|
Paul Mérault Monneron
Paul Mérault Monneron or de Monneron (23 February 1748, Annonay, Ardèche – May 1788, Vanikoro) was an engineer officer in the French armed forces and from 1785 to 1788 a member of Jean-François de Galaup, comte de La Pérouse, Lapérouse's expedition. Family His eldest brother Charles Claude Ange Monneron was député to the Estates General of 1789, for the Sénéchaussée of Annonay, his brothers Louis Monneron (1742–1805) and Pierre Antoine Monneron (1747–1801) were respectively députés of the National Constituent Assembly (France), National Constituent Assembly for the West Indies and Mauritius. Another brother, Joseph François Augustin Monneron (1756–1826) was député for Paris at the Legislative Assembly (France), Legislative Assembly and retired from it in 1792, before becoming Director General of the Caisse des Comptes Courants and going bankrupt in 1798. Life Entering the École du génie de Mézières and received as an engineer on 1 January 1770, he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annonay
Annonay (; ) is a Communes of France, commune and largest city in the north of the Ardèche department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of southeastern France. It is the most populous commune in the Ardèche department although it is not the capital which is the smaller town of Privas. Other communes in the Ardèche department are Aubenas, Guilherand-Granges, and Tournon-sur-Rhône. Geography The commune consists of the city of Annonay and the hamlets of Vissenty, Chatinais, and Boucieu. With residential development, these four entities have merged into one today. Further away is the hamlet of Toissieu. Annonay was built over several small hills at the confluence of the rivers Cance (Canse) and Deûme (Deôme). Annonay is a crossroads of trade routes: from the Rhône Valley to the region of Saint-Étienne (east-west) and from Lyon to south of the Massif Central (north-south). It is located south of Lyon, south-west of Saint-Rambert-d'Albon, and north-west of Saint-Vallier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominique (pays)
"Dominique" is a 1963 French language popular song, written and performed by Belgian singer Jeannine Deckers, better known as Sœur Sourire ("Sister Smile" in French) or The Singing Nun. The song is about Saint Dominic, a Spanish-born priest and founder of the Dominican Order, of which she was a member (as Sister Luc-Gabrielle). The English-version lyrics of the song were written by Noël Regney. In addition to French and English, Deckers recorded versions in Dutch, German, Hebrew, Japanese, Korean, and Portuguese. It was a top selling record in 11 countries in late 1963 and early 1964. Commercial performance "Dominique" reached the Top 10 in 11 countries in late 1963 and early 1964, topping the chart in the United States, Canada, Australia and New Zealand. It reached the Top 5 in Norway, Denmark, Ireland and South Africa, with the song making it into the lower reaches of the Top 10 in the Netherlands, West Germany, and the United Kingdom. The song reached and stayed at No. 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
28 Mai
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9. Etymology English ''eight'', from Old English '', æhta'', Proto-Germanic ''*ahto'' is a direct continuation of Proto-Indo-European '' *oḱtṓ(w)-'', and as such cognate with Greek and Latin , both of which stems are reflected by the English prefix oct(o)-, as in the ordinal adjective ''octaval'' or ''octavary'', the distributive adjective is ''octonary''. The adjective ''octuple'' (Latin ) may also be used as a noun, meaning "a set of eight items"; the diminutive ''octuplet'' is mostly used to refer to eight siblings delivered in one birth. The Semitic numeral is based on a root ''*θmn-'', whence Akkadian ''smn-'', Arabic ''ṯmn-'', Hebrew ''šmn-'' etc. The Chinese numeral, written (Mandarin: ''bā''; Cantonese: ''baat''), is from Old Chinese ''*priāt-'', ultimately from Sino-Tibetan ''b-r-gyat'' or ''b-g-ryat'' which also yielded Tibetan '' brgyat''. It has been argued that, as the cardinal num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Fleuriot De Langle
Paul Antoine Fleuriot de Langle (1 August 1744, château de Kerlouët at Quemper-Guézennec, Côtes-d'Armor – 11 December 1787, Maouna, Samoa) was a French vicomte, académicien de marine, naval commander and explorer. He was second in command of the La Pérouse expedition, which departed France on 1 August 1785 and was eventually lost in the Pacific. Fleuriot de Langle died in an encounter with natives in what is now American Samoa before the expedition was lost; his remains were returned to France, and were buried in the choir of the church of Saint-Louis at Brest. Biography In 1771, aged only 27, Fleuriot de Langle was admitted as a member of the Académie de Marine. He was promoted to Lieutenant in 1778. Fleuriot de Langle took part in the American Revolutionary War. In April 1781, Fleuriot de Langle was given command of the 32-gun frigate ''Résolue''. From March 1782, he commanded the 50-gun ''Experiment'', and then commanded the frigate ''Astrée'' in the Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Île Maurice
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Agaléga, and St. Brandon (Cargados Carajos shoals). The islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues, along with nearby Réunion (a French overseas department), are part of the Mascarene Islands. The main island of Mauritius, where the population is concentrated, hosts the capital and largest city, Port Louis. The country spans and has an exclusive economic zone covering approximately . The 1502 Portuguese Cantino planisphere has led some historians to speculate that Arab sailors were the first to discover the uninhabited island around 975, naming it ''Dina Arobi''. Called ''Ilha do Cirne'' or ''Ilha do Cerne'' on early Portuguese maps, the island was visited by Portuguese sailors in 1507. A Dutch fleet, under the command of Admiral Van Warwyck, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ship Astrolabe (1781)
''Astrolabe'' was a converted En flûte, flûte of the French Navy, famous for her travels with Jean-François de Galaup, comte de Lapérouse. She was built in 1781 at Le Havre as the flûte ''Autruche'' for the French Navy. In May 1785 she and her sister ship French ship Boussole (1782), ''Boussole'' (previously ''Portefaix'') were renamed, rerated as frigates, and fitted for round-the-world scientific exploration. The two ships departed from Brest, France, Brest on 1 August 1785, ''Boussole'' commanded by Lapérouse and ''Astrolabe'' under Paul Antoine Fleuriot de Langle. Disappearance The expedition vanished mysteriously in 1788 after leaving Botany Bay on 10 March 1788. Captain Peter Dillon in solved the mystery in 1827 when he found remnants of both ships at Vanikoro Island in the Solomon Islands. Local inhabitants reported that the ships had been wrecked in a storm. Survivors from one ship had been massacred, while survivors from the other had constructed their own small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
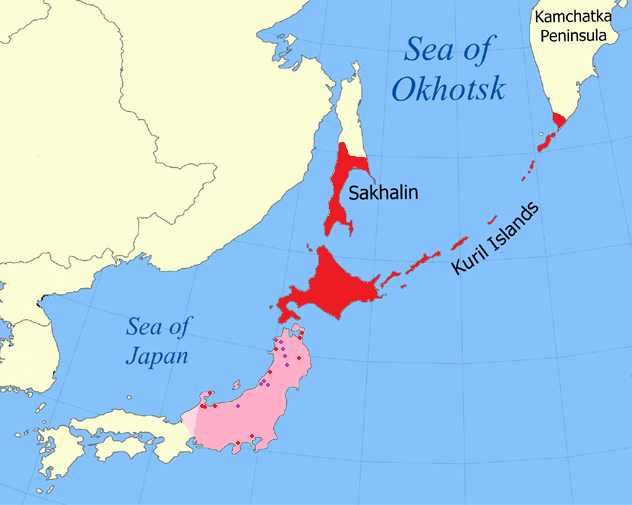
Sakhalin Island
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, p=səxɐˈlʲin) is an island in Northeast Asia. Its north coast lies off the southeastern coast of Khabarovsk Krai in Russia, while its southern tip lies north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido. An island of the West Pacific, Sakhalin divides the Sea of Okhotsk to its east from the Sea of Japan to its southwest. It is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast and is the largest island of Russia, with an area of . The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of whom are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (), which was the name of the Qing dynasty city of Aigun. The Ainu people of Sakhalin paid tribute to the Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties and accepted official appointments from them. Sometimes the relationship was forced but control from dynasties in China was loose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moneron Island
Moneron Island, (, , , Ainu: ) is a small island off Sakhalin Island. It is a part of the Russian Federation. Description Moneron has an area of about and a highest point of . It is approximately long (N/S axis) by wide, and is located from Sakhalin's port of Nevelsk and about directly southwest of Sakhalin Island itself at the northeastern end of the Sea of Japan. It is the only landmass in the whole Tatar Straits and has no permanent population. On a clear day, the Japanese Rishiri Island is visible. History The island was known as ''Todomoshiri'' ("island of sea lions") by its original Ainu inhabitants. It came under the ''daimyō'' of Matsumae clan in the 18th century and was known as Ishiyokotan; it got its current European name from a visit of the French navigator La Perouse, who named it Moneron after Paul Mérault Monneron, the chief engineer of his expedition. Paul Monneron was tasked with mapping the island named after him. The first authentic map of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Pierre Claret De Fleurieu
Charles Pierre Claret, comte de Fleurieu ( ; ) (2 July 1738 – 18 August 1810) was a French Navy officer, explorer, hydrographer and politician. He served as Minister of the Navy under Louis XVI, and was a member of the Institut de France. His brother was botanist Marc Antoine Louis Claret de La Tourrette. Life Ancien Regime Fleurieu was born in Lyon. He joined the Navy on 31 October 1755 at Toulon as a Garde-marine, aged just 13 and a half. He subsequently took part in the campaigns of the Seven Years' War — which ended in 1763 — participating in the battles of Mahon, Lagos, and Les Sablettes and rising to brigadier in the ''gardes de la marine'' company, and then '' enseigne de vaisseau''. In suggesting de Fleurieu's promotion to ensign, on 23 March 1762, the Minister wrote to the king: On 1 July 1765, he was made Enseigne de port, and on 27 July he went to Paris to study horology with Ferdinand Berthoud. He took part in a one-year sea campaign to test Berthou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |