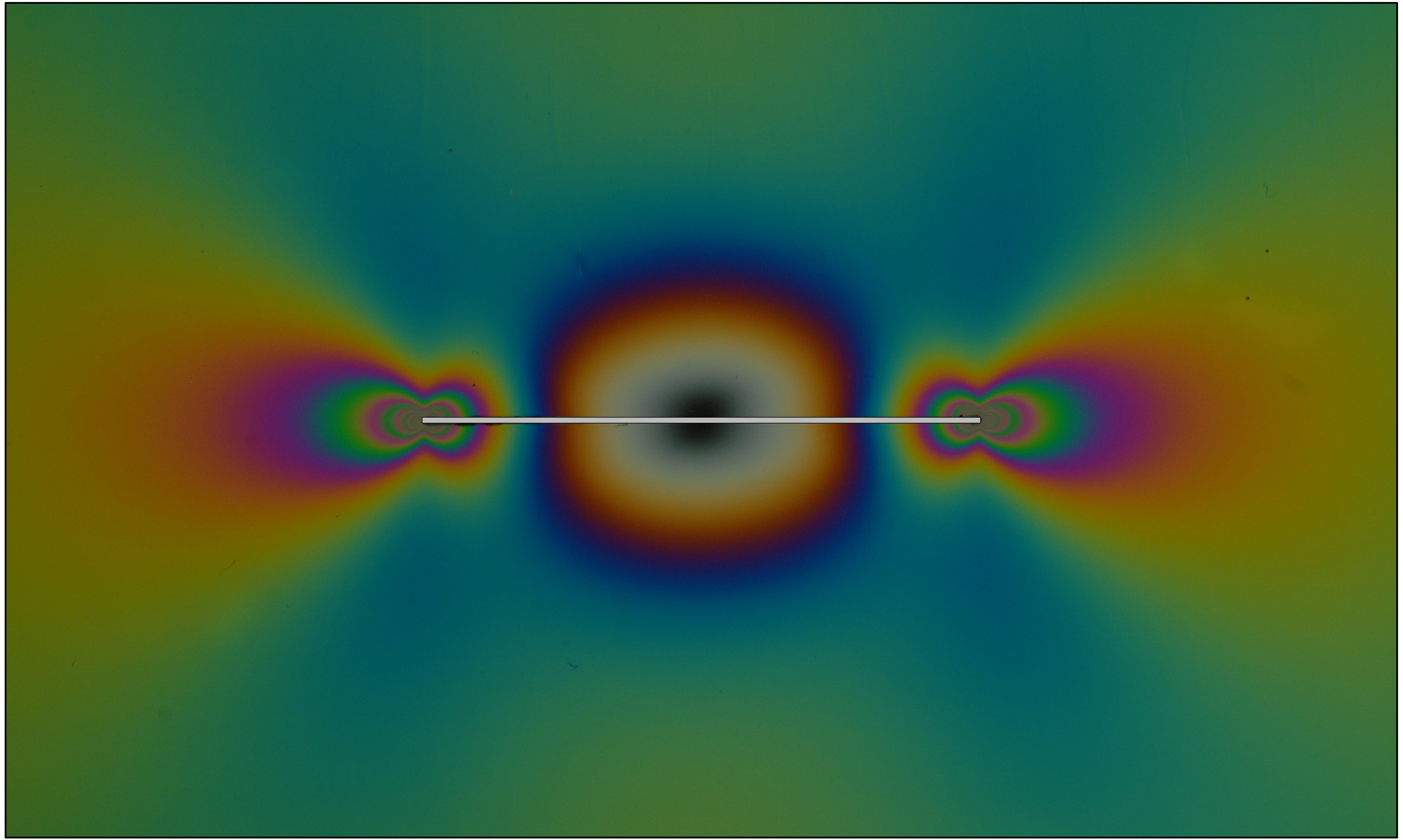
Photoelasticity
In materials science, photoelasticity describes changes in the optical properties of a material under mechanical deformation. It is a property of all dielectric media and is often used to experimentally determine the stress distribution in a material. History The photoelastic phenomenon was first discovered by the Scottish physicist David Brewster, who immediately recognized it as stress-induced birefringence. That diagnosis was confirmed in a direct refraction experiment by Augustin-Jean Fresnel. * Reprinted in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), ''Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel'', vol. 1 (1866)pp. 713–18* Translated as Experimental frameworks were developed at the beginning of the twentieth century with the works of E.G. Coker and L.N.G. Filon of University of London. Their book ''Treatise on Photoelasticity'', published in 1930 by Cambridge Press, became a standard text on the subject. Between 1930 and 1940, many othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelasticity Stiffener
In materials science, photoelasticity describes changes in the optical properties of a material under mechanical Deformation (engineering), deformation. It is a property of all dielectric, dielectric media and is often used to experimentally determine the Stress (mechanics), stress distribution in a material. History The photoelastic phenomenon was first discovered by the Scottish physicist David Brewster, who immediately recognized it as stress-induced birefringence. That diagnosis was confirmed in a direct refraction experiment by Augustin-Jean Fresnel. * Reprinted in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), ''Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel'', vol. 1 (1866)pp. 713–18* Translated as Experimental frameworks were developed at the beginning of the twentieth century with the works of Ernest George Coker, E.G. Coker and Louis Napoleon George Filon, L.N.G. Filon of University of London. Their book ''Treatise on Photoelasticity'', publish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refraction, refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where and are the angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices and . The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflectivity, reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index, n, can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigid Line Inclusion (stiffener, Anticrack)
A rigid line inclusion, also called stiffener, is a mathematical model used in solid mechanics to describe a narrow hard phase, dispersed within a matrix material. This inclusion is idealised as an infinitely rigid and thin reinforcement, so that it represents a sort of ‘inverse’ crack, from which the nomenclature ‘anticrack’ derives. From the mechanical point of view, a stiffener introduces a kinematical constraint, imposing that it may only suffer a rigid body motion along its line. Theoretical model The stiffener model has been used to investigate different mechanical problems in classical elasticity (load diffusion, inclusion at bi material interface ). The main characteristics of the theoretical solutions are basically the following. # Similarly to a fracture, a square-root singularity in the stress/strain fields is present at the tip of the inclusion. # In a homogeneous matrix subject to uniform stress at infinity, such singularity only arises when a normal stres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birefringence
Birefringence, also called double refraction, is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are described as birefringent or birefractive. The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress. Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in Iceland spar (calcite) crystals which have one of the strongest birefringences. In the 19th century Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and " rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress (mechanics)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that describes forces present during deformation. For example, an object being pulled apart, such as a stretched elastic band, is subject to ''tensile'' stress and may undergo elongation. An object being pushed together, such as a crumpled sponge, is subject to ''compressive'' stress and may undergo shortening. The greater the force and the smaller the cross-sectional area of the body on which it acts, the greater the stress. Stress has dimension of force per area, with SI units of newtons per square meter (N/m2) or pascal (Pa). Stress expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while ''strain'' is the measure of the relative deformation of the material. For example, when a solid vertical bar is supporting an overhead weight, each particle in the bar pushes on the particles immediately below it. When a liquid is in a closed container under pressure, each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Brewster
Sir David Brewster Knight of the Royal Guelphic Order, KH President of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, PRSE Fellow of the Royal Society of London, FRS Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland, FSA Scot Fellow of the Scottish Society of Arts, FSSA Member of the Institution of Civil Engineers, MICE (11 December 178110 February 1868) was a British scientist, inventor, author, and academic administrator. In science he is principally remembered for his experimental work in physical optics, mostly concerned with the study of the Polarization (waves), polarization of light and including the discovery of Brewster's angle. He studied the birefringence of crystals under compression and discovered photoelasticity, thereby creating the field of optical mineralogy.A. D. Morrison-Low (2004) "Brewster, Sir David (1781–1868)" in ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' For this work, William Whewell dubbed him the "father of modern experimental optics" and "the Johannes Kepler of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
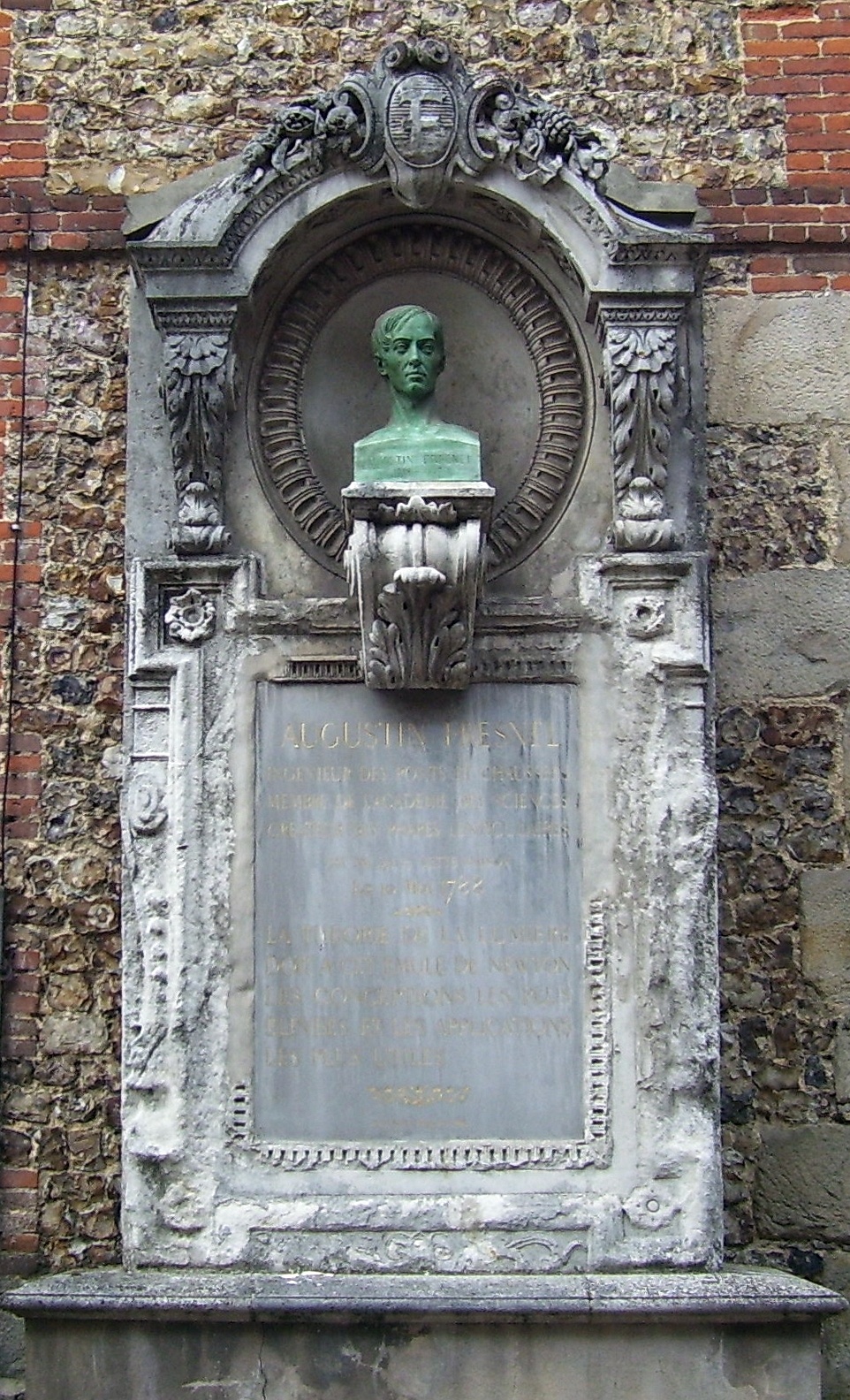
Augustin-Jean Fresnel
Augustin-Jean Fresnel (10 May 1788 – 14 July 1827) was a French civil engineer and physicist whose research in optics led to the almost unanimous acceptance of the wave theory of light, excluding any remnant of Isaac Newton, Newton's corpuscular theory of light, corpuscular theory, from the late 1830s until the end of the 19th century. He is perhaps better known for inventing the Catadioptric system, catadioptric (reflective/refractive) Fresnel lens and for pioneering the use of "stepped" lenses to extend the visibility of lighthouses, saving countless lives at sea. The simpler Dioptrics, dioptric (purely refractive) stepped lens, first proposed by Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon, Count Buffon and independently reinvented by Fresnel, is used in screen magnifying glass, magnifiers and in condenser lenses for overhead projectors. By expressing Christiaan Huygens, Huygens's principle of secondary waves and Thomas Young (scientist), Young's principle of interference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'', locally known as ''The'' ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'' or ''WP'', is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C., the national capital. It is the most widely circulated newspaper in the Washington metropolitan area and has a national audience. As of 2023, the ''Post'' had 130,000 print subscribers and 2.5 million digital subscribers, both of which were the List of newspapers in the United States, third-largest among U.S. newspapers after ''The New York Times'' and ''The Wall Street Journal''. The ''Post'' was founded in 1877. In its early years, it went through several owners and struggled both financially and editorially. In 1933, financier Eugene Meyer (financier), Eugene Meyer purchased it out of bankruptcy and revived its health and reputation; this work was continued by his successors Katharine Graham, Katharine and Phil Graham, Meyer's daughter and son-in-law, respectively, who bought out several rival publications. The ''Post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary Element Method
The boundary element method (BEM) is a numerical computational method of solving linear partial differential equations which have been formulated as integral equations (i.e. in ''boundary integral'' form), including fluid mechanics, acoustics, electromagnetics (where the technique is known as method of moments or abbreviated as MoM), fracture mechanics, and contact mechanics. Mathematical basis The integral equation may be regarded as an exact solution of the governing partial differential equation. The boundary element method attempts to use the given boundary conditions to fit boundary values into the integral equation, rather than values throughout the space defined by a partial differential equation. Once this is done, in the post-processing stage, the integral equation can then be used again to calculate numerically the solution directly at any desired point in the interior of the solution domain. BEM is applicable to problems for which Green's functions can be calculated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentistry
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the Human tooth, teeth, gums, and Human mouth, mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions of the mouth, most commonly focused on dentition (the development and arrangement of teeth) as well as the oral mucosa. Dentistry may also encompass other aspects of the craniofacial complex including the temporomandibular joint. The practitioner is called a dentist. The history of dentistry is almost as ancient as the history of humanity and civilization, with the earliest evidence dating from 7000 BC to 5500 BC. Dentistry is thought to have been the first specialization in medicine which has gone on to develop its own accredited degree with its own specializations. Dentistry is often also understood to subsume the now largely defunct medical specialty of stomatology (the study of the mouth and its disorders and dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |