|
Perpendicular Axis Theorem
The perpendicular axis theorem (or plane figure theorem) states that for a planar lamina the moment of inertia about an axis perpendicular to the plane of the lamina is equal to the sum of the moments of inertia about two mutually perpendicular axes in the plane of the lamina, which intersect at the point where the perpendicular axis passes through. This theorem applies only to planar bodies and is valid when the body lies entirely in a single plane. Define perpendicular axes x, y, and z (which meet at origin O) so that the body lies in the xy plane, and the z axis is perpendicular to the plane of the body. Let ''I''''x'', ''I''''y'' and ''I''''z'' be moments of inertia about axis ''x'', ''y'', ''z'' respectively. Then the perpendicular axis theorem states that :I_z = I_x + I_y This rule can be applied with the parallel axis theorem and the stretch rule to find polar moments of inertia for a variety of shapes. If a planar objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
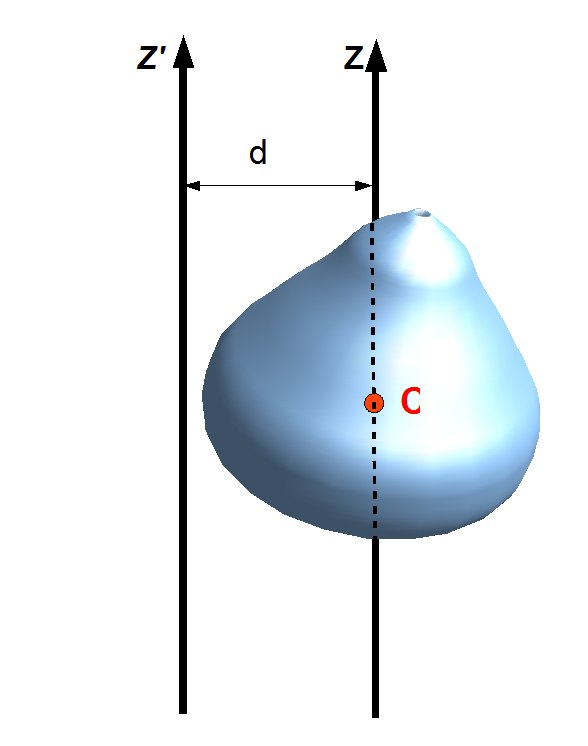
Parallel Axis Theorem
The parallel axis theorem, also known as Huygens–Steiner theorem, or just as Steiner's theorem, named after Christiaan Huygens and Jakob Steiner, can be used to determine the moment of inertia or the second moment of area of a rigid body about any axis, given the body's moment of inertia about a parallel axis through the object's center of gravity and the perpendicular distance between the axes. Mass moment of inertia Suppose a body of mass is rotated about an axis passing through the body's center of mass. The body has a moment of inertia with respect to this axis. The parallel axis theorem states that if the body is made to rotate instead about a new axis , which is parallel to the first axis and displaced from it by a distance , then the moment of inertia with respect to the new axis is related to by : I = I_\mathrm + md^2. Explicitly, is the perpendicular distance between the axes and . The parallel axis theorem can be applied with the stretch rule and perp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stretch Rule
In classical mechanics, the stretch rule (sometimes referred to as Routh's rule) states that the moment of inertia of a rigid object is unchanged when the object is stretched parallel to an axis of rotation that is a principal axis, provided that the distribution of mass remains unchanged except in the direction parallel to the axis. This operation leaves cylinders oriented parallel to the axis unchanged in radius. This rule can be applied with the parallel axis theorem The parallel axis theorem, also known as Huygens–Steiner theorem, or just as Steiner's theorem, named after Christiaan Huygens and Jakob Steiner, can be used to determine the moment of inertia or the second moment of area of a rigid body abo ... and the perpendicular axis theorem to find moments of inertia for a variety of shapes. Derivation The (scalar) moment of inertia of a rigid body around the z-axis is given by: : I_z = \int_V d^3 r \, \rho(\mathbf)\,r^2 Where r is the distance of a point from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartesian Coordinates
In geometry, a Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of real numbers called ''coordinates'', which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, called '' coordinate lines'', ''coordinate axes'' or just ''axes'' (plural of ''axis'') of the system. The point where the axes meet is called the '' origin'' and has as coordinates. The axes directions represent an orthogonal basis. The combination of origin and basis forms a coordinate frame called the Cartesian frame. Similarly, the position of any point in three-dimensional space can be specified by three ''Cartesian coordinates'', which are the signed distances from the point to three mutually perpendicular planes. More generally, Cartesian coordinates specify the point in an -dimensional Euclidean space for any dimension . These coordinates are the signed distances from the point to mutually perpendicular fixed h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Axis Theorem
The parallel axis theorem, also known as Huygens–Steiner theorem, or just as Steiner's theorem, named after Christiaan Huygens and Jakob Steiner, can be used to determine the moment of inertia or the second moment of area of a rigid body about any axis, given the body's moment of inertia about a parallel axis through the object's center of gravity and the perpendicular distance between the axes. Mass moment of inertia Suppose a body of mass is rotated about an axis passing through the body's center of mass. The body has a moment of inertia with respect to this axis. The parallel axis theorem states that if the body is made to rotate instead about a new axis , which is parallel to the first axis and displaced from it by a distance , then the moment of inertia with respect to the new axis is related to by : I = I_\mathrm + md^2. Explicitly, is the perpendicular distance between the axes and . The parallel axis theorem can be applied with the stretch rule and perp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stretch Rule
In classical mechanics, the stretch rule (sometimes referred to as Routh's rule) states that the moment of inertia of a rigid object is unchanged when the object is stretched parallel to an axis of rotation that is a principal axis, provided that the distribution of mass remains unchanged except in the direction parallel to the axis. This operation leaves cylinders oriented parallel to the axis unchanged in radius. This rule can be applied with the parallel axis theorem The parallel axis theorem, also known as Huygens–Steiner theorem, or just as Steiner's theorem, named after Christiaan Huygens and Jakob Steiner, can be used to determine the moment of inertia or the second moment of area of a rigid body abo ... and the perpendicular axis theorem to find moments of inertia for a variety of shapes. Derivation The (scalar) moment of inertia of a rigid body around the z-axis is given by: : I_z = \int_V d^3 r \, \rho(\mathbf)\,r^2 Where r is the distance of a point from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigid Bodies
In physics, a rigid body, also known as a rigid object, is a solid body in which deformation is zero or negligible, when a deforming pressure or deforming force is applied on it. The distance between any two given points on a rigid body remains constant in time regardless of external forces or moments exerted on it. A rigid body is usually considered as a continuous distribution of mass. Mechanics of rigid bodies is a field within mechanics where motions and forces of objects are studied without considering effects that can cause deformation (as opposed to mechanics of materials, where deformable objects are considered). In the study of special relativity, a perfectly rigid body does not exist; and objects can only be assumed to be rigid if they are not moving near the speed of light, where the mass is infinitely large. In quantum mechanics, a rigid body is usually thought of as a collection of point masses. For instance, molecules (consisting of the point masses: electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics Theorems
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of the human intellect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articles Containing Proofs
Article often refers to: * Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness * Article (publishing), a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication Article(s) may also refer to: Government and law * Elements of treaties of the European Union * Articles of association, the regulations governing a company, used in India, the UK and other countries; called articles of incorporation in the US * Articles of clerkship, the contract accepted to become an articled clerk * Articles of Confederation, the predecessor to the current United States Constitution * Article of impeachment, a formal document and charge used for impeachment in the United States * Article of manufacture, in the United States patent law, a category of things that may be patented * Articles of organization, for limited liability organizations, a US equivalent of articles of association Other uses * Article element , in HTML * "Articles", a song ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Mechanics
Classical mechanics is a Theoretical physics, physical theory describing the motion of objects such as projectiles, parts of Machine (mechanical), machinery, spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. The development of classical mechanics involved Scientific Revolution, substantial change in the methods and philosophy of physics. The qualifier ''classical'' distinguishes this type of mechanics from physics developed after the History of physics#20th century: birth of modern physics, revolutions in physics of the early 20th century, all of which revealed limitations in classical mechanics. The earliest formulation of classical mechanics is often referred to as Newtonian mechanics. It consists of the physical concepts based on the 17th century foundational works of Sir Isaac Newton, and the mathematical methods invented by Newton, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Leonhard Euler and others to describe the motion of Physical body, bodies under the influence of forces. Later, methods bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |