|
Phlebitis
Phlebitis (or venitis) is inflammation of a vein, usually in the legs. It most commonly occurs in superficial veins. Phlebitis often occurs in conjunction with thrombosis (clotting inside blood vessels) and is then called thrombophlebitis or superficial thrombophlebitis. Unlike deep vein thrombosis, the probability that superficial thrombophlebitis will cause a clot to break up and be transported in pieces to the lung is very low. Signs and symptoms * Localized redness and swelling * Pain or burning along the length of the vein * Vein being hard and cord-like There is usually a slow onset of a tender red area along the superficial veins on the skin. A long, thin red area may be seen as the inflammation follows a superficial vein. This area may feel hard, warm, and tender. The skin around the vein may be itchy and swollen. The area may begin to throb or burn. Symptoms may be worse when the leg is lowered, especially when first getting out of bed in the morning. A low-grade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is a phlebitis (inflammation of a vein) related to a thrombus (blood clot). When it occurs repeatedly in different locations, it is known as thrombophlebitis migrans (migratory thrombophlebitis). Signs and symptoms The following symptoms or signs are often associated with thrombophlebitis, although thrombophlebitis is not restricted to the veins of the lower limbs, legs. * Pain (area affected) * Skin redness/inflammation * Edema * Veins (hard and cord-like) * Tenderness Complications Complications of thrombophlebitis include infection of the vein, concurrent thromboembolism, or recurrent thrombophlebitis. Infection of the vein can include symptoms such as high fever, redness of the site that can spread, and Pus, purulent drainage, making it Septic shock, septic or suppurative thrombophlebitis. Septic thrombophlebitis is not common if there has not been a history of recent disruption of the vein such as catheterization or venipuncture. If left untreated, it can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation, arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, in the deep veins. There are three sizes of veins: large, medium, and small. Smaller veins are called venules, and the smallest the post-capillary venules are microscopic that make up the veins of the microcirculation. Veins are often closer to the skin than arteries. Veins have less smooth muscle and connective tissue and wider internal diameters than arteries. Because of their thinner walls and wider lumens they are able to expand and hold more blood. This greater capacity gives them the term of ''capacitance vessels''. At any time, nearly 70% o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enlarged veins in the affected area, but some DVTs have no symptoms. The most common life-threatening concern with DVT is the potential for a clot to embolize (detach from the veins), travel as an embolus through the right side of the heart, and become lodged in a pulmonary artery that supplies blood to the lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism (PE). DVT and PE comprise the cardiovascular disease of venous thromboembolism (VTE). About two-thirds of VTE manifests as DVT only, with one-third manifesting as PE with or without DVT. The most frequent long-term DVT Complication (medicine), complication is post-thrombotic syndrome, which can cause pain, swelling, a sensation of heaviness, itching, and in severe cases, ulcers. Recurrent VTE o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compression Stockings
Compression stockings (Flight Socks, Support Bandage) are a specialized hosiery designed to help prevent the occurrence of, and guard against further progression of, venous disorders such as edema, phlebitis and thrombosis. Compression stockings are elastic compression garments worn around the leg, compressing the limb. This reduces the diameter of distended veins and increases venous blood flow velocity and valve effectiveness. Compression therapy helps decrease venous pressure, prevents venous stasis and impairments of venous walls, and relieves heavy and aching legs. Knee-high compression stockings are used not only to help increase circulation, but also to help prevent the formation of blood clots in the lower legs. They also aid in the treatment of ulcers of the lower legs. Unlike traditional dress or athletic stockings and socks, compression stockings use stronger elastics to create significant pressure on the legs, ankles and feet. Compression stockings are tightest at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombosis
Thrombosis () is the formation of a Thrombus, blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. Even when a blood vessel is not injured, blood clots may form in the body under certain conditions. A clot, or a piece of the clot, that breaks free and begins to travel around the body is known as an embolus. Thrombosis can cause serious conditions such as stroke and heart attack. Thrombosis may occur in veins (venous thrombosis) or in arteries (arterial thrombosis). Venous thrombosis (sometimes called DVT, deep vein thrombosis) leads to a blood clot in the affected part of the body, while arterial thrombosis (and, rarely, severe venous thrombosis) affects the blood supply and leads to damage of the tissue supplied by that artery (ischemia and necrosis). A piece of either an arterial or a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thromboangiitis Obliterans
Thromboangiitis obliterans, also known as Buerger disease (English ; ) or Winiwarter-Buerger disease, is a recurring progressive inflammation and thrombosis (clotting) of small and medium arteries and veins of the hands and feet. It is strongly associated with use of tobacco products, primarily from smoking, but is also associated with smokeless tobacco. Signs and symptoms There is a recurrent acute and chronic inflammation and thrombosis of arteries and veins of the hands and feet. The main symptom is pain in the affected areas, at rest and while walking (claudication). The impaired circulation increases sensitivity to cold. Peripheral pulses are diminished or absent. There are color changes in the extremities. The colour may range from cyanotic blue to reddish blue. Skin becomes thin and shiny. Hair growth is reduced. Ulcerations and gangrene in the extremities are common complications, often resulting in the need for amputation of the involved extremity. Pathophysiology T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desomorphine
Desomorphine (or in some formulations known as Krokodil) is a semi-synthetic opioid commercialized by Roche, with powerful, fast-acting effects, such as sedation and analgesia. It was first discovered and patented in Germany by a German team working for Knoll in 1920DE Patent 414598C 'Verfahren zur Herstellung von Dihydrodesoxymorphin und Dihydrodesoxycodein' but was not generally recognized. It was later synthesized in 1932 by American chemist Lyndon Frederick Small. Small also successfully patented it in 1934 in the United States. Desomorphine was used in Germany, Austria, and Switzerland under the brand name Permonid and was described as having a fast onset and a short duration of action, with relatively little nausea compared to equivalent doses of morphine. Dose for dose it is roughly ten times more potent than morphine, with 1 mg desomorphine being equivalent 10 mg morphine, via the intravenous (IV) or intramuscular (IM) routes. Desomorphine is a morphine analog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collapsed Vein
Collapsed veins are a common injury that results from repeated use of intravenous injections. They can result from intravenous chemotherapy or when injection conditions are less than ideal, such as in the context of drug abuse. Causes Dehydration can cause temporary vein collapse. Permanent vein collapse occurs as a consequence of: * Repeated injections, especially with blunt needles. * Poor injection technique. * Injection of substances which irritate the veins; in particular, fluids that are hypertonic (high osmolality), vasoactive, irritants, with an extreme pH (very acidic or alkaline), many chemotherapeutic drugs or liquid methadone intended for oral use. Smaller veins may collapse as a consequence of too much suction being used when pulling back against the syringe's plunger to check that the needle is in the vein. This will pull the sides of the vein together and, especially if inflamed, they may stick together causing the vein to block. Removing the needle too quic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
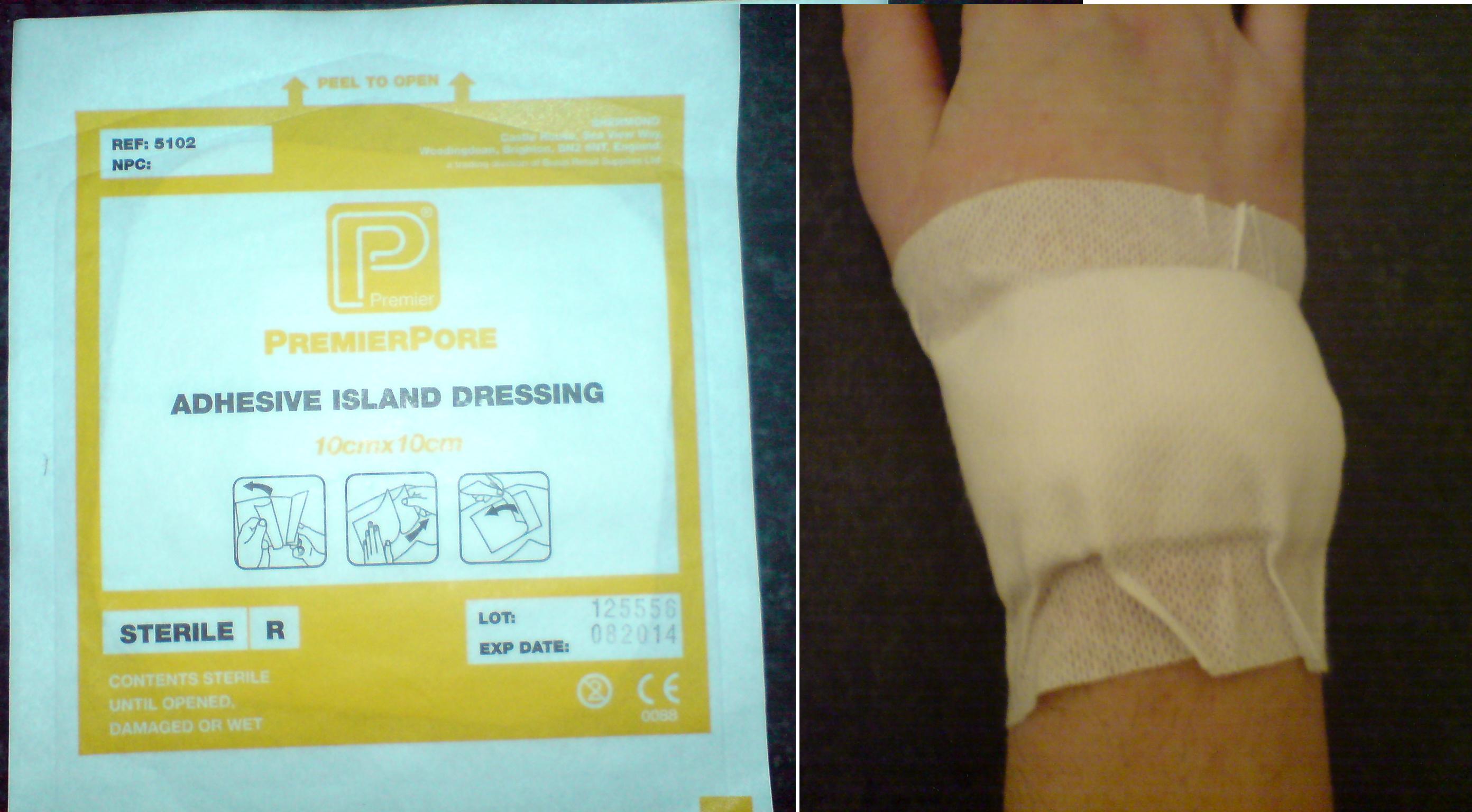
Dressing (medical)
A dressing or compress is a piece of material such as a pad applied to a wound to promote healing and protect the wound from further harm. A dressing is designed to be in direct contact with the wound, as distinguished from a bandage, which is most often used to hold a dressing in place. Modern dressings are sterile. Medical uses A dressing can have a number of purposes, depending on the type, severity and position of the wound, although all purposes are focused on promoting recovery and protecting from further harm. Key purposes of a dressing are: * Stop bleeding – to help to seal the wound to expedite the clotting process; * Protection from infection – to defend the wound against germs and mechanical damage; * Absorb exudate – to soak up blood, plasma, and other fluids exuded from the wound, containing it/them in one place and preventing maceration; * Ease pain – either by a medicated analgesic effect, compression or simply preventing pain from further trauma; * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |