|
Peloponnesian League
The Peloponnesian League () was an alliance of ancient Greek city-states, dominated by Sparta and centred on the Peloponnese, which lasted from c. 550 to 366 BC. It is known mainly for being one of the two rivals in the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), against the Delian League, which was dominated by Athens. Name The Peloponnesian League is the modern name given to the Spartan system of alliances, but it is inaccurate because there were members outside the Peloponnese, and it was not really a league. The ancient name of the League was "the Lacedemonians and their allies". This is misleading as well, because Sparta could have allies outside of the Peloponnesian League. History Foundation (c. 550 BC) In its early history, Sparta expanded by conquering Laconia and Messenia and reducing their population into slavery (as helots), but the subjugation of Tegea on its northern border failed at the battle of the Fetters. Following this defeat, Sparta abandoned its military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Map Peloponnesian War 431 BC-en
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geography, geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
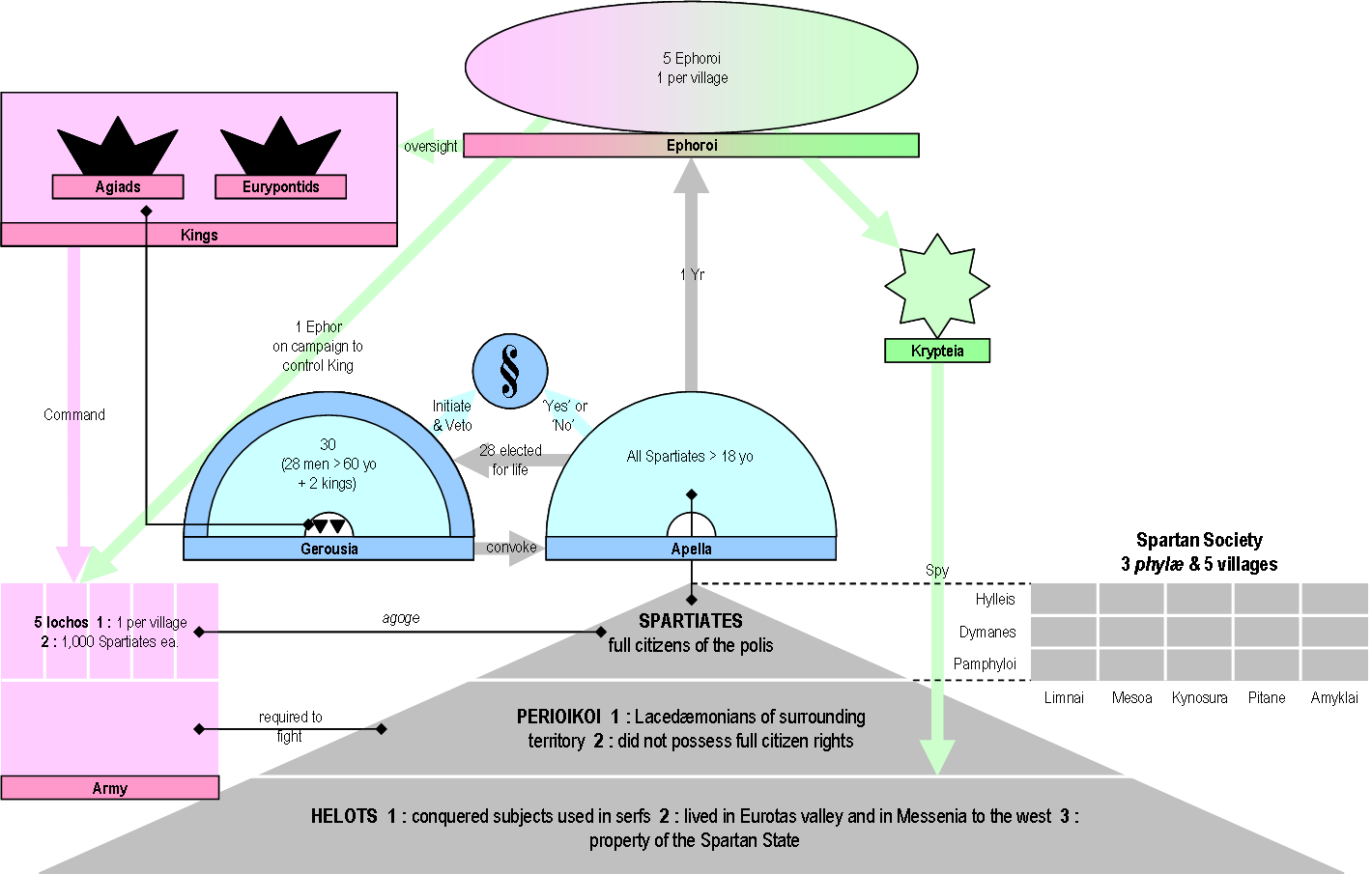
Ephor
The ephors were a board of five magistrates in ancient Sparta. They had an extensive range of judicial, religious, legislative, and military powers, and could shape Sparta's home and foreign affairs. The word "''ephors''" (Ancient Greek ''éphoroi'', plural form of ''éphoros'') comes from the Ancient Greek ''epi'', "on" or "over", and ''horaō'', "to see", i.e., "one who oversees" or "overseer". The ephors were a council of five Spartan men elected annually who swore an oath monthly on the behalf of the state. The Spartan kings, however, would swear on behalf of themselves. The ephors did not have to kneel before the Kings of Sparta, and were held in high esteem by the citizens because of the importance of their powers and because of the holy role that they earned throughout their functions. Donald Kagan, ''The Outbreak of the Peloponnesian War''. p. 29. Ithaca/New York 1969, . Several other Greek city-states with a Spartan ancestry also had ephors, such as Taras or Cyre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oligarchy
Oligarchy (; ) is a form of government in which power rests with a small number of people. Members of this group, called oligarchs, generally hold usually hard, but sometimes soft power through nobility, fame, wealth, or education; or through corporate, religious, political, or military control. Throughout history, power structures considered to be oligarchies have often been viewed as coercive, relying on public obedience or oppression to exist. Aristotle pioneered the use of the term as meaning rule by the rich, contrasting it with aristocracy, arguing that oligarchy was a corruption of aristocracy. Types Minority rule The consolidation of power by a dominant minority, whether religious or ethnic, can be considered a form of oligarchy. Examples include South Africa during apartheid, Liberia under Americo-Liberians, the Sultanate of Zanzibar, and Rhodesia. In these cases, oligarchic rule was often tied to the legacy of colonialism. In the early 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hegemony
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one State (polity), state over other states, either regional or global. In Ancient Greece (ca. 8th BC – AD 6th c.), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' city-state over other city-states. In the 19th century, ''hegemony'' denoted the "social or cultural predominance or ascendancy; predominance by one group within a society or milieu" and "a group or regime which exerts undue influence within a society". In theories of imperialism, the hegemonic order dictates the internal politics and the societal character of the subordinate states that constitute the hegemonic sphere of influence, either by an internal, vassal state, sponsored government or by an external, puppet state, installed government. The term ''hegemonism'' denoted the geopolitical and the cultural predominance of one country over other countries, e.g. the hegemony of the Great power, Great Powers established wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Achaea
Achaea () or Achaia (), sometimes transliterated from Greek language, Greek as Akhaia (, ''Akhaḯa'', ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Western Greece and is situated in the northwestern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. The capital is Patras which is the third largest city in Greece. Geography Achaea is bordered by Elis (regional unit), Elis to the west and southwest, Arcadia (regional unit), Arcadia to the south, and Corinthia to the east and southeast. The Gulf of Corinth lies to its northeast, and the Gulf of Patras to its northwest. The mountain Panachaiko (1926 m), though not the highest of Achaea, dominates the coastal area near Patras. Higher mountains are found in the south, such as Aroania (mountain), Aroania (2341 m) and Mount Erymanthos, Erymanthos (2224 m). Other mountain ranges in Achaea are Skollis, Omplos, Kombovouni and Movri. Its main rivers ordered from west to east are the Laris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arcadia (region)
Arcadia (; ) is a region in the central Peloponnese, Greece. It takes its name from the mythological character Arcas, and in Greek mythology it was the home of the gods Hermes and Pan. In European Renaissance arts, Arcadia was celebrated as an unspoiled, harmonious wilderness; as such, it was referenced in popular culture. The modern regional unit of the same name more or less overlaps with the historical region, but is slightly larger. History Arcadia was gradually linked in a loose confederation that included all the Arcadian towns and was named League of the Arcadians. In the 7th century BC, it successfully faced the threat of Sparta and the Arcadians managed to maintain their independence. They participated in the Persian Wars alongside other Greeks by sending forces to Thermopylae and Plataea. During the Peloponnesian War, Arcadia allied with Sparta and Corinth. In the following years, during the period of the hegemony of Thebes, the Theban general Epaminondas re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ancient Elis
Elis () or Eleia (; ; Elean: ; ) is an ancient district in Greece that corresponds to the modern regional unit of Elis. Elis is in southern Greece on the Peloponnese, bounded on the north by Achaea, east by Arcadia, south by Messenia, and west by the Ionian Sea. Over the course of the archaic and classical periods, the '' polis'' "city-state" of Elis controlled much of the region of Elis, most probably through unequal treaties with other cities; many inhabitants of Elis were Perioeci—autonomous free non-citizens. Perioeci, unlike other Spartans, could travel freely between cities. Thus the polis of Elis was formed. The local form of the name was Valis, or Valeia, and its meaning, in all probability was, "the lowland" (compare with the word "valley"). In its physical constitution Elis is similar to Achaea and Arcadia; its mountains are mere offshoots of the Arcadian highlands, and its principal rivers are fed by Arcadian springs. According to Strabo, the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Argolis
Argolis or Argolida ( , ; , in ancient Greek and Katharevousa) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, situated in the eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula and part of the tripoint area of Argolis, Arcadia (ancient region), Arcadia and Corinthia. Much of the territory of this region is situated in the Argolid Peninsula. Geography Most arable land lies in the central part of Argolis. Its primary agricultural resources are orange (fruit), oranges and olives. Argolis has a coastline on the Saronic Gulf in the northeast and on the Argolic Gulf in the south and southeast. Notable mountains ranges are the Oligyrtos in the northwest, Lyrkeio and Ktenia in the west, and Arachnaio and Didymo (mountain), Didymo in the east. Argolis has land borders with Arcadia (regional unit), Arcadia to the west and southwest, Corinthia to the north, and the Islands (regional unit), Islands regional unit (Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Epidaurus
Epidaurus () was a small city (''polis'') in ancient Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula at the Saronic Gulf. Two modern towns bear the name Epidavros: ''Palaia Epidavros'' and ''Nea Epidavros''. Since 2010 they belong to the new municipality of Epidaurus, part of the regional unit of Argolis. The seat of the municipality is the town Lygourio. The nearby Temple of Asclepius, Epidaurus, sanctuary of Asclepius and Ancient Theatre of Epidaurus, ancient theatre were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1988 because of their exemplary architecture and importance in the development and spread of healing sanctuaries and cults across the ancient Greek and Roman worlds. Name and etymology The name "Epidaurus" is of Greek language, Greek origin. It was named after the hero Epidaurus (mythology), Epidauros, son of Apollo. According to Strabo, the city was originally named Ἐπίκαρος (Epíkaros) under the Carians, (Aristotle claimed that Caria, as a naval empire, occupied Epidau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ancient Corinth
Corinth ( ; ; ; ) was a city-state (''polis'') on the Isthmus of Corinth, the narrow stretch of land that joins the Peloponnese peninsula to the mainland of Greece, roughly halfway between Ancient Athens, Athens and Sparta. The modern city of Corinth is located approximately northeast of the ancient ruins. Since 1896, systematic archaeological investigations of the Corinth Excavations by the American School of Classical Studies at Athens have revealed large parts of the ancient city, and recent excavations conducted by the Greek Ministry of Culture have brought to light important new facets of antiquity. For Christianity, Christians, Corinth is well known from the two letters from Paul the Apostle in the New Testament, the First Epistle to the Corinthians and the Second Epistle to the Corinthians. Corinth is also mentioned in the Acts of the Apostles as part of Paul the Apostle's missionary travels. In addition, the second book of Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias' ''Descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phlius
Phlius (; ) or Phleius () was an independent polis (city-state) in the northeastern part of Peloponnesus. Phlius' territory, called Phliasia (), was bounded on the north by Sicyonia, on the west by Arcadia, on the east by Cleonae, and on the south by Argolis. This territory is a small valley about above the level of the sea, surrounded by mountains, from which streams flow down on every side, joining the river Asopus in the middle of the plain. The mountain in the southern part of the plain, from which the principal source of the Asopus springs, was called Carneates (Καρνεάτης). The territory of Phlius was celebrated in antiquity for its wine. According to Strabo, the ancient capital of the country was Araethyrea (Ἀραιθυρέα) on Mt. Celosse, which city is mentioned by Homer; but the inhabitants subsequently deserted it and built Phlius at the distance of 30 stadia. Pausanias, however, does not speak of any migration, but says that the ancient capital w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mantineia
Mantinea (; ''Mantineia''; also Koine Greek ''Antigoneia'') was a city in ancient Arcadia, Greece, which was the site of two significant battles in Classical Greek history. In modern times it is a former municipality in Arcadia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Tripoli, of which it is a municipal unit. Its seat was the village of Nestani (pop. 486 in 2011). It is located in the northeastern part of Arcadia. The municipal unit has a land area of 205.393 km2 and a population of 1,693 inhabitants (2021). Its largest other towns are Artemisio, Loukas, and Kapsas. History The city emerged from the amalgamation of several neighbouring villages around 500 BC. Its patron god was Poseidon. It was a large city with numerous temples. The fortifications originally were polygonal. The temple of Artemis Hymnia, just on the north of the city, is mentioned by Pausanias. Diotima, who influenced Socrates, supposedly was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |