|
Peking Man
Peking Man (''Homo erectus pekinensis'', originally "''Sinanthropus pekinensis''") is a subspecies of '' H. erectus'' which inhabited what is now northern China during the Middle Pleistocene. Its fossils have been found in a cave some southwest of Beijing (referred to in the West as Peking upon its first discovery), known as the Zhoukoudian Peking Man Site. The first fossil, a tooth, was discovered in 1921, and Zhoukoudian has since become the most productive ''H. erectus'' site in the world. Peking Man was instrumental in the foundation of Chinese anthropology, and fostered an important dialogue between Western and Eastern science. Peking Man became the centre of anthropological discussion, and was classified as a direct human ancestor, propping up the Out of Asia theory that humans evolved in Asia. Peking Man also played a vital role in the restructuring of Chinese identity following the Chinese Communist Revolution, and it was used to introduce the general populace to M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, more widely known as the Middle Pleistocene (its previous informal name), is an Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale or a Stage (stratigraphy), stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. The Chibanian name was officially ratified in January 2020. It is currently estimated to span the time between 0.7741 annum, Ma (774,100 years ago) and 0.129 Ma (129,000 years ago), also expressed as 774.1–129 ka. It includes the transition in palaeoanthropology from the Lower Paleolithic, Lower to the Middle Paleolithic over 300 ka. The Chibanian is preceded by the Calabrian (stage), Calabrian and succeeded by the Late Pleistocene. The beginning of the Chibanian is the Brunhes–Matuyama reversal, when the Earth's magnetic field last underwent reversal. Its end roughly coincides with the termination of the Penultimate Glacial Period and the onset of the Last Interglacial period (correspondin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brow Ridge
The brow ridge, or supraorbital ridge known as superciliary arch in medicine, is a bony ridge located above the eye sockets of all primates and some other animals. In humans, the eyebrows are located on their lower margin. Structure The brow ridge is a nodule or crest of bone situated on the frontal bone of the skull. It forms the separation between the forehead portion itself (the squama frontalis) and the roof of the eye sockets (the pars orbitalis). Normally, in humans, the ridges arch over each eye, offering mechanical protection. In other primates, the ridge is usually continuous and often straight rather than arched. The ridges are separated from the frontal eminences by a shallow groove. The ridges are most prominent medially, and are joined to one another by a smooth elevation named the glabella. Typically, the arches are more prominent in men than in women, and vary between different human populations. Behind the ridges, deeper in the bone, are the frontal sinuses. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
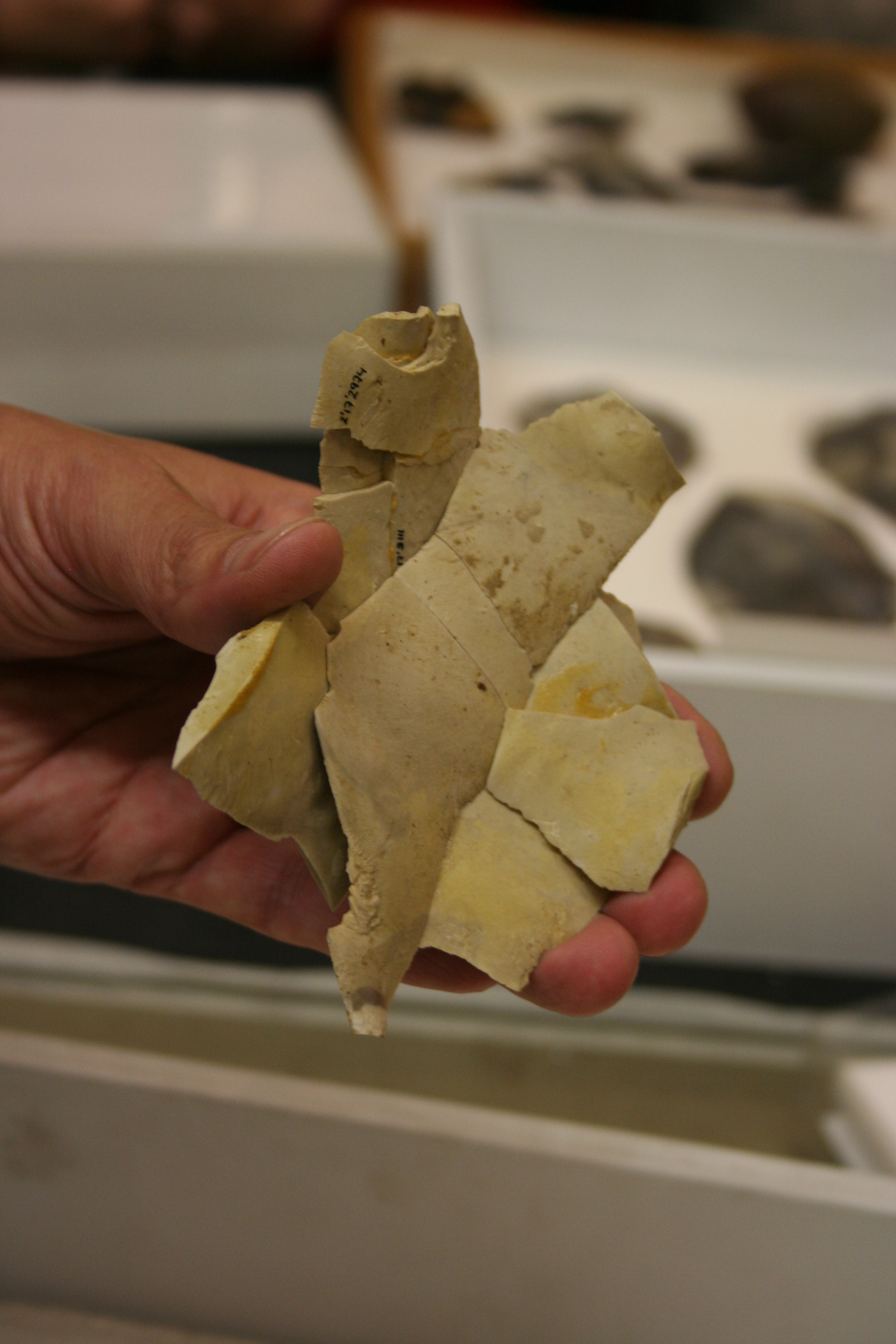
Chopper (archaeology)
Archaeologists define a chopper as a pebble tool with an irregular cutting edge formed through the removal of lithic flake, flakes from one side of a stone. Choppers are crude forms of stone tool and are found in archaeological industry, industries as early as the Lower Palaeolithic from around 2.5 million years ago. These earliest known specimens were found in the Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania by Louis Leakey in the 1930s. The name Oldowan was given to the tools after the site in which they were excavated. These types of tools were used an estimated time range of 2.5 to 1.2 million years ago. Formation To create this tool, one would have to use a hammerstone to chip away flakes on the stone to create a side of the stone with a very sharp edge, allowing for the cutting and hacking of an object. This is a unique type of lithic reduction, as only a single side of the stone is retouched to produce the cutting surface of the stone. The side that does not do the cutting is left unscathed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debitage
In archaeology, debitage is all the material produced during the process of lithic reduction – the production of stone tools and weapons by knapping stone. This Assemblage (archaeology), assemblage may include the different kinds of lithic flakes and lithic blades, but most often refers to the shatter and production debris, and production rejects. Debitage analysis Debitage analysis, a sub-field of lithic analysis, considers the entire lithic waste assemblage. The analysis is undertaken by investigating differing patterns of debris morphology, size, and shape, among other things. This allows researchers to make more accurate assumptions regarding the purpose of the lithic reduction. Quarrying activities, core reduction, biface creation, tool manufacture, and retooling are believed to leave significantly different debitage assemblages. Lithic manufacture from a quarried source, or from found cobbles also leave different signatures. Some claim that they can determine the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Tool
Stone tools have been used throughout human history but are most closely associated with prehistoric cultures and in particular those of the Stone Age. Stone tools may be made of either ground stone or knapped stone, the latter fashioned by a craftsman called a flintknapper. Stone has been used to make a wide variety of tools throughout history, including arrowheads, spearheads, hand axes, and querns. Knapped stone tools are nearly ubiquitous in pre-metal-using societies because they are easily manufactured, the tool stone raw material is usually plentiful, and they are easy to transport and sharpen. The study of stone tools is a cornerstone of prehistoric archaeology because they are essentially indestructible and therefore a ubiquitous component of the archaeological record. Ethnoarchaeology is used to further the understanding and cultural implications of stone tool use and manufacture. Knapped stone tools are made from cryptocrystalline materials such as chert, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachycrocuta
''Pachycrocuta'' is an extinct genus of hyena. The largest and most well-researched species is ''Pachycrocuta brevirostris'', colloquially known as the giant short-faced hyena as it stood about at the shoulder and it is estimated to have averaged in weight, approaching the size of a lioness, making it one the largest known hyenas. It is often hypothesised to have been a specialised kleptoparasitic scavenger, using its imposing size to force other predators off of carcasses, though some authors have suggested they may have been effective pack hunters like living spotted hyenas. The precise time of the origin of the genus depends on what species are included, though the only unquestioned species of the genus, ''P. brevirostris'', had emerged by the Early Pleistocene (around 2.6-2 million years ago). Around 800,000 years ago at the end of the Early Pleistocene, it became locally extinct in Europe, with it surviving in East Asia until at least 500,000 years ago, and possibly later e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Of Fire By Early Humans
The control of fire by early humans was a critical technology enabling the evolution of humans. Fire provided a source of warmth and lighting, protection from predators (especially at night), a way to create more advanced hunting tools, and a method for cooking food. These cultural advances allowed human geographic dispersal, cultural innovations, and changes to diet and behavior. Additionally, creating fire allowed human activity to continue into the dark and colder hours of the evening. Claims for the earliest definitive evidence of control of fire by a member of ''Homo'' range from 1.7 to 2.0 million years ago ( Mya). Evidence for the "microscopic traces of wood ash" as controlled use of fire by ''Homo erectus'', beginning roughly 1 million years ago, has wide scholarly support. Some of the earliest known traces of controlled fire were found at the Daughters of Jacob Bridge, Israel, and dated to ~790,000 years ago. At the site, archaeologists also found the oldest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistory Of Nakedness And Clothing
Nakedness and clothing use are characteristics of humans related by evolutionary and social prehistory. The major loss of body hair distinguishes humans from other primates. Current evidence indicates that anatomically modern humans were naked in prehistory for at least 90,000 years before they invented clothing. Today, isolated Indigenous peoples in tropical climates continue to be without clothing in many everyday activities. Evolution of hairlessness upHumans' closest living relatives have both extensive areas of fur and also bare patches The general hairlessness of humans in comparison to related species may be due to loss of functionality in the pseudogene KRT41P (which helps produce keratin) in the human lineage about 240,000 years ago. On an individual basis, mutations in the gene HR can lead to complete hair loss, though this is not typical in humans. Humans may also lose their hair as a result of hormonal imbalance due to drugs or pregnancy. In order to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interglacial
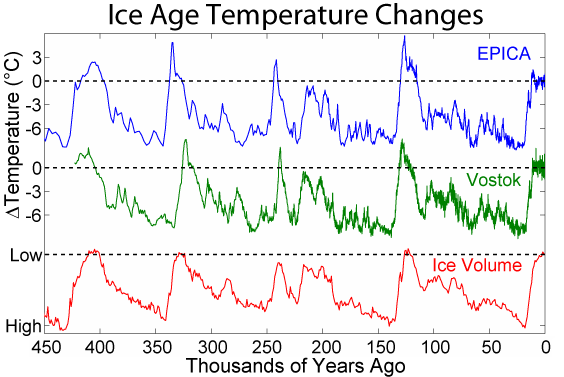
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial Period
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate between glacial periods. The Last Glacial Period ended about 15,000 years ago. The Holocene is the current interglacial. A time with no glaciers on Earth is considered a Greenhouse and icehouse Earth, greenhouse climate state. Quaternary Period Within the Quaternary, which started about 2.6 million years before present, there have been a number of glacials and interglacials. At least eight glacial cycles have occurred in the last 740,000 years alone. Changes in atmospheric and associated radiative forcing were among the primary drivers of globally cold glacial and warm interglacial climates, with changes in ocean physical circulation, biological productivity and seawater acid-base chemistry likely causing most of the recorded changes Penul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shovel-shaped Incisors
Shovel-shaped incisors (or, more simply, shovel incisors) are incisors whose Glossary of dentistry, lingual surfaces are scooped as a consequence of lingual marginal ridges, Crown (tooth), crown curvature, or Basal (anatomy), basal Tubercle (anatomy), tubercles, either alone or in combination. Shovel-shaped incisors are significantly common in Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Amerindians from North America, North, Central America, Central, and South America. They are also common in East Asians and Central Asians, Inuit, and Aleut peoples of Siberian Yupik, Northeast Asia and North America (including but not limited to Inuit in eastern Alaska, Northern Canada, Arctic Canada, and Greenland). In certain European peoples, European and Demographics of Africa, African groups, shovel-shaped upper incisors are uncommon or not present. There is a spectrum of the degree of shoveled-ness, ranging on a scale from 0 to 7 of spatulate incisors to shoveled incisors. It was theorized that pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, whereas armadillos, anteaters and other animals in the order Edentata have none. Structure Adult humans normally have eight incisors, two of each type. The types of incisors are: * maxillary central incisor (upper jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * maxillary lateral incisor (upper jaw, beside the maxillary central incisor) * mandibular central incisor (lower jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * mandibular lateral incisor (lower jaw, beside the mandibular central incisor) Children with a full set of deciduous teeth (primary teeth) also have eight incisors, named the same way as in permanent teeth. Young children may have from zero to eight incisors depending on the stage of their tooth eruption and tooth development. Typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |