|
Phandar
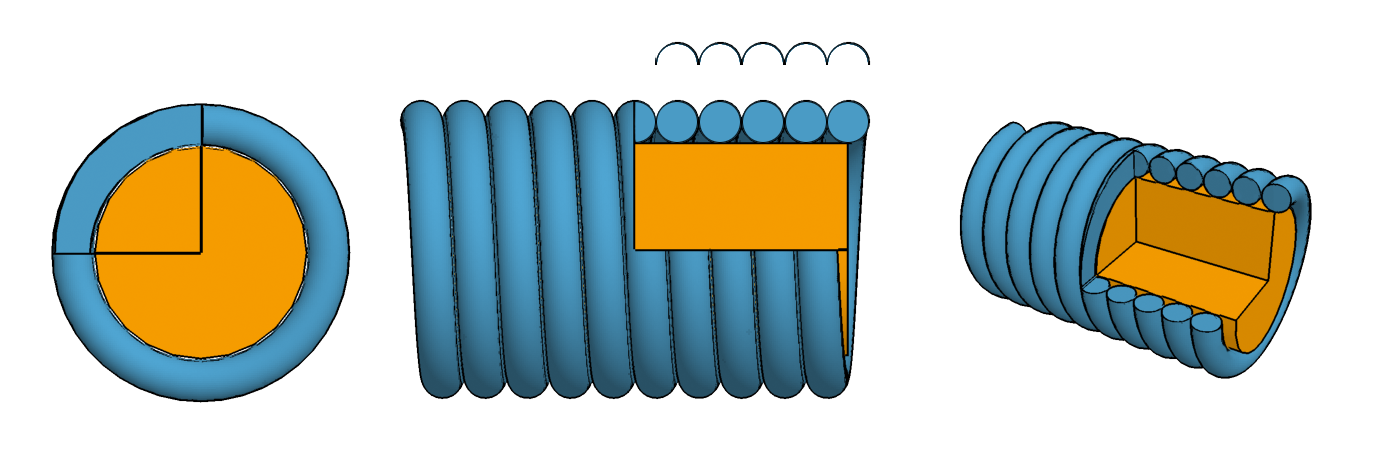
The Phandar (, ; , ) is a traditional Vainakhish three-string plucked instrument from Chechnya and Ingushetia in the Northern Caucasus. The sound produced by the Phandar is similar to the Panduri, but it is easy to hear the difference between these two similar instruments. Vainakhish Phandar Phandar is the most popular and commonly used string folk instrument in Chechnya and Ingushetia. Construction Phandars have a wooden elongated body, carved from one piece of wood, with a flat top and a curved lower deck. They are traditionally made of walnut wood. Traditional phandar's frets were made of cord or gut string, but modern versions can be made using the same plastic or steel frets used for guitars and other modern fretted instruments. Phandar are customarily 750–900 mm long, end-to-end, but can vary in size depending on the maker. Originally phanders had 3 separate strings, but some modern instruments have 6 strings in 3 double- courses. Modern phandar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panduri
The panduri ( ka, ფანდური) is a Music of Georgia (country)#Folk music, traditional Georgian three-string plucked string instrument, plucked instrument common in all regions of Eastern Georgia (country), Eastern Georgia: such as Pshavi, Pshav-Khevsureti, Tusheti, Kakheti and Kartli. The panduri is generally used to accompany solo heroic, comic and love songs, as well as dance. Tuning *Three-stringed panduri: G-A-C# or E-B-A# or A-C#-E *Two-stringed panduri: D-C# Construction The frets on the panduri are traditionally made of wood inlaid in the fingerboard, usually seven frets to an octave, but nowadays chromatic fretting with metal frets can also be found. The body of the panduri is usually made more in the shape of a spade, less often with a parallel sided endblock. It is traditionally carved from a single block of wood, but a staved construction (like a lute) is also common. Image:Panduri_back_dusepo.jpg, Back view of panduri with body made of ribs Image:Pandur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandura
The pandura (, ''pandoura'') or pandore, an ancient Greek string instrument, belonged in the broad class of the lute and guitar instruments. Akkadian Empire, Akkadians played similar instruments from the 3rd millennium BC. Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek artwork depicts such lutes from the 3rd or 4th century BC onward. Ancient Greece The Ancient Greece, ancient Greek ''pandoura'' was a medium or long-necked lute with a small resonating chamber, used by the ancient Greeks. It commonly had three strings: such an instrument was also known as the ''trichordon'' (three-stringed) (τρίχορδον, McKinnon 1984:10). Its descendants still survive as the Kartvelian panduri, the Greek tambouras and bouzouki, the North African Kwitra, kuitra, the Eastern Mediterranean Bağlama, saz and the Balkan tamburica and remained popular also in the near east and eastern Europe, too, usually acquiring a third string in the course of time, since the fourth century BC. Renato Meucci (1996) suggests t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; ; ), officially the Republic of Dagestan, is a republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe, along the Caspian Sea. It is located north of the Greater Caucasus, and is a part of the North Caucasian Federal District. The republic is the southernmost tip of Russia, sharing land borders with the countries of Azerbaijan and Georgia to the south and southwest, the Russian republics of Chechnya and Kalmykia to the west and north, and with Stavropol Krai to the northwest. Makhachkala is the republic's capital and largest city; other major cities are Derbent, Kizlyar, Izberbash, Kaspiysk, and Buynaksk. Dagestan covers an area of , with a population of over 3.1 million, consisting of over 30 ethnic groups and 81 nationalities. With 14 official languages, and 12 ethnic groups each constituting more than 1% of its total population, the republic is one of Russia's most linguistically and ethnically diverse, and one of the most heteroge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
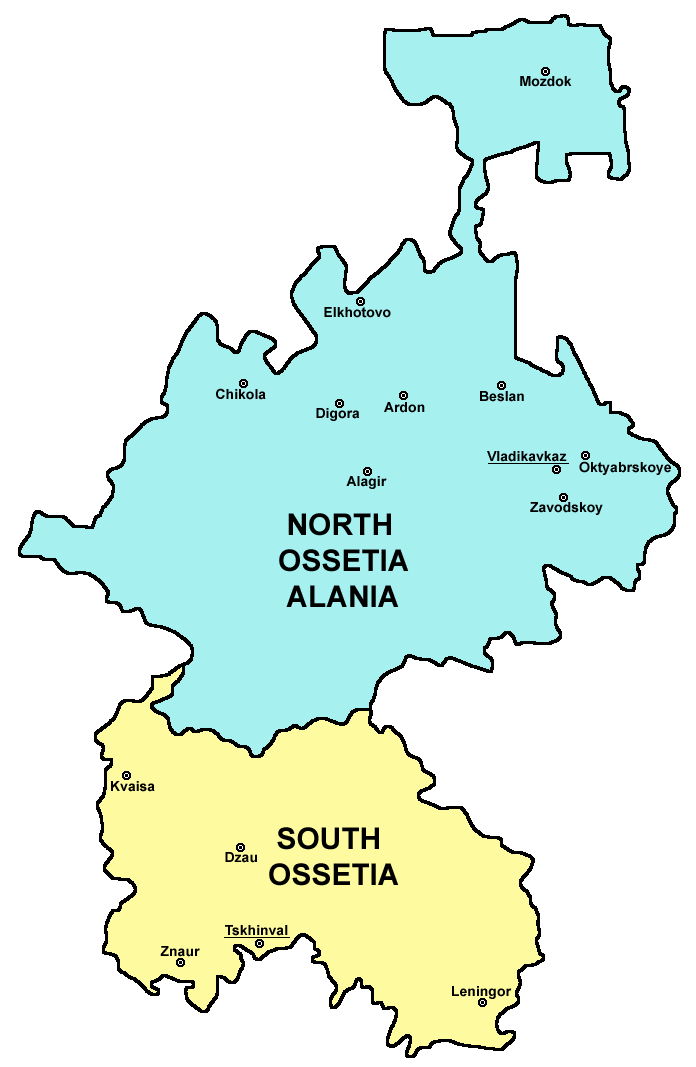
Ossetia
Ossetia ( , ; or , or , ) is an Ethnolinguistics, ethnolinguistic region on both sides of the Greater Caucasus Mountains, largely inhabited by the Ossetians. The Ossetian language is part of the Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian branch of the family of Indo-European languages. Most countries recognize the Ossetian-speaking area south of the main Caucasus ridge as lying within the borders of Georgia (country), Georgia, but it has come under the control of the ''de facto'' government of the Russian-backed South Ossetia, Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania. The northern portion of the region consists of the North Ossetia–Alania, Republic of North Ossetia–Alania within the Russian Federation. Recent history * 1774-1830 – Expansion of the Russian Empire on Ossetian territory. * 1922 – Creation of the South Ossetian Autonomous Oblast, South Ossetian autonomous oblast. North Ossetia remains a part of Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Repub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a country in the Caucasus region on the coast of the Black Sea. It is located at the intersection of Eastern Europe and West Asia, and is today generally regarded as part of Europe. It is bordered to the north and northeast by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. Georgia covers an area of . It has a Demographics of Georgia (country), population of 3.7 million, of which over a third live in the capital and List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), largest city, Tbilisi. Ethnic Georgians, who are native to the region, constitute a majority of the country's population and are its titular nation. Georgia has been inhabited since prehistory, hosting the world's earliest known sites of winemaking, gold mining, and textiles. The Classical antiquity, classical era saw the emergence of several kingdoms, such as Colchis and Kingdom of Iberia, Iberia, that formed the nucleus of the modern Georgian state. In the early fourth centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmholtz Pitch Notation
Helmholtz pitch notation is a system for naming musical notes of the Western chromatic scale. Fully described and normalized by the German scientist Hermann von Helmholtz, it uses a combination of upper and lower case letters (A to G), and the sub- and super- prime symbols ( ͵ or ) to denote each individual note of the scale. It is one of two formal systems for naming notes in a particular octave, the other being scientific pitch notation. History Helmholtz proposed this system in order to accurately define pitches in his classical work on acoustics ''Die Lehre von den Tonempfindungen als physiologische Grundlage für die Theorie der Musik'' (1863) translated into English by A.J. Ellis as '' On the Sensations of Tone'' (1875). Helmholtz based his notation on the practice of German organ builders for labelling their pipes, itself derived from the old German organ tablature in use from late medieval times until the early 18th century. His system is widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gut String
Catgut (also known as gut) is a type of cord that is prepared from the natural fiber found in the walls of animal intestines. Catgut makers usually use sheep or goat intestines, but occasionally use the intestines of cattle, hogs, horses, mules, or donkeys. Despite the name, catgut is not made from cat intestines. Etymology The word ''catgut'' may have been an abbreviation of the word ''cattlegut''. Alternatively, it may derive by folk etymology from ''kitgut'' or ''kitstring'' — the dialectal word ''kit'', meaning fiddle, having at some point been confused with the word ''kit'' for a young cat, the word "kit" being possibly derived from Welsh. In the 16th century a ''kit'' was a "small fiddle used by dancing teachers," a name probably derived from a shortening of Old English ''cythere'', from Latin , from Greek (see guitar). Common uses Musical instruments Historically, catgut was the most common material for the strings of harps, lutes, violins, violas, cellos, dou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String (music)
In music, strings are long flexible structures on string instruments that produce sound through vibration. Strings are held under tension so that they can vibrate freely. The pitch (frequency) at which a string will vibrate is primarily related to its vibrating length (also called speaking length), its tension, and its mass per unit of length. A vibrating string produces very little sound by itself. Therefore, most string instruments have a soundboard to amplify the sound. There are two main kinds of strings; plain and wound. "Plain" strings are simply one piece of long cylindrical material, commonly consisted of nylon or gut. "Wound" strings have a central core, with other material being tightly wound around the string . Prior to World War II, strings of many instruments (including violins and guitars) were composed of a material known as catgut, a type of cord made from refined natural fibers of animal intestines. During the mid-twentieth century however, steel and nylo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Course (music)
In organology, a course is either one string or two or more adjacent strings that are closely spaced relative to the other strings, and typically played as a single string. The strings in each multiple-string course are typically tuned in unison or an octave. Normally, the term ''course'' is used to refer to a single string only on an instrument that also has multi-string courses. For example, a nine-string baroque guitar has five courses: most are two-string courses but sometimes the lowest or the highest consists of a single string. An instrument with at least one multiple-string course is referred to as ''coursed'', while one whose strings are all played individually is ''uncoursed''. Rationale and types Multiple string courses were probably originally employed to increase the volume of instruments, in eras in which electrical amplification did not exist, and stringed instruments might be expected to accompany louder instruments (such as woodwinds or brass). Eventu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guitar
The guitar is a stringed musical instrument that is usually fretted (with Fretless guitar, some exceptions) and typically has six or Twelve-string guitar, twelve strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or Plucked string instrument, plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing selected strings against frets with the fingers of the opposite hand. A guitar pick may also be used to strike the strings. The sound of the guitar is projected either Acoustics, acoustically, by means of a resonant hollow chamber on the guitar, or Amplified music, amplified by an electronic Pickup (music technology), pickup and an guitar amplifier, amplifier. The guitar is classified as a chordophone, meaning the sound is produced by a vibrating string stretched between two fixed points. Historically, a guitar was constructed from wood, with its strings made of catgut. Steel guitar strings were introduced near the end of the nineteen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingushetia
Ingushetia or Ingushetiya, officially the Republic of Ingushetia, is a republic of Russia located in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe. The republic is part of the North Caucasian Federal District, and shares land borders with the country of Georgia to its south; and borders the Russian republics of North Ossetia–Alania to its west and north and Chechnya to its east and northeast. Its capital is the town of Magas, while the largest city is Nazran. At 3,600 square km in terms of area, the republic is the smallest of Russia's non-city federal subjects. It was established on 4 June 1992, after the Checheno-Ingush Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic was split in two.Law of 4 June 1992Official website of the Republic of IngushetiaSocial-Economic Characteristics The republic is home to the indigenous Ingush, a people of Nakh ancestry. As of the 2021 Census, its population was estimated to be 527,220. Largely due to the insurgency in the North Caucasus, I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |