|
Peltasts
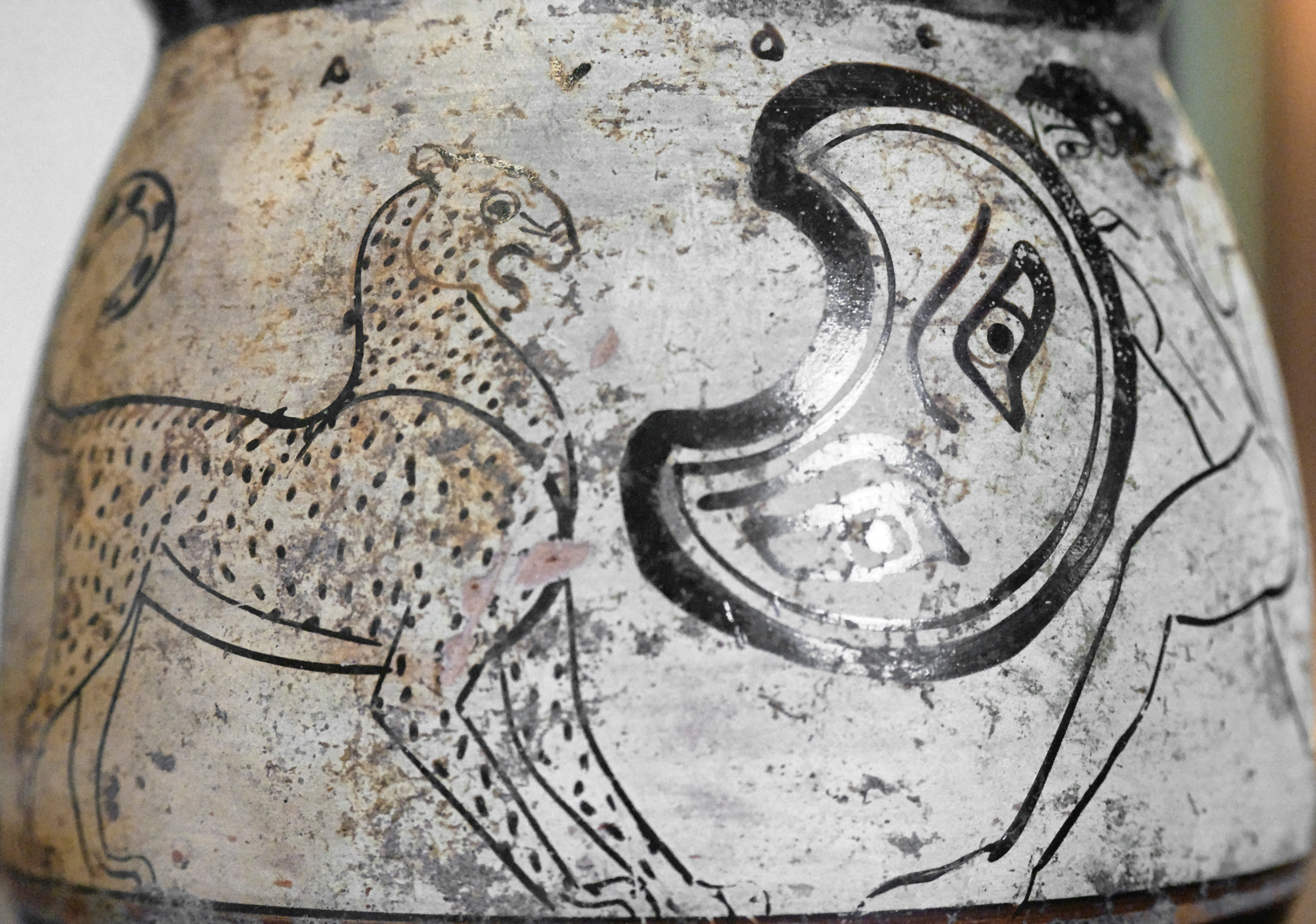
A ''peltast'' (, ) was a type of light infantry originating in Thrace and Paeonia and named after the kind of shield he carried.Williams, Mary Frances. "Philopoemen's special forces: Peltasts and a new kind of greek light-armed warfare (Livy 35.27) " ''Historia: Zeitschrift Für Alte Geschichte'' H. 3 (2004): 257-277. mentions the Thracian peltasts, while in the |
Peltast
A ''peltast'' (, ) was a type of light infantry originating in Thracians, Thrace and Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia and named after the kind of shield he carried.Williams, Mary Frances. "Philopoemen's special forces: Peltasts and a new kind of greek light-armed warfare (Livy 35.27) " ''Historia: Zeitschrift Für Alte Geschichte'' H. 3 (2004): 257-277. Thucydides mentions the Thracian peltasts, while Xenophon in the Anabasis (Xenophon), Anabasis distinguishes the Thracian and Greek peltast troops. The peltast often served as a skirmisher in Hellenistic period, Hellenistic armies. In the Middle Ages, the same term was used for a type of Byzantine Empire, Byzantine infantryman. Description ''Pelte'' shield ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javelins
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon. Today, the javelin is predominantly used for sporting purposes such as the javelin throw. The javelin is nearly always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with the aid of a hand-held mechanism. However, devices do exist to assist the javelin thrower in achieving greater distances, such as spear-throwers or the amentum. A warrior or soldier armed primarily with one or more javelins is a javelineer. The word javelin comes from Middle English and it derives from Old French ''javelin'', a diminutive of ''javelot'', which meant spear. The word ''javelot'' probably originated from one of the Celtic languages. Prehistory There is archaeological evidence that javelins and throwing sticks were already in use by the last phase of the Lower Paleolithic. Seven spear-like objects were found in a coal mine in the city of Schöningen, Germany. Stratigraphy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic Period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the Roman conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year, which eliminated the last major Hellenistic kingdom. Its name stems from the Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás''), which was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the modern historiographical term ''Hellenistic'' was derived. The term "Hellenistic" is to be distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all the ancient territories of the period that had come under significant Greek influence, particularly the Hellenized Middle East, after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian conquest of the Achaemenid Empire in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Infantry
Light infantry refers to certain types of lightly equipped infantry throughout history. They have a more mobile or fluid function than other types of infantry, such as heavy infantry or line infantry. Historically, light infantry often fought as Reconnaissance, scouts, Raid (military), raiders, and skirmishers. These are loose formations that fight ahead of the main army to harass, delay, disrupt supply lines, engage the enemy's own skirmishing forces, and generally "soften up" an enemy before the main battle. Light infantrymen were also often responsible for Screening (tactical), screening the main body of a military formation. Following World War II, the term "light infantry" has evolved to include rapid-deployment units (including commando and Airborne forces, airborne units) that emphasize speed and mobility over armor and firepower. Some units or battalions that historically held a skirmishing role retain their designation "light infantry" for the sake of tradition. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, and the arts. As the founder of the Peripatetic school of philosophy in the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum in Athens, he began the wider Aristotelianism, Aristotelian tradition that followed, which set the groundwork for the development of modern science. Little is known about Aristotle's life. He was born in the city of Stagira (ancient city), Stagira in northern Greece during the Classical Greece, Classical period. His father, Nicomachus (father of Aristotle), Nicomachus, died when Aristotle was a child, and he was brought up by a guardian. At around eighteen years old, he joined Plato's Platonic Academy, Academy in Athens and remained there until the age of thirty seven (). Shortly after Plato died, Aristotle left Athens and, at the request ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Mercenaries
There is evidence of mercenaries (''misthophoroi (plural), misthios (singular male), misthia (singular female)'' in Greek) being hired in Ancient Greece from the 6th century BC. The tyrants of that time hired bodyguards from other city-states. It is not known if earlier Aegean armies and navies, such as the Minoans and Mycenaeans, used mercenaries. Mercenary troops from Caria and Ionia are known to have fought with Psamtik I against the Assyrians. These were the "bronze men from the sea" whose arrival in Egypt, according to Herodotus, was foretold to Psamtik by an oracle. They entered the country as raiders but Psamtik made a truce with them and hired them to his cause. Afterwards, he granted land to them alongside the Nile and they are traditionally held to have been the first Greeks to settle in Egypt. In the 5th century BC, Arcadian soldiers fought for Xerxes I in 480 when he led the Persian invasion of Greece. Later in the century, many Greek mercenaries were employ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrygian Cap
The Phrygian cap ( ), also known as Thracian cap and liberty cap, is a soft Pointed hat, conical Hat, cap with the apex bent over, associated in Classical antiquity, antiquity with several peoples in Eastern Europe, Anatolia, and Asia. The Phrygian cap was worn by Thracians, Dacians, Persians, Medes, Scythians, Troy, Trojans, and Phrygians after whom it is named. The oldest known depiction of the Phrygian cap is from Persepolis in Iran. Although Phrygian caps did not originally function as liberty caps, they came to signify freedom and the pursuit of liberty first in the American Revolution and then in the French Revolution, particularly as a symbol of Jacobinism (in which context it has been also called a Jacobin cap). The original cap of liberty was the Roman ''Pileus (hat), pileus'', the felt cap of emancipated slaves of ancient Rome, which was an attribute of Libertas, the Roman goddess of liberty. In the 16th century, the Roman iconography of liberty was revived in emblem b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east, it comprises present-day southeastern Bulgaria (Northern Thrace), northeastern Greece (Western Thrace), and the European part of Turkey (East Thrace). Lands also inhabited by ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into Macedonia (region), Macedonia. Etymology The word ''Thrace'', from ancient Greek ''Thrake'' (Θρᾴκη), referred originally to the Thracians (ancient Greek ''Thrakes'' Θρᾷκες), an ancient people inhabiting Southeast Europe. The name ''Europe'' (ancient Greek Εὐρώπη), also at first referred to this region, before that term expanded to include its Europe, modern sense. It has been suggested that the name ''Thrace'' derives from the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoplites
Hoplites ( ) ( ) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greek city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with fewer soldiers. The formation discouraged the soldiers from acting alone, for this would compromise the formation and minimize its strengths. The hoplites were primarily represented by free citizens – propertied farmers and artisans – who were able to afford a linen or bronze armour suit and weapons (estimated at a third to a half of its able-bodied adult male population). Some states maintained a small elite professional unit, known as the '' epilektoi'' or logades ('the chosen') because they were picked from the regular citizen infantry. These existed at times in Athens, Sparta, Argos, Thebes, and Syracuse, among other places. Hoplite soldiers made up the bulk of ancient Greek armies. In the 8th or 7th century BC, Greek armies adopted the phalanx formation. The formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaic Greece
Archaic Greece was the period in History of Greece, Greek history lasting from to the second Persian invasion of Greece in 480 BC, following the Greek Dark Ages and succeeded by the Classical Greece, Classical period. In the archaic period, the Greeks settled across the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea: by the end of the period, they were part of a trade network that spanned the entire Mediterranean. The archaic period began with a massive increase in the Greek population and of significant changes that rendered the Greek world at the end of the 8th century entirely unrecognizable from its beginning. According to Anthony Snodgrass, the archaic period was bounded by two revolutions in the Greek world. It began with a "structural revolution" that "drew the political map of the Greek world" and established the ''Polis, poleis'', the distinctively Greek city-states, and it ended with the intellectual revolution of the Classical period. The archaic period saw developments in Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubit
The cubit is an ancient unit of length based on the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger. It was primarily associated with the Sumerians, Egyptians, and Israelites. The term ''cubit'' is found in the Bible regarding Noah's Ark, the Ark of the Covenant, the Tabernacle, and Solomon's Temple. The ''common cubit'' was divided into 6 palm (unit), palms × 4 Finger (unit), fingers = 24 digit (unit), digits. ''Royal cubits'' added a palm for 7 palms × 4 fingers = 28 digits. These lengths typically ranged from , with an ancient Roman cubit being as long as . Cubits of various lengths were employed in many parts of the world in ancient history, antiquity, during the Middle Ages and as recently as Early modern Europe, early modern times. The term is still used in hedgelaying, the length of the forearm being frequently used to determine the interval between stakes placed within the hedge. Etymology The English word "cubit" comes from the Latin language, Latin noun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |