|
Phenom II
Phenom II is a family of AMD's multi-core 45 nm central processing unit, processors using the AMD K10 microarchitecture, succeeding the original AMD Phenom, Phenom. Advanced Micro Devices released the Socket AM2+ version of Phenom II in December 2008, while Socket AM3 versions with DDR3 support, along with an initial batch of triple- and quad-core processors were released on February 9, 2009. Dual-processor systems require Socket F+ for the AMD Quad FX platform, Quad FX platform. The next-generation Phenom II X6 was released on April 27, 2010. The Phenom II X4 operates as the processor component of AMD's AMD Dragon, Dragon Platform, which also includes the AMD 700 chipset series, 790 series chipset and Radeon hd 4870, Radeon HD 4800 series graphics. The Thuban Phenom II X6 is the CPU in the Leo Platform which also includes the AMD 800 chipset series, AMD 890 chipset and the Evergreen (GPU family), Radeon HD 5800 series graphics. Features The Phenom II triples the shared L3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of AMD Phenom Processors
The AMD Phenom family is a 64-bit microprocessor family from Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), based on the AMD 10h, K10 microarchitecture. It includes the AMD Phenom II X6 hex-core series, Phenom X4 and Phenom II X4 quad-core series, Phenom X3 and Phenom II X3 tri-core series, and Phenom II X2 dual-core series. Other related processors based on the K10 microarchitecture include the Athlon X2 ''Kuma'' processors, Athlon II processors, and various Opteron, Sempron, and Turion series. The first Phenoms were released in November 2007. An improved second generation was released in December 2008, named Phenom II. Processors with an ''e'' following the model number (e.g., 910e) are low-power models, usually 45 W for Athlons, 65 W for Phenoms. Processors with a "u" following the model number (e.g., 270u) are ultra-low-power models, usually 20 W for single core chips or 25 W for dual core chips. Features overview Desktop processors Phenom series "''Agena''" (B2/B3, 65 nm, Quad-core) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMD Quad FX Platform
The AMD Quad FX platform is an AMD platform targeted at enthusiasts which allows users to plug two Socket F Athlon 64 FX or 2-way Opteron processors (CPUs) into a single motherboard for a total of four physical cores. This is a type of dual processor setup, where two CPUs are installed on a motherboard to increase computing power. The major difference between the platform and past dual processor systems like Xeon (pre Intel 5000X/P chipset) is that each processor has its own dedicated memory stores. The Quad FX platform also has HyperTransport capability targeted toward consumer platforms. In May 2007, AMD officially codenamed the eight core setup with two Phenom FX processors to be the ''FASN8'' (pronounced as "fascinate", , in short for ''First AMD Silicon Next-gen 8-core Platform'') from the previous codename "''4x4+''" used in Analyst Day presentations. Configuration In each socket resides an AMD Athlon 64 FX CPU. Each socket is connected using AMD's Direct Chip Module, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Device Fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuits (ICs) such as microprocessors, microcontrollers, and memories (such as Random-access memory, RAM and flash memory). It is a multiple-step Photolithography, photolithographic and physico-chemical process (with steps such as thermal oxidation, thin-film deposition, ion-implantation, etching) during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer (electronics), wafer, typically made of pure single-crystal semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications. This article focuses on the manufacture of integrated circuits, however steps such as etching and photolithography can be used to manufacture other devices such as LCD and OLED displays. The fabrication process is performed in highly specialized semiconductor fabrication plants, also called foundries or "fabs", with the cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desktop Computer
A desktop computer, often abbreviated as desktop, is a personal computer designed for regular use at a stationary location on or near a desk (as opposed to a portable computer) due to its size and power requirements. The most common configuration has a computer case, case that houses the power supply unit (computer), power supply, motherboard (a printed circuit board with a microprocessor as the central processing unit, computer memory, memory, bus (computing), bus, certain peripherals and other electronic components), disk storage (usually one or more hard disk drives, solid-state drives, optical disc drives, and in early models floppy disk drives); a computer keyboard, keyboard and computer mouse, mouse for input (computer science), input; and a computer monitor, monitor, computer speakers, speakers, and, often, a printer (computing), printer for output. The case may be oriented horizontally or vertically and placed either underneath, beside, or on top of a desk. Desktop Comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overclocking
In computing, overclocking is the practice of increasing the clock rate of a computer to exceed that certified by the manufacturer. Commonly, operating voltage is also increased to maintain a component's operational stability at accelerated speeds. Semiconductor devices operated at higher frequencies and voltages increase power consumption and heat. An overclocked device may be unreliable or fail completely if the additional heat load is not removed or power delivery components cannot meet increased power demands. Many device warranties state that overclocking or over-specification voids any warranty, but some manufacturers allow overclocking as long as it is done (relatively) safely. Overview The purpose of overclocking is to increase the operating speed of a given component. Normally, on modern systems, the target of overclocking is increasing the performance of a major chip or subsystem, such as the main processor or graphics controller, but other components, such as sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbo Core
AMD Turbo Core a.k.a. AMD Core Performance Boost (CPB) is a dynamic frequency scaling technology implemented by AMD that allows the processor to dynamically adjust and control the processor operating frequency in certain versions of its processors which allows for increased performance when needed while maintaining lower power and thermal parameters during normal operation. AMD Turbo Core technology has been implemented beginning with the Phenom II X6 microprocessors based on the AMD K10 microarchitecture. AMD Turbo Core is available with some AMD A-Series accelerated processing units. AMD Turbo Core is similar to Intel Turbo Boost, which is another dynamic processor frequency adjustment technology used to increase performance, as well as AMD PowerNow!, which is used to dynamically adjust laptop processor's operating frequencies in order to decrease power consumption (saving battery life), reduce heat, and lower noise. AMD PowerNow! is used to ''decrease'' processor freque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
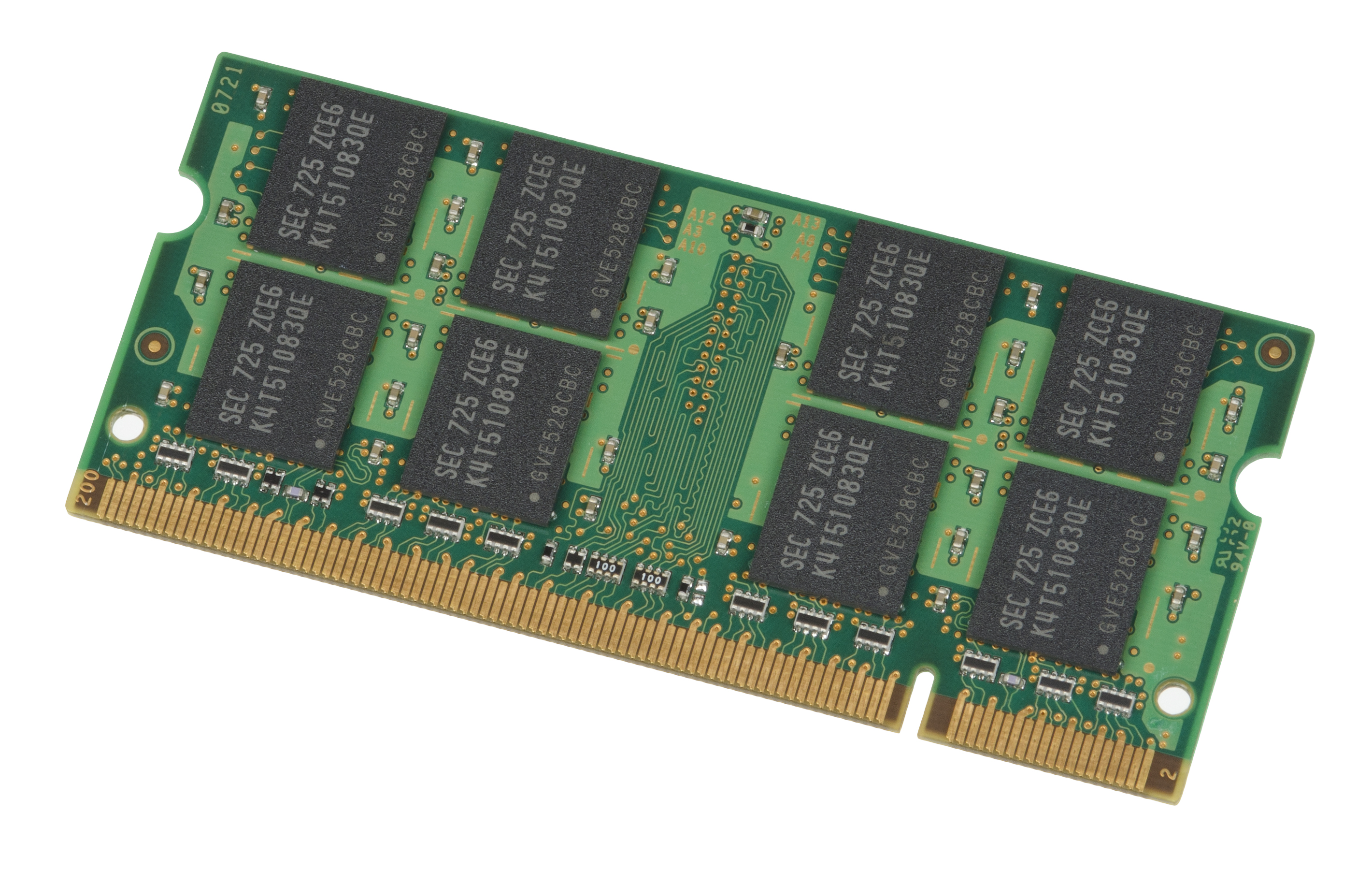
DDR2 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR2 SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It is a JEDEC standard (JESD79-2); first published in September 2003. DDR2 succeeded the original DDR SDRAM specification, and was itself succeeded by DDR3 SDRAM in 2007. DDR2 DIMMs are neither forward compatible with DDR3 nor backward compatible with DDR. In addition to double pumping the data bus as in DDR SDRAM (transferring data on the rising and falling edges of the bus clock signal), DDR2 allows higher bus speed and requires lower power by running the internal clock at half the speed of the data bus. The two factors combine to produce a total of four data transfers per internal clock cycle. Since the DDR2 internal clock runs at half the DDR external clock rate, DDR2 memory operating at the same external data bus clock rate as DDR results in DDR2 being able to provide the same bandwidth but with better la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Controller
A memory controller, also known as memory chip controller (MCC) or a memory controller unit (MCU), is a digital circuit that manages the flow of data going to and from a computer's main memory. When a memory controller is integrated into another chip, such as an integral part of a microprocessor, it is usually called an integrated memory controller (IMC). Memory controllers contain the logic necessary to read and write to dynamic random-access memory (DRAM), and to provide the critical memory refresh and other functions. Reading and writing to DRAM is performed by selecting the row and column data addresses of the DRAM as the inputs to the multiplexer circuit, where the demultiplexer on the DRAM uses the converted inputs to select the correct memory location and return the data, which is then passed back through a multiplexer to consolidate the data in order to reduce the required bus width for the operation. Memory controllers' bus widths range from 8-bit in earlier systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft Windows. It was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on November 8, 2006, and over the following two months, it was released in stages to business customers, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released internationally and was made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; it is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform. Development of Windows Vista began in 2001 under the codename "Longhorn"; originally envisioned as a minor successor to Windows XP, it feature creep, gradually included numerous new features from the then-next major release of Windows codenamed "Blackc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cool'n'Quiet
AMD Cool'n'Quiet is a CPU dynamic frequency scaling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon XP processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat generation, allowing for slower (thus quieter) cooling fan operation. The objectives of cooler and quieter result in the name Cool'n'Quiet. The technology is similar to Intel's SpeedStep and AMD's own PowerNow!, which were developed with the aim of increasing laptop battery life by reducing power consumption. Due to their different usage, ''Cool'n'Quiet'' refers to desktop and server chips, while ''PowerNow!'' is used for mobile chips; the technologies are similar but not identical. This technology was also introduced on "e-stepping" Opterons, however it is called ''Optimized Power Management'', which is essentially a re-tooled Cool'n'Quiet scheme designed to work with reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evergreen (GPU Family)
TeraScale is the codename for a family of graphics processing unit microarchitectures developed by ATI Technologies/AMD and their second microarchitecture implementing the unified shader model following '' Xenos''. TeraScale replaced the old fixed-pipeline microarchitectures and competed directly with Nvidia's first unified shader microarchitecture named Tesla. TeraScale was used in Radeon HD 2000 manufactured in 80 nm and 65 nm, Radeon HD 3000 manufactured in 65 nm and 55 nm, Radeon HD 4000 manufactured in 55 nm and 40 nm, Radeon HD 5000 and Radeon HD 6000 manufactured in 40 nm. TeraScale was also used in the AMD Accelerated Processing Units code-named "Brazos", "Llano", "Trinity" and "Richland". TeraScale is even found in some of the succeeding graphics cards brands. TeraScale is a VLIW SIMD architecture, while Tesla is a RISC SIMD architecture, similar to TeraScale's successor Graphics Core Next. TeraScale implements HyperZ. An LLVM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMD 800 Chipset Series
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California and maintains significant operations in Austin, Texas. AMD is a hardware and fabless company that designs and develops central processing units (CPUs), graphics processing units (GPUs), field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), system-on-chip (SoC), and high-performance computer solutions. AMD serves a wide range of business and consumer markets, including gaming, data centers, artificial intelligence (AI), and embedded systems. AMD's main products include microprocessors, motherboard chipsets, embedded processors, and graphics processors for servers, workstations, personal computers, and embedded system applications. The company has also expanded into new markets, such as the data center, gaming, and high-performance computing markets. AMD's processors are used in a wide range of computing devices, including personal compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |