|
Phosphenium
Phosphenium ions, not to be confused with phosphonium or phosphirenium, are divalent cations of phosphorus of the form R2sup>+. Phosphenium ions have long been proposed as reaction intermediates. Synthesis Legacy methods The first cyclic phosphenium compounds were reported in 1972 by Suzanne Fleming and coworkers. Acyclic phosphenium compounds were synthesized by Fleming's thesis advisor Robert Parry in 1976. Methods Several methods exist for the preparation of two-coordinate phosphorus ions. A common method involves halide abstraction from halophosphines: :R2PCl + AlCl3 → 2P+] Protonolysis of tris(dimethylamino)phosphine affords the phosphenium salt: :P(NMe2)3 + 2 HOTf → (NMe2)2Tf + NMe2Tf Weakly coordinating anions are desirable. Triflic acid is often used. N-heterocyclic phosphenium (NHP) have also been reported. Reaction of PI3 with the α-diimine yields the NHP cation by reduction of the diimine and oxidation of iodine. Structure and bond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphirenium Ion
Phosphirenium ions () are a series of organophosphorus compounds containing unsaturated three-membered ring phosphorus (V) Heterocyclic compound, heterocycles and σ*-aromaticity is believed to be present in such molecules. Many of the salts containing phosphirenium ions have been isolated and characterized by Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography. Synthesis The first series of phosphirenium ions were synthesized by reacting alkynes with methyl- or phenylphosphonous dichloride and aluminum trichloride. These reactions may be regarded as formal addition of "RClP+" to alkynes. [2+1]-cycloaddition reactions between phosphaalkynes and chlorocarbene give phosphirenes, which serve as starting materials for the generation of phosphirenium species. Treatment of diphenylphosphine oxide with diphenylacetylene affords phosphirenium species. Phosphirenium ions can also be obtained from reaction between phosphiranes and alkynes, where "RClP+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
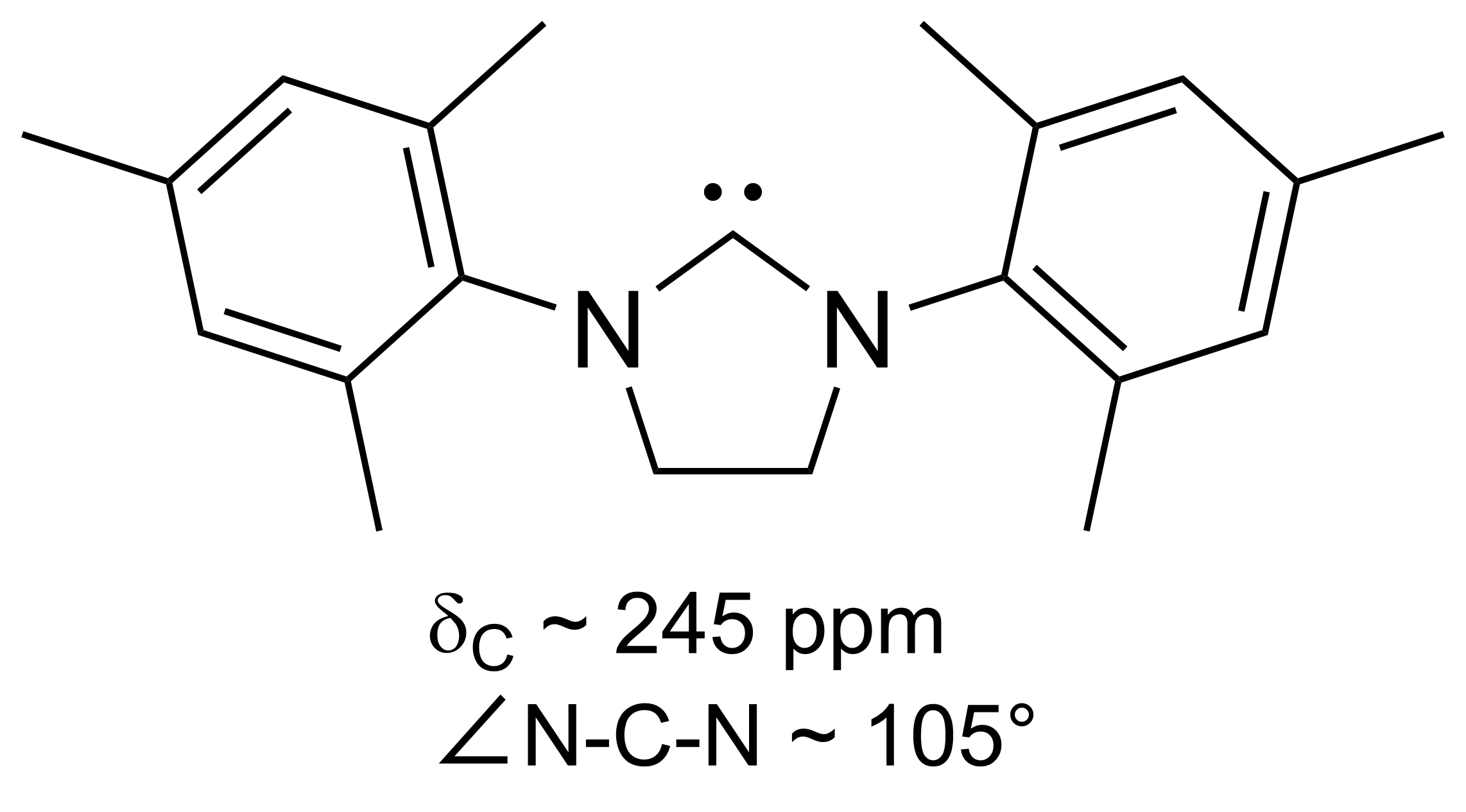
General Phosphenium Line Structure
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry. In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The term ''general'' is used in two ways: as the generic title for all grades of general officer and as a specific rank. It originates in the 16th century, as a shortening of ''captain general'', which rank was taken from Middle French ''capitaine général''. The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. Today, the title of ''general'' is known in some countries as a four-star rank. However, different countries use different systems of stars or other insignia for senior ranks. It has a NATO rank scal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. For example, NH3 is a Lewis base, because it can donate its lone pair of electrons. Trimethylborane (Me3B) is a Lewis acid as it is capable of accepting a lone pair. In a Lewis adduct, the Lewis acid and base share an electron pair furnished by the Lewis base, forming a dative bond. In the context of a specific chemical reaction between NH3 and Me3B, a lone pair from NH3 will form a dative bond with the empty orbital of Me3B to form an adduct NH3•BMe3. The terminology refers to the contributions of Gilbert N. Lewis. From p. 142: "We are inclined to think of substances as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Nitrosyl Complex
Sodium nitroprusside, a medicinally significant metal nitrosyl-pentacyanoferrate (Fe-III) compound, used to treat complexes that contain nitric oxide">hypertension. Metal nitrosyl complexes are complex (chemistry)">complexes that contain nitric oxide, NO, bonded to a transition metal. Many kinds of nitrosyl complexes are known, which vary both in structure and coligand. Bonding and structure Most complexes containing the NO ligand can be viewed as derivatives of the nitrosyl cation, NO+. The nitrosyl cation is isoelectronic with carbon monoxide, thus the bonding between a nitrosyl ligand and a metal follows the same principles as the bonding in carbonyl complexes. The nitrosyl cation serves as a two-electron donor to the metal and accepts electrons from the metal via back-bonding. The compounds Co(NO)(CO)3 and Ni(CO)4 illustrate the analogy between NO+ and CO. In an electron-counting sense, two linear NO ligands are equivalent to three CO groups. This trend is illustrated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-heterocyclic Carbenes
A persistent carbene (also known as stable carbene) is a type of carbene demonstrating particular stability. The best-known examples and by far largest subgroup are the ''N''-heterocyclic carbenes (NHC) (sometimes called Arduengo carbenes), for example diaminocarbenes with the general formula (R2N)2C:, where the four R moieties are typically alkyl and aryl groups. The groups can be linked to give heterocyclic carbenes, such as those derived from imidazole, imidazoline, thiazole or triazole. Traditionally carbenes are viewed as so reactive that were only studied indirectly, such as by trapping reactions. This situation has changed dramatically with the emergence of persistent carbenes. Although they are fairly reactive substances, undergoing dimerization, many can be isolated as pure substances. Persistent carbenes tend to exist in the singlet. Their stability is only partly due to steric hindrance by bulky groups. Some singlet carbenes are thermodynamically stable and can be iso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoelectronicity
Isoelectronicity is a phenomenon observed when two or more molecules have the same structure (positions and connectivities among atoms) and the same electronic configurations, but differ by what specific elements are at certain locations in the structure. For example, , , and are isoelectronic, while and = are not. This definition is sometimes termed ''valence isoelectronicity''. Definitions can sometimes be not as strict, sometimes requiring identity of the ''total'' electron count and with it the entire electronic configuration. More usually, definitions are broader, and may extend to allowing different numbers of atoms in the species being compared.A. A. Aradi & T. P. Fehlner, "Isoelectronic Organometallic Molecules", in F. G. A. Stone & Robert West (eds.) ''Advances in Organometallic Chemistry Vol. 30'' (1990), Chapter 5 (at p. 190google books link/ref> The importance of the concept lies in identifying significantly related species, as pairs or series. Isoelectron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroboration Of Pyridine Catalyzed By NHP
In organic chemistry, hydroboration refers to the addition of a hydrogen- boron bond to certain double and triple bonds involving carbon (, , , and ). This chemical reaction is useful in the organic synthesis of organic compounds. Hydroboration produces organoborane compounds that react with a variety of reagents to produce useful compounds, such as alcohols, amines, or alkyl halides. The most widely known reaction of the organoboranes is oxidation to produce alcohols typically by hydrogen peroxide. This type of reaction has promoted research on hydroboration because of its mild condition and a wide scope of tolerated alkenes. Another research subtheme is metal-catalysed hydroboration. The development of this technology and the underlying concepts were recognized by the Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Herbert C. Brown. He shared the prize with Georg Wittig in 1979 for his pioneering research on organoboranes as important synthetic intermediates. Addition of a H-B bond to C-C double ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen( H−). The term is applied loosely. At one extreme, all compounds containing covalently bound H atoms are called hydrides: water (H2O) is a hydride of oxygen, ammonia is a hydride of nitrogen, etc. For inorganic chemists, hydrides refer to compounds and ions in which hydrogen is covalently attached to a less electronegative element. In such cases, the H centre has nucleophilic character, which contrasts with the protic character of acids. The hydride anion is very rarely observed. Almost all of the elements form binary compounds with hydrogen, the exceptions being He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Pm, Os, Ir, Rn, Fr, and Ra. Exotic molecules such as positronium hydride have also been made. Bonds Bonds between hydrogen and the other elements range from highly to somewhat covalent. Some hydrides, e.g. boron hydrides, do not conform to classical electron-counting rules and the bonding is described in terms of multi-cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |