|
Peñasquito Mine
The Peñasquito Polymetallic Mine is the fifth largest silver mine in the world and the second largest in Mexico. It is located in north-eastern corner of the Zacatecas, State of Zacatecas and is wholly owned by Newmont. It is an open pit operation which began commercial operations in March 2010, but still managed to produce 13,952,600 ounces of silver that year. Estimated reserves for the Peñasquito Mine are 17.82 million oz of gold, 1,070.1 million oz of silver, 3,214 tons of lead and 7,098 million tons of zinc. The mine has its own radio station, XHESP-FM (Zacatecas), XHESP-FM 98.9 "Radio Peñasco". Geology The country rock (geology), country rock consists of Mesozoic sediments that were deposited in the Basin of Mexico (Mexico Geosyncline). These sediments were intruded by quartz-feldspar porphyries, quartz monzonite porphyries, and other feldspar-phyric intrusives in the late Eocene to the mid-Oligocene, which form Sill (geology), sills, Dike (geology), dikes, and Stock (geolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial View Of Peñasquito Mine
Aerial may refer to: Music *Aerial (album), ''Aerial'' (album), by Kate Bush, and that album's title track *Aerials (song), "Aerials" (song), from the album ''Toxicity'' by System of a Down Bands *Aerial (Canadian band) *Aerial (Scottish band) *Aerial (Swedish band) Recreation and sport *Aerial (dance move) *Aerial (skateboarding) *Front aerial, gymnastics move performed in acro dance * Aerial cartwheel * Aerial silk, a form of acrobatics * Aerial skiing Technology *Aerial (radio), a radio ''antenna'' or transducer that transmits or receives electromagnetic waves **Aerial (television), an over-the-air television reception antenna *Aerial photography Other uses *Aerial, Georgia, a community in the United States *Aerial (magazine), ''Aerial'' (magazine), a poetry magazine *Aerials (film), ''Aerials'' (film), a 2016 Emirati science-fiction film *''Aerial'', a BBC Two '1991–2001' idents, TV ident for BBC Two from 1997 to 2001 See also * Arial * Ariel (disambiguat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock (geology)
In geology, a stock is an igneous Intrusion (geology), intrusion that has a surface exposure of less than ,Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984, p. 513. . differing from batholiths only in being smaller. A stock has a Intrusive rock#Related terms, discordant relationship with the rocks that it intrudes. Many stocks are cupola (geology), cupolas of hidden batholiths. Some circular or elliptical stocks may be volcanic plugs, which fill the vents of now extinct volcanoes. A boss is a small stock. Examples * the Alta and Clayton Peak stocks (composed of granodiorite), near Park City, Utah * the Hellroaring Creek and Salal Creek Pluton, Salal Creek stocks (of granite-granodiorite and quartz monzonite, respectively) in British Columbia, Canada * the Céret stock (of gabbro and diorite) in Pyrénées-Orientales, France * the Parashi stock (of tonalite) in La Guajira Department, Colombia * stocks of syenite in the Caldera de Tejeda on Gran Canar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrothermal Alteration
Metasomatism (from the Greek μετά ''metá'' "change" and σῶμα ''sôma'' "body") is the chemical alteration of a Rock (geology), rock by hydrothermal and other fluids. It is traditionally defined as metamorphism which involves a change in the chemical composition, excluding volatile components. It is the replacement of one rock by another of different mineralogical and chemical composition. The minerals which compose the rocks are dissolved and new mineral formations are deposited in their place. Dissolution (chemistry), Dissolution and deposition occur simultaneously and the rock remains solid. Synonyms of the word ''metasomatism'' are metasomatosis and metasomatic process. The word ''metasomatose'' can be used as a name for specific varieties of metasomatism (for example ''Magnesium, Mg-metasomatose'' and ''sodium, Na-metasomatose''). Metasomatism can occur via the action of hydrothermal fluids from an igneous or Metamorphism, metamorphic source. In the Igneous rock, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidote
Epidote is a calcium aluminium iron sorosilicate mineral. Description Well developed crystals of epidote, Ca2Al2(Fe3+;Al)(SiO4)(Si2O7)O(OH), crystallizing in the monoclinic system, are of frequent occurrence: they are commonly prismatic in habit, the direction of elongation being perpendicular to the single plane of symmetry. The name Epidote is derived from the Greek word 'epidosis', meaning "increase", in allusion to the crystal characteristic of one longer side at the base of the prism. The faces are often deeply striated and crystals are often twinned. Many of the characters of the mineral vary with the amount of iron present for instance, the color, the optical constants, and the specific gravity. The color is green, grey, brown or nearly black, but usually a characteristic shade of yellowish-green or pistachio-green. It displays strong pleochroism, the pleochroic colors being usually green, yellow and brown. Clinozoisite is green, white or pale rose-red group species c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorite Group
The chlorites are the group of phyllosilicate minerals common in low-grade metamorphic rocks and in Mineral alteration, altered igneous rocks. Greenschist, formed by metamorphism of basalt or other low-silica volcanic rock, typically contains significant amounts of chlorite. Chlorite minerals show a wide variety of compositions, in which magnesium, iron, aluminium, and silicon substitute for each other in the crystal structure. A complete solid solution series exists between the two most common end members, magnesium-rich clinochlore and iron-rich chamosite. In addition, manganese, zinc, lithium, and calcium species are known. The great range in composition results in considerable variation in physical, optical, and X-ray diffraction, X-ray properties. Similarly, the range of chemical composition allows chlorite group minerals to exist over a wide range of temperature and pressure conditions. For this reason chlorite minerals are ubiquitous minerals within low and medium temperat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propylitic Alteration
Propylitic alteration is the chemical alteration of a Rock (geology), rock, caused by iron and magnesium bearing hydrothermal fluids, altering biotite or amphibole within the rock Matrix (geology), groundmass. It typically results in epidote–Chlorite group, chlorite–albite alteration and Vein (geology), veining or Fracture (geology), fracture filling with the mineral assemblage along with pyrite. The alteration occurs due to hot fluids that have a high sodium ion composition. This is typically due to fluids that have lost potassium ions in potassic alteration and gained sodium ions. See also * Metasomatism References * Geological processes {{geological-process-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of Silicon dioxide, SiO2. Quartz is, therefore, classified structurally as a Silicate mineral#Tectosilicates, framework silicate mineral and compositionally as an oxide mineral. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrite
The mineral pyrite ( ), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Fe S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral. Pyrite's metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue give it a superficial resemblance to gold, hence the well-known nickname of ''fool's gold''. The color has also led to the nicknames ''brass'', ''brazzle'', and ''brazil'', primarily used to refer to pyrite found in coal. The name ''pyrite'' is derived from the Greek (), 'stone or mineral which strikes fire', in turn from (), 'fire'. In ancient Roman times, this name was applied to several types of stone that would create sparks when struck against steel; Pliny the Elder described one of them as being brassy, almost certainly a reference to what is now called pyrite. By Georgius Agricola's time, , the term had become a generic term for all of the sulfide minerals. Pyrite is usually found associated with other sulfides or oxides in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sericite
Sericite is the name given to very fine, ragged grains and Aggregate (geology), aggregates of white (colourless) micas, typically made of muscovite, illite, or paragonite. Sericite is produced by the alteration of orthoclase or plagioclase feldspars in areas that have been subjected to hydrothermal alteration (also see Sericitic alteration) typically associated with copper, tin, or other hydrothermal ore deposits. Sericite also occurs as the fine mica that gives the sheen to phyllite and schistose metamorphic rocks. The name comes from Latin ''sericus'', meaning "silken" in reference to the location from which silk was first utilized, which in turn refers to the silky sheen of rocks with abundant sericite. File:Granite pmg ss 2006.jpg, Granite in thin section under cross-polarized light in which feldspar crystals exhibit sericite alteration File:Staurolite garnet schist 3mm xp 2007.jpg, Staurolite-garnet schist in thin section under cross-polarized light with sericite Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllic Alteration
Phyllic alteration is a hydrothermal alteration zone in a permeable rock that has been affected by circulation of hydrothermal fluids. It is commonly seen in copper porphyry ore deposits in calc-alkaline rocks. Phyllic alteration is characterised by the assemblage of quartz + sericite + pyrite, and occurs at high temperatures and moderately acidic (low pH) conditions. Hydrogen-ion metasomatism is the process that causes phyllic alteration. While the mineralogy of the rock is altered throughout, texture is preserved and primary porphyry structure (including position of original veins) may still be visible. If a rock undergoes phyllic alteration, then orthoclase feldspar, biotite and various silicates are altered in addition to plagioclase. Plagioclase will be altered to sericite (a fine-grained white mica) by sericitic alteration, and mafic minerals are replaced by quartz. Tourmaline may appear as radiating aggregate or prismatic crystals between the quartz-sericite assemblage. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfosalt
Sulfosalt minerals are sulfide minerals with the general formula , where *A represents a metal such as copper, lead, silver, iron, and rarely mercury, zinc, vanadium *B usually represents semi-metal such as arsenic, antimony, bismuth, and rarely germanium, or metals like tin and rarely vanadium *X is sulfur or rarely selenium and/or tellurium. The Strunz classification includes the sulfosalts in a ''sulfides and sulfosalts'' superclass. A group which have similar appearing formulas are the sulfarsenides (for example cobaltite (Co,Fe)AsS). In sulfarsenides the arsenic substitutes for sulfide anions whereas in the sulfosalts the arsenic substitutes for a metal cation.Klein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut (1985). ''Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York . About 200 sulfosalt minerals are known. Examples include: File:Proustite (long prismatic crystal) - Chanarcillo, Copiapo Province, Atacama Region, Chile.jpg, As illustrated by this specimen of prousti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
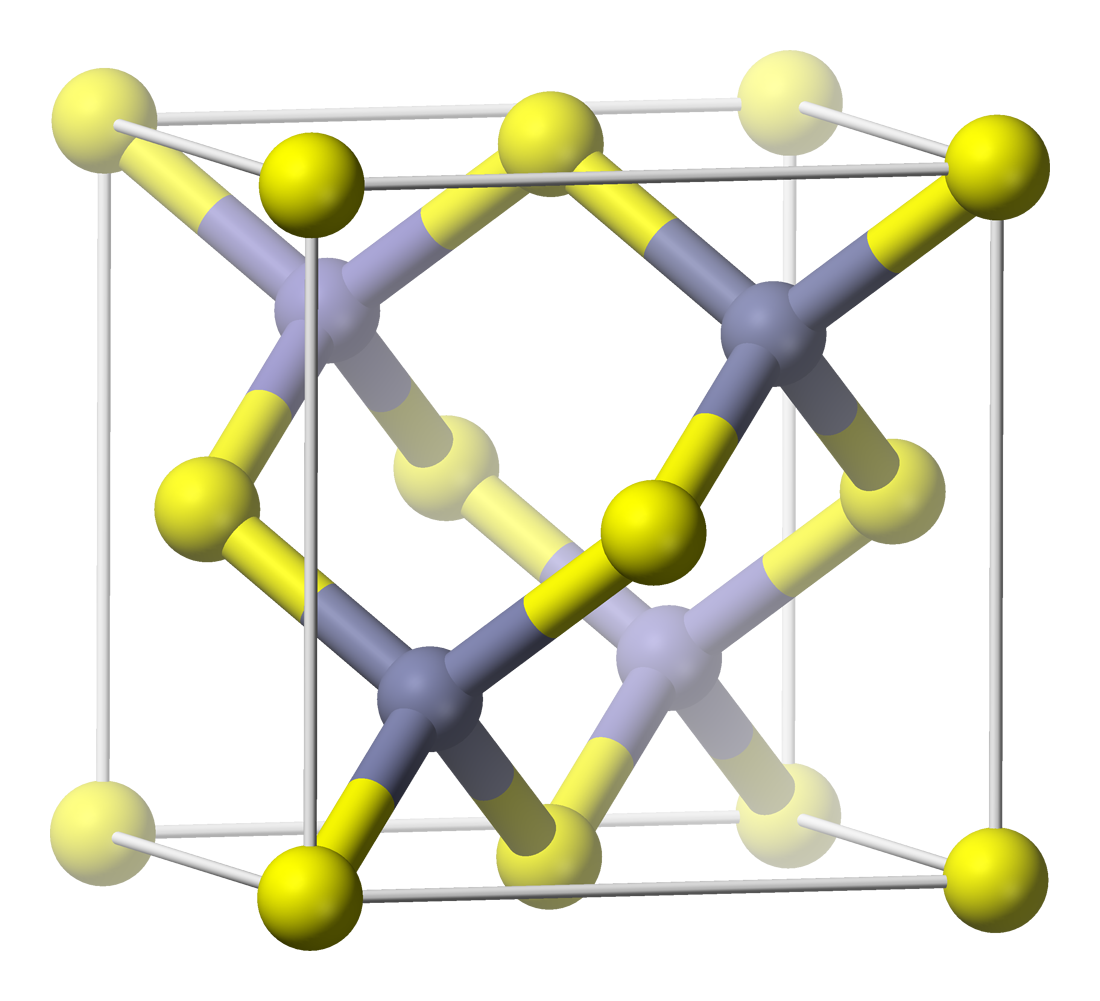
Sphalerite
Sphalerite is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimentary exhalative, Carbonate-hosted lead-zinc ore deposits, Mississippi-Valley type, and Volcanogenic massive sulfide ore deposit, volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. It is found in association with galena, chalcopyrite, pyrite (and other sulfide mineral, sulfides), calcite, dolomite (mineral), dolomite, quartz, rhodochrosite, and fluorite. German geologist Ernst Friedrich Glocker discovered sphalerite in 1847, naming it based on the Greek word ''sphaleros'', meaning "deceiving", due to the difficulty of identifying the mineral. In addition to zinc, sphalerite is an ore of cadmium, gallium, germanium, and indium. Miners have been known to refer to sphalerite as ''zinc blende'', ''black-jack'', and ''ruby blende''. Marmatite is an opaque black variety with a high iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |