|
Phosphonium Compounds
In chemistry, the term phosphonium (more obscurely: phosphinium) describes polyatomic ion, polyatomic cations with the chemical formula (where R is a hydrogen or an alkyl, aryl, organyl or halogen group). These cations have Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedral structures. The Salt (chemistry), salts are generally colorless or take the color of the anions. Types of phosphonium cations Protonated phosphines The parent phosphonium is as found in the iodide salt, phosphonium iodide. Salts of the parent are rarely encountered, but this ion is an intermediate in the preparation of the industrially useful tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride: :PH3 + HCl + 4 CH2O → Many organophosphonium salts are produced by protonation of phosphine#Phosphines, primary, secondary, and tertiary phosphines: :PR3 + H+ → The basicity of phosphines follows the usual trends, with R = alkyl being more basic than R = aryl. Tetraorganophosphonium cations The most common phosphonium co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetraphenylphosphonium Chloride
Tetraphenylphosphonium chloride is the chemical compound with the formula , abbreviated or or , where Ph stands for phenyl. Tetraphenylphosphonium and especially tetraphenylarsonium salts were formerly of interest in gravimetric analysis of perchlorate and related oxyanions. This colourless salt is used to generate lipophilic salts from inorganic and organometallic anions. Thus, is useful as a phase-transfer catalyst, again because it allows inorganic anions to dissolve in organic solvents. Structure and basic properties The structure of this salt is . It consists of tetraphenylphosphonium cations and chloride anions . The cation is tetrahedral around the phosphorus atom. PPh4Cl crystallises as the anhydrous salt, which is the normal item of commerce, as well as a monohydrate and a dihydrate. In X-ray crystallography, salts are of interest as they often crystallise easily. The rigidity of the phenyl groups facilitates packing and elevates the melting point relative to alkyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
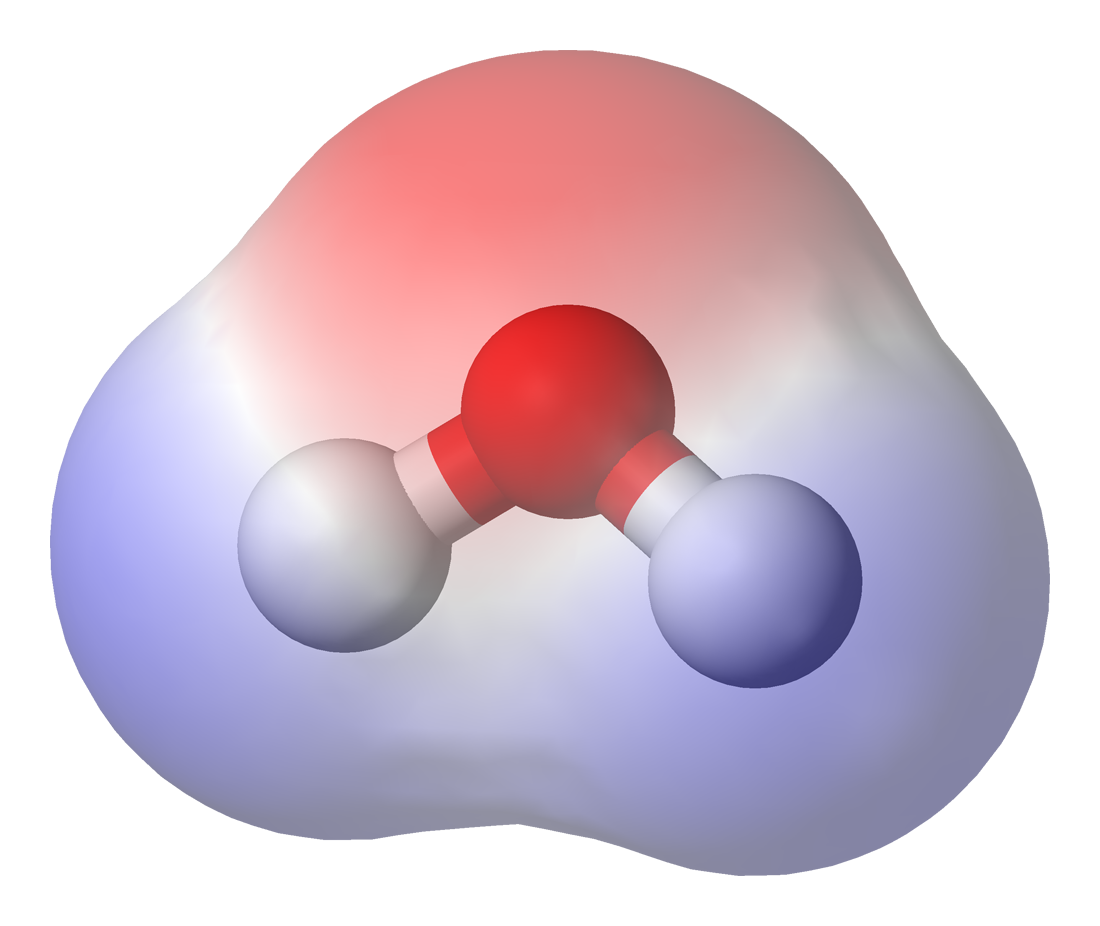
Polar Solution
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole-dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Communications
''ChemComm'' (or ''Chemical Communications''), formerly known as ''Journal of the Chemical Society D: Chemical Communications'' (1969–1971), ''Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications'' (1972–1995), is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Royal Society of Chemistry. It covers all aspects of chemistry. In January 2012, the journal moved to publishing 100 issues per year. The current chair of the editorial board is Douglas Stephan (University of Toronto, Canada), while the executive editor is Richard Kelly. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: * Chemical Abstracts * Science Citation Index * Current Contents/Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences * Scopus * Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor of 4.3. See also * '' New Journal of Chemistry'' * ''Chemical Society Reviews ''Chemical Society Reviews'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
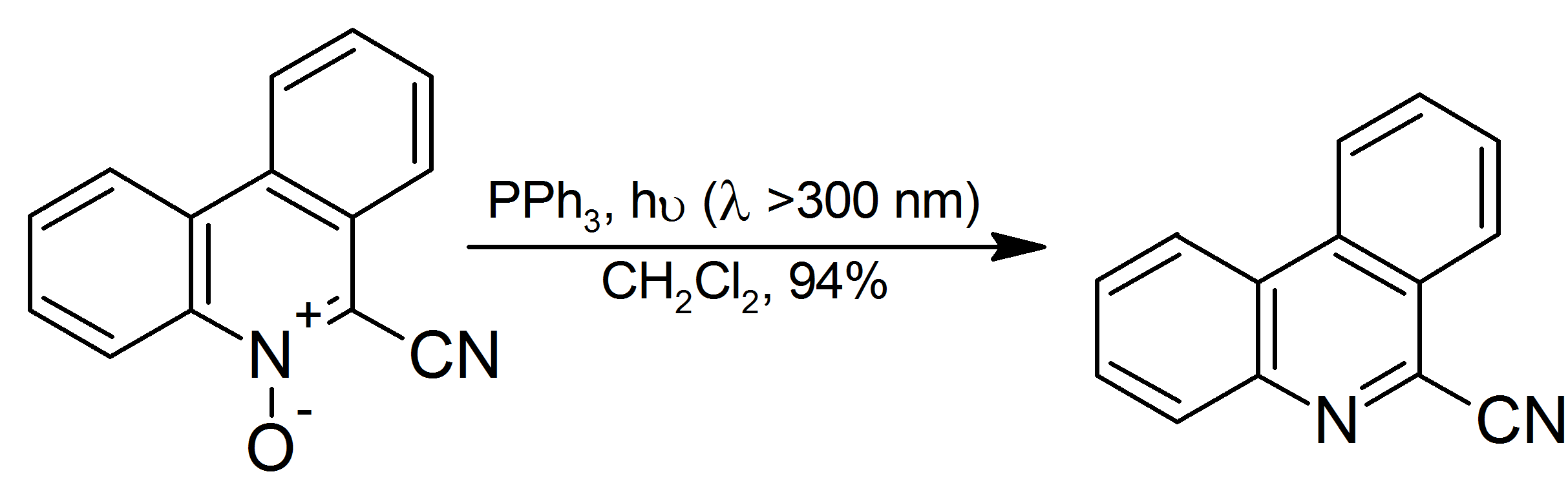
Triphenylphosphine Dichloride
Triphenylphosphine dichloride is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula , often abbreviated as , where Ph is phenyl. It is a chlorinating agent widely used in organic chemistry. Applications include the conversion of alcohols and ethers to alkyl chlorides, the cleavage of epoxides to vicinal dichlorides and the chlorination of carboxylic acids to acyl chlorides. Structure In polar solvents such as acetonitrile, adopts an ionic phosphonium salt structure, (chlorotriphenylphosphonium chloride), whereas in non-polar solvents like diethyl ether it exists as a non-solvated trigonal bipyramidal molecule. Two species can also adopt an unusual dinuclear ionic structure—both interacting with a via long Cl–Cl contacts. File:Chlorotriphenylphosphonium-chloride-2D.png File:Chlorotriphenylphosphonium-chloride-DCM-solvate-from-xtal-3D-balls.png File:Chlorotriphenylphosphonium-chloride-DCM-solvate-from-xtal-3D-vdW.png Synthesis Triphenylphosphine dichloride ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The American Chemical Society
The ''Journal of the American Chemical Society'' (also known as JACS) is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1879 by the American Chemical Society. The journal has absorbed two other publications in its history, the ''Journal of Analytical and Applied Chemistry'' (July 1893) and the ''American Chemical Journal'' (January 1914). It covers all fields of chemistry. Since 2021, the editor-in-chief is Erick M. Carreira (ETH Zurich). In 2014, the journal moved to a hybrid open access publishing model. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 14.4. Editors-in-chief The following people are or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Compound
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions (Cation, cations) and negatively charged ions (Anion, anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrically neutral). The constituent ions are held together by Coulomb's law, electrostatic forces termed ionic bonding, ionic bonds. The component ions in a salt can be either inorganic compound, inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic chemistry, organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic ion, monatomic, such as sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) in sodium chloride, or polyatomic ion, polyatomic, such as ammonium () and carbonate () ions in ammonium carbonate. Salts containing basic ions hydroxide (OH−) or oxide (O2−) are classified as Base (chemistry), bases, such as sodium hydroxide and potassium oxide. Individual ions within a salt usually have multiple near neighbours, so they are not considered to be part of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus Pentachloride
Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula . It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides/oxychlorides, others being and . finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive solid, although commercial samples can be yellowish and contaminated with hydrogen chloride. Structure The structures for the phosphorus chlorides are invariably consistent with VSEPR theory. The structure of depends on its environment. Gaseous and molten is a neutral molecule with trigonal bipyramidal geometry and (''D''3h) symmetry. The hypervalent nature of this species (as well as of , see below) can be explained with the inclusion of non-bonding molecular orbitals (molecular orbital theory) or resonance (valence bond theory). This trigonal bipyramidal structure persists in nonpolar solvents, such as and . In the solid state is an ionic compound called tetrachlorophosphonium hexachlorophosphate formulated . In solutions of polar solvents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wittig Reagents
In organic chemistry, Wittig reagents are organophosphorus compounds of the formula R3P=CHR', where R is usually phenyl. They are used to convert ketones and aldehydes to alkenes: : Preparation Because they typically hydrolyze and oxidize readily, Wittig reagents are prepared using air-free techniques. They are typically generated and used in situ. THF is a typical solvent. Some are sufficiently stable to be sold commercially. Formation of phosphonium salt Wittig reagents are usually prepared from a phosphonium salt, which is in turn prepared by the quaternization of triphenylphosphine with an alkyl halide. Wittig reagents are usually derived from a primary alkyl halide. Quaternization of triphenylphosphine with secondary halides is typically inefficient. For this reason, Wittig reagents are rarely used to prepare tetrasubstituted alkenes. Bases for deprotonation of phosphonium salts The alkylphosphonium salt is deprotonated with a strong base such as ''n''-butyllithium: : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyltriphenylphosphonium Bromide
Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide is the organophosphorus compound with the formula C6H5)3PCH3r. It is the bromide salt of a phosphonium cation. It is a white salt that is soluble in polar organic solvents. Synthesis and reactions Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide is produced by treating triphenylphosphine with methyl bromide: :Ph3P + CH3Br → Ph3PCH3Br Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide is the principal precursor to methylenetriphenylphosphorane Methylenetriphenylphosphorane is an organophosphorus compound with the formula Ph3PCH2. It is the parent member of the phosphorus ylides, popularly known as Wittig reagents. It is a highly polar, highly basic species. Preparation and use Methylene ..., a useful methylenating reagent. This conversion is achieved by treating methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide with strong base.{{cite journal, doi = 10.1080/00397918508063883, title = The Wittig Reaction Using Potassium-tert-butoxide High Yield Methylenations of Sterically Hindered K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Bromide
Bromomethane, commonly known as methyl bromide, is an organobromine compound with chemical formula, formula Carbon, CHydrogen, H3Bromine, Br. This colorless, odorless, nonflammable gas is Bromine cycle, produced both industrially and biologically. It is a recognized ozone depletion, ozone-depleting chemical. According to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report, it has a Global warming potential, global warming potential of 2. The compound was used extensively as a pesticide until being phased out by most countries in the early 2000s. From a chemistry perspective, it is one of the halomethanes. Occurrence and manufacture Marine organisms are estimated to produce 56,000 tonnes annually. It is also produced in small quantities by certain terrestrial plants, such as members of the family Brassicaceae. In 2009, an estimated 24,000 tonnes of methyl bromide were produced. Its production was curtailed by the Montreal Protocol, such that in 1983, production was nearly twice that of 2009 level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to P Ph3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether. Preparation and structure Triphenylphosphine can be prepared in the laboratory by treatment of phosphorus trichloride with phenylmagnesium bromide or phenyllithium. The industrial synthesis involves the reaction between phosphorus trichloride, chlorobenzene, and sodium: :PCl3 + 3 PhCl + 6 Na → PPh3 + 6 NaCl Triphenylphosphine crystallizes in triclinic and monoclinic modification. In both cases, the molecule adopts a pyramidal structure with propeller-like arrangement of the thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |