|
Pergamino
Pergamino () is an Argentine city in the Province of Buenos Aires. It has a population of about 104,985 inhabitants as per the and is the administrative seat of its county, Pergamino Partido. Its UN/LOCODE is ARPGO. History Long valued for its many springs and fertile land, the area had been home to the Charrúa and Araucanian people when it was first noticed by Spanish colonist around 1620. Becoming a posada along the trade route between colonial Buenos Aires and Córdoba, the settlement was given its name on 3 January 1626, for the parchment paper (document lost by a group of Spaniards) found there and conforming to an Araucanian term meaning "red soil." The settlement's first businesses were established in 1700 and in 1749, recurrent attacks by displaced natives led to the construction of a fort. These attacks did not cease, however, and on 8 August 1751 the settlement was destroyed. The site continued to be of interest, and Commander Juan González ordered the village rebuil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pergamino Partido
Pergamino Partido is a partido in the north of Buenos Aires Province in Argentina. The provincial subdivision has a population of about 100,000 inhabitants in an area of , and its capital city is Pergamino, which is around from Buenos Aires. Settlements Pergamino has 23 (districts): # Pergamino Pergamino () is an Argentine city in the Buenos Aires Province, Province of Buenos Aires. It has a population of about 104,985 inhabitants as per the and is the administrative seat of its county, Pergamino Partido. Its UN/LOCODE is ARPGO. History ...: capital # Francisco Ayerza # Ortíz Basualdo # Rancagua # Urquiza # Maguire # Villa Dafonte # Fontezuela # Manantiales Grande # Manantiales Chico # La Violeta # Pujol # Guerrico # Manuel Ocampo # Colonia Buena Vista # J.A. de la Peña # Acevedo # Mariano Benítez # El Socorro # Arroyo del Medio # Colonia Santa Rosa] # Mariano H. Alfonzo # Pinzón External links Pergamino Ciudad y su Regiónprovincial site Partidos of Buenos Aires P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partidos Of Buenos Aires
A ''partido'' is the second-level administrative subdivision only in the . They are formally considered to be a single administrative unit, usually contain one or more population centers (i.e., towns and cities), and are divided into ''localidades''. The subdivision in partidos in Buenos Aires Province is distinct from all other provinces of Argentina, which call their second-level subdivisions '' departamento'' and are further subdivided into distinct municipalities. History By the end of 18th century the town council ( cabildo) of Buenos Aires established the first partidos in the countryside: San Isidro del Pago de la Costa ( San Isidro) in 1779 and San Vicente, Quilmes, Magdalena, La Matanza, Cañada de Morón ( Morón), Las Conchas ( Tigre) and San Pedro in 1784. At the head of every partido, the cabildo appointed a rural judge called '' Alcalde de la Santa Hermandad''. The judge, or alcalde, had the mission to maintain the law and order in the surrounding rural ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
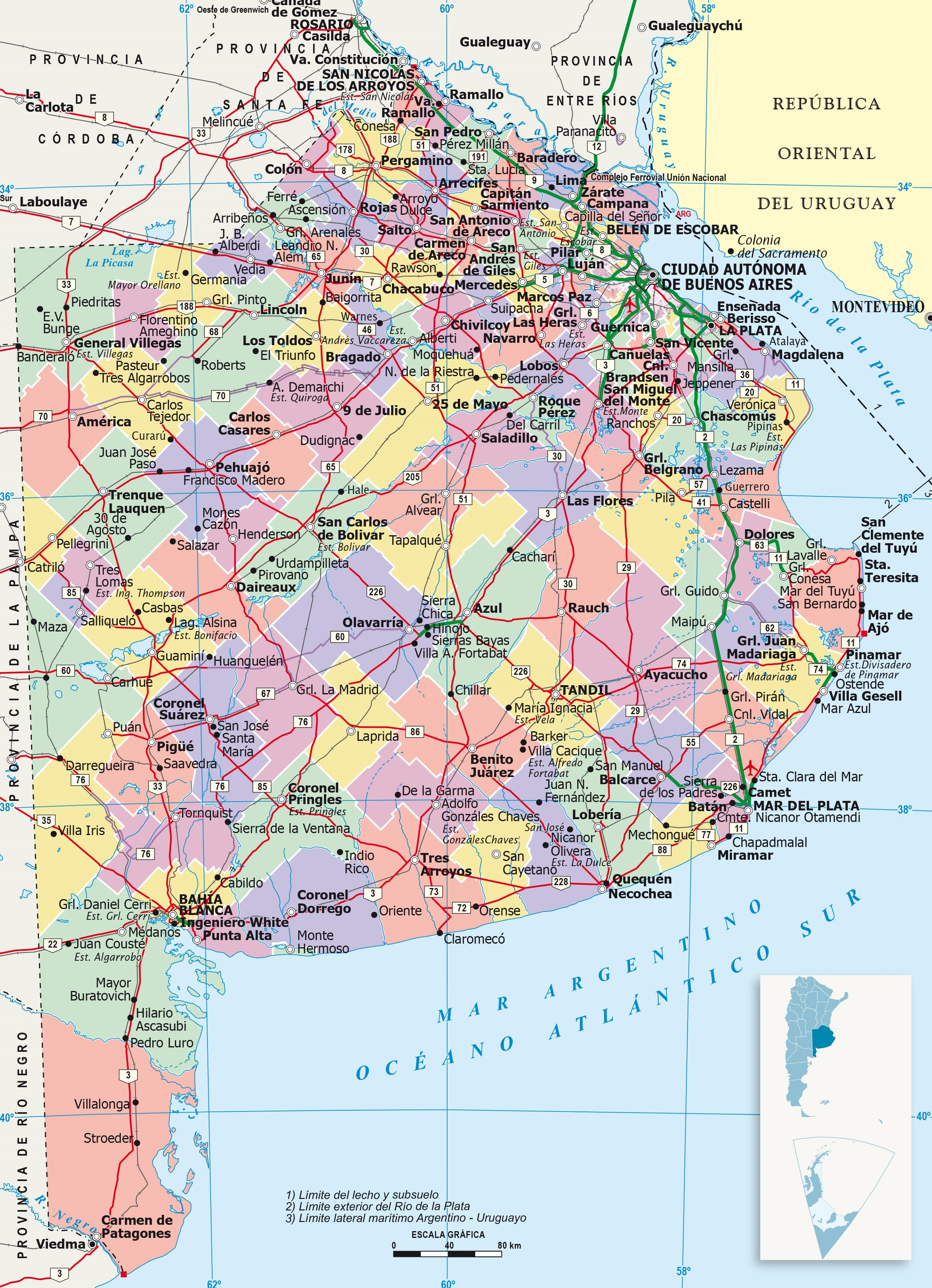
Buenos Aires Province
Buenos Aires (), officially the Buenos Aires Province (''Provincia de Buenos Aires'' ), is the largest and most populous Argentine province. It takes its name from the city of Buenos Aires, the capital of the country, which used to be part of the province and the province's capital until it was federalized in 1880. Since then, in spite of bearing the same name, the province does not include Buenos Aires proper, though it does include all other parts of the Greater Buenos Aires metropolitan area. The capital of the province is the city of La Plata, founded in 1882. It is bordered by the provinces of Entre Ríos to the northeast, Santa Fe to the north, Córdoba to the northwest, La Pampa to the west, Río Negro to the south and west and the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires to the northeast. Uruguay is just across the Rio de la Plata to the northeast, and both are on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean to the east. Almost the entire province is part of the Pampas geographical re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, 2 United Nations General Assembly observers#Present non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (2 states, both in associated state, free association with New Zealand). Compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abattoir
A slaughterhouse, also called abattoir (), is a facility where animals are Animal slaughter, slaughtered to provide food. Slaughterhouses supply meat, which then becomes the responsibility of a Meat packing industry, packaging facility. Slaughterhouses that produce meat that is not intended for human consumption are sometimes referred to as Knacker, ''knacker's yards'' or ''knackeries''. This is where animals are slaughtered that are not fit for human consumption or that can no longer work on a farm, such as retired working animal, work horses. Slaughtering animals on a large scale poses significant issues in terms of logistics, animal welfare, and the environment, and the process must meet public health requirements. Due to public aversion in different cultures, determining where to build slaughterhouses is also a matter of some consideration. Frequently, animal rights groups raise concerns about the methods of transport to and from slaughterhouses, preparation prior to slau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plaza Merced, Pergamino
A town square (or square, plaza, public square, city square, urban square, or ''piazza'') is an open public space, commonly found in the heart of a traditional town but not necessarily a true geometric square, used for community gatherings. Related concepts are the civic center, the market square and the village green. Most squares are hardscapes suitable for open markets, concerts, political rallies, and other events that require firm ground. Being centrally located, town squares are usually surrounded by small shops such as bakeries, meat markets, cheese stores, and clothing stores. At their center is often a well, monument, statue or other feature. Those with fountains are sometimes called fountain squares. By country Australia The city centre of Adelaide and the adjacent suburb of North Adelaide, in South Australia, were planned by Colonel William Light in 1837. The city streets were laid out in a grid plan, with the city centre including a central public square, Vict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iglesia Merced Pergamino
Iglesia may refer to: * Iglesia Department * Iglesia ni Cristo * Iglesia Filipina Independiente , native_name_lang = fil , icon = Logo of the Philippine Independent Church (Aglipayan Church).svg , icon_width = 80px , icon_alt = Coat of arms of the Philippine Independent Church , image ... * Iglesia (Metro Madrid), a station on Line 1 {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
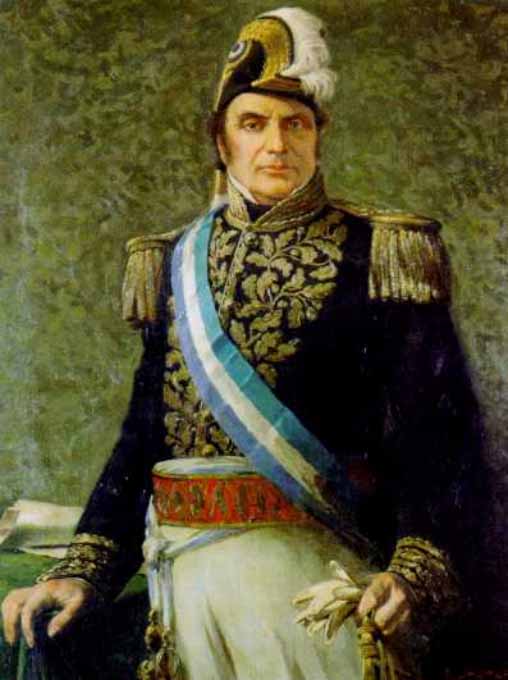
Martín Rodríguez (politician)
Martín Rodríguez (4 July 1771 – 5 March 1845) was an Argentina, Argentine politician and soldier. Biography Born in Buenos Aires to Rufina and Fermín Rodríguez, he inherited a ranch and managed the estate until 1806. He then took part in the resistance to the British invasions of the Río de la Plata, during the Napoleonic Wars and later played an important role in the events of the May Revolution of 1810. Upon the establishment of the First Junta which resulted, he was sent to the province of Entre Ríos Province, Entre Ríos to support the activities of Manuel Belgrano in the Paraguay campaign. He married Manuela Carrasco in 1810, and they had 14 children. Later, as colonel of a unit of Hussars, Rodríguez organized the militias that menaced a political meeting in April 1811, in an attempt to support Cornelio Saavedra. As a result of this, Rodríguez was temporarily imprisoned in San Juan, Argentina. The following year Rodríguez intervened in the Battle of Salta. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justice Of The Peace
A justice of the peace (JP) is a judicial officer of a lower or '' puisne'' court, elected or appointed by means of a commission (letters patent) to keep the peace. In past centuries the term commissioner of the peace was often used with the same meaning. Depending on the jurisdiction, such justices dispense summary justice or merely deal with local administrative applications in common law jurisdictions. Justices of the peace are appointed or elected from the citizens of the jurisdiction in which they serve, and are (or were) usually not required to have any formal legal education in order to qualify for the office. Some jurisdictions have varying forms of training for JPs. History In 1195, Richard I ("the Lionheart") of England and his Minister Hubert Walter commissioned certain knights to preserve the peace in unruly areas. They were responsible to the King in ensuring that the law was upheld and preserving the " King's peace". Therefore, they were known as "keepers of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartolomé Mitre
Bartolomé Mitre Martínez (26 June 1821 – 19 January 1906) was an Argentine statesman, soldier and author. He was President of Argentina from 1862 to 1868 and the first president of unified Argentina. Mitre is known as the most versatile statesman, military man, politician, journalist, historian, writer and poet. He was a major figure in the history of Argentina during second half of the 19th century. He was the figure that best characterized liberalism in Argentina, but he was a moderate and flexible liberal, not dogmatic. Early life Mitre was born on 26 June 1821 in Buenos Aires. His father was of Greek descent and the family name was originally Mitropoulos.Gardner, James. "Buenos Aires: The Biography of a City", 110. (St Martin's Press, 2015, ). In 1831, his family settled in Uruguay. He became a soldier, and graduated in 1839 from the Military School of Montevideo, with the rank of second lieutenant of artillery. Also a journalist, his writings supported Fruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Manuel De Rosas
Juan Manuel José Domingo Ortiz de Rosas (30 March 1793 – 14 March 1877), nicknamed "Restorer of the Laws", was an Argentine politician and army officer who ruled Buenos Aires Province and briefly the Argentine Confederation. Although born into a wealthy family, Rosas independently amassed a personal fortune, acquiring large tracts of land in the process. Rosas enlisted his workers in a private militia, as was common for rural proprietors, and took part in the disputes that led to numerous civil wars in his country. Victorious in warfare, personally influential, and with vast landholdings and a loyal private army, Rosas became a caudillo, as provincial warlords in the region were known. He eventually reached the rank of brigadier general, the highest in the Argentine Army, and became the undisputed leader of the Federalist Party. In December 1829, Rosas became governor of the province of Buenos Aires and established a dictatorship backed by state terrorism. In 1831, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Caseros
The Battle of Caseros ( es, Batalla de Caseros) was fought near the town of El Palomar, Buenos Aires Province, Argentina, on 3 February 1852, between the Army of Buenos Aires commanded by Juan Manuel de Rosas and the Grand Army (''Ejército Grande'') led by Justo José de Urquiza. The forces of Urquiza, '' caudillo'' and governor of Entre Ríos, defeated Rosas, who fled to the United Kingdom. This defeat marked a sharp division in the history of Argentina. As provisional Director of the Argentine Confederation, Urquiza sponsored the creation of the Constitution in 1853, and became the first constitutional President of Argentina in 1854. Background Argentine Civil Conflict From 1814 onwards, Argentina faced on serious internal challenges, resulting from disagreements over the proper form of government. This resulted in a series of civil wars that destabilized the young nation. End of the Anglo-French Bloc A British-French alliance had stymied Argentine leader Jua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)
