|
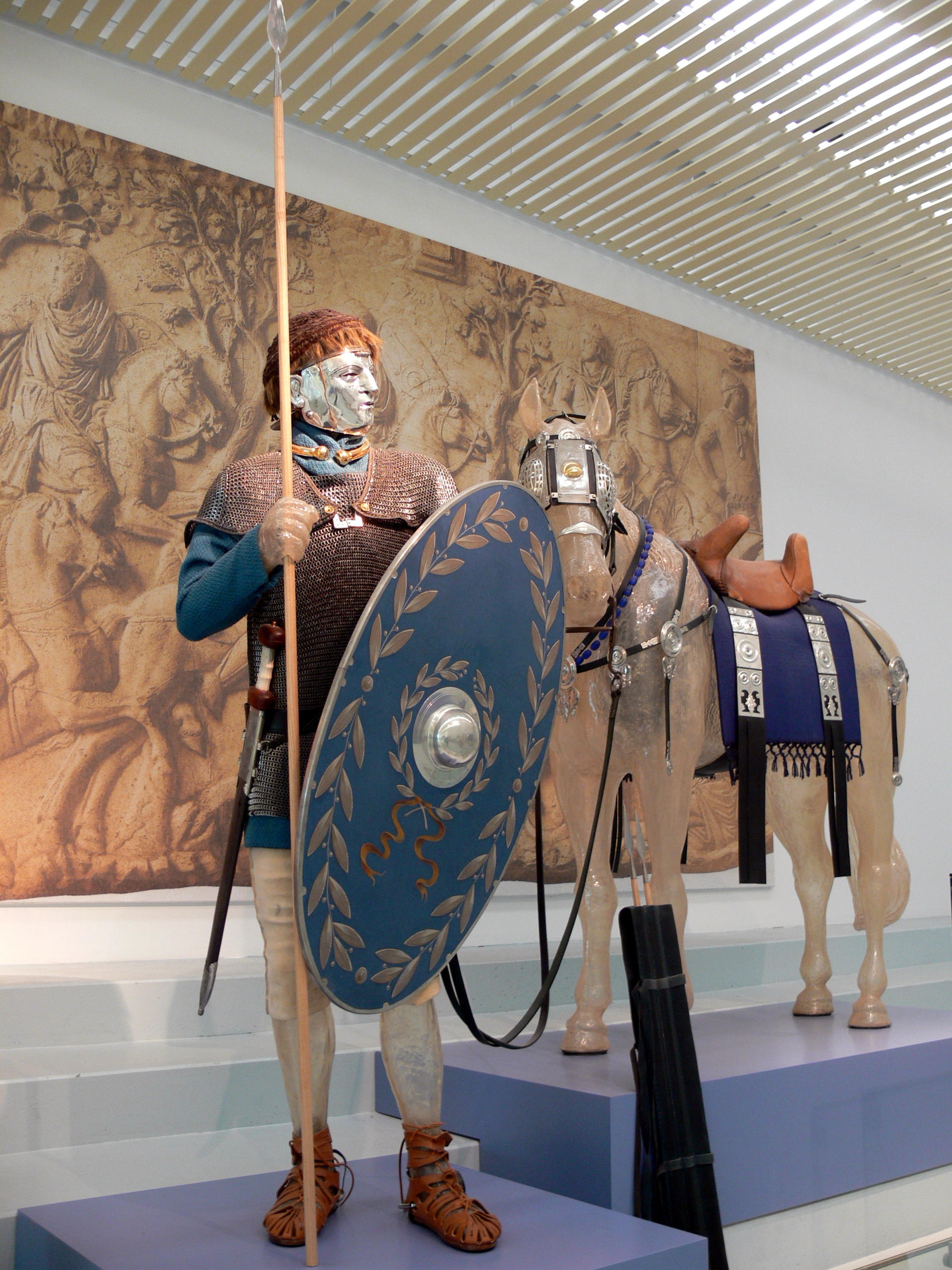
Parma (shield)
A ''parma'' or ''parmula'' (the diminutive of ''parma'') was a type of round shield used by the Roman army, especially during the later period of Roman Empire, imperial history since the 3rd century. Characteristics The ''parma'' was about 36 inches (91 cm) across (or less) and had iron in its frame, making it a very effective piece of armour. ''Parmae'' had handles and shield bosses (''umbones''). The ''parma'' was used by legionaries in the early republican period of Rome's history, by the lowest class division of the army— the ''velites''. Their equipment consisted of a ''parma'', javelin, sword and helmet. Later, the ''parma'' was replaced by the body-length ''scutum'' as ''velites'' were phased out with the so-called "Marian reforms". War use It was used mainly by Auxilia, auxiliary infantry and cavalry, with the Legionary, legionaries preferring the heavier but more protective ''scutum'', during earlier periods. It was used also by ''signiferi'' (standard bear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Army
The Roman army () served ancient Rome and the Roman people, enduring through the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (509–27 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC–AD 1453), including the Western Roman Empire (collapsed Fall of the Western Roman Empire, AD 476/480) and the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman Empire (collapsed Fall of Constantinople, AD 1453). It is thus a term that broadly spans approximately 2,206 years, during which the force underwent numerous permutations in Size of the Roman army, size, Military of ancient Rome, composition, Structural history of the Roman military, organization, Roman military equipment, equipment and Strategy of the Roman military, tactics, while conserving a core of lasting traditions. Early Roman army (c. 550 – c. 300 BC) Until , there was no "national" Roman army, but a series of clan-based war-bands which only coalesced into a united force in periods of serious external threat. Around 550 BC, during the period conventiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Teucer
In Greek mythology, King Teucer (or Teukros) (; Ancient Greek: Τεῦκρος ''Teûkros'') was said to have been the son of the river-god Scamander and the nymph Idaea. Mythology Before the arrival of Dardanus, the land that would eventually be called Dardania (and later still the Troad) was known as Teucria and the inhabitants as Teucrians, after Teucer. According to Virgil, Teucer was originally from Crete but left the island during a great famine with a third of its inhabitants. They settled near the Scamander river, named after Teucer's father, not far from the Rhaetean promontory. However, Dionysius of Halicarnassus states that Teucer had come to the Troad from Attica where he was a chief of the Xypetȇ region. In both cases he ended up in the region which would be known as the Troad. His company was said to have been greatly annoyed by a vast number of mice during their first night in the region. Teucer had previously been directed by an oracle before leaving Crete t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Weapons
European, or Europeans, may refer to: In general * ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe ** Ethnic groups in Europe ** Demographics of Europe ** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe and other Western countries * ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to the European Union ** European Union citizenship ** Demographics of the European Union In publishing * ''The European'' (1953 magazine), a far-right cultural and political magazine published 1953–1959 * ''The European'' (newspaper), a British weekly newspaper published 1990–1998 * ''The European'' (2009 magazine), a German magazine first published in September 2009 *''The European Magazine'', a magazine published in London 1782–1826 *''The New European'', a British weekly pop-up newspaper first published in July 2016 Other uses * * Europeans (band), a British post-punk group, from Bristol See also * * * Europe (other) * The Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LacusCurtius
LacusCurtius is the ancient Graeco-Roman part of a large history website, hosted as of March 2025 on a server at the University of Chicago. Starting in 1995, as of January 2004 it gave "access to more than 594 photos, 559 drawings and engravings, 69 plans, and 59 maps".Others have stated that, "as of October 2024 it had '3916 webpages, 779 photos, 772 drawings & engravings, 120 plans, 139 maps.' The overall site is the creation of William P. Thayer. Overview The main resources to be found on it include: * a number of Latin and Greek texts, usually in English translation, and often in the original language also * '' Smith's Dictionary of Greek and Roman Antiquities'' * '' Platner's Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome'' * several secondary works, mostly on Rome and Roman Britain * a photogazetteer of Roman remains and medieval churches of central Italy including the city of Rome * an often-cited online copy of Richard Hinckley Allen's '' Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clipeus
In the military of classical antiquity, a ''clipeus'' (; Ancient Greek: Aspis, ἀσπίς) was a large shield worn by the Ancient Greece, Greek Hoplite, hoplites and Ancient Rome, Romans as a piece of defensive armor, which they carried upon the arm, to protect them from the blows of their enemies. It was round in shape and in the middle was a bolt of iron, or of some other metal, with a sharp point. The ''clipeus'' was more-or-less identical to the earlier ''aspis''. In art Pliny the Elder also describes the custom of having a bust-portrait of an ancestor painted on a ''clipeus'', and having it hung in a temple or other public place. From this round Relief#Low relief or bas-relief, bas-reliefs in a Medallion (architecture), medallion on Sarcophagus, sarcophagi and in other forms are known as ''imago clipeata'' or "''clipeus'' portraits", a term usually restricted to Roman art. Roman use The ''clipeus'' was used by Romans during the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic, early re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
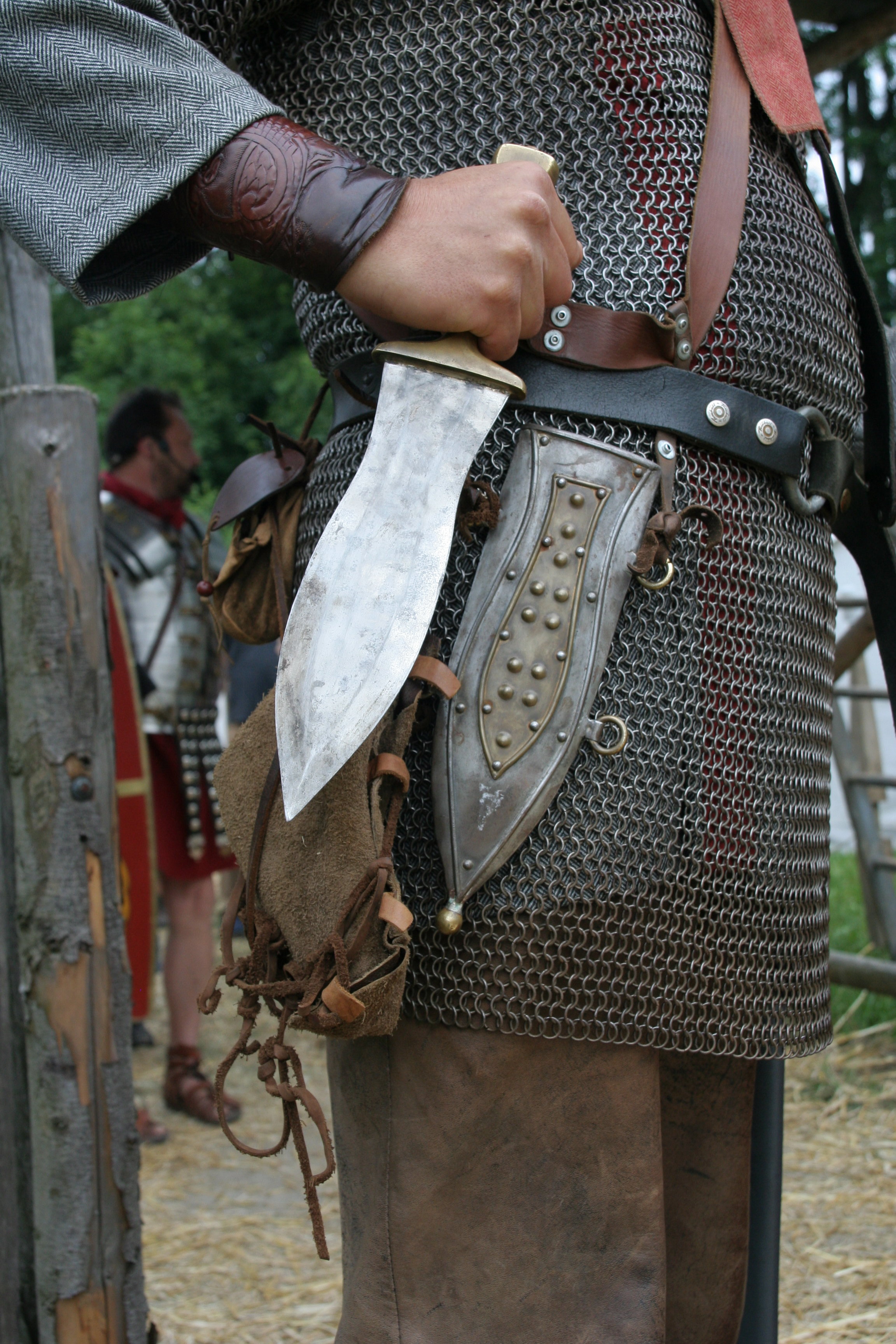
Roman Military Personal Equipment
Roman military personal equipment was produced in large numbers to established patterns, and used in an established manner. These standard patterns and uses were called the ''res militaris'' or ''disciplina''. Its regular practice during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire led to military excellence and victory. The equipment gave the Romans a very distinct advantage over their "barbarian" enemies, especially so in the case of armour. This does not mean that every Roman soldier had better equipment than the richer men among his opponents. Roman equipment was not of a better quality than that used by the majority of Rome's adversaries. Other historians and writers have stated that the Roman army's need for large quantities of "mass produced" equipment after the so-called "Marian Reforms" and subsequent civil wars led to a decline in the quality of Roman equipment compared to the earlier Republican era: Initially, they used weapons based on Greek and Etruscan models. On encou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrrhichios
The Pyrrhichios or Pyrrhike dance ("Pyrrhic dance"; Ancient Greek: πυρρίχιος or πυρρίχη, but often misspelled as πυρρίχειος or πυρήχειος) was the best known war dance of the Greeks. It was probably of Dorian origin and practiced at first solely as a training for war. According to ancient sources, it was a weapon dance. Overview Plato ('' Leges'', 815a) describes it as imitating by quick movements the ways in which blows and darts are to be avoided and also the modes in which an enemy is to be attacked. It was danced to the sound of the aulos; its time was quick and light, as is also shown by the metric foot called pyrrhic. It was described by Xenophon in his work the ''Anabasis''. In that work he writes that the dance was performed at a banquet held in Kotyora during which Greek and Paphalagonian forces settled their differences. The following is the part in which the Pyrrhic dance is mentioned: According to a tradition reported by Aristotl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cohort (military Unit)
A cohort (from the Latin ''cohors'', : ''cohortes''; see wikt:cohors for full inflection table) was a standard tactical military unit of a Roman legion. Although the standard size changed with time and situation, it was generally composed of 480 soldiers. A cohort is considered to be the equivalent of a modern military battalion. The cohort was the most important tactical unit in the Roman army. They could operate independently and offered flexibility and maneuverability, allowing the legions to quickly adapt to different combat situations. The cohort replaced the maniple. From the late second century BC and until the middle of the third century AD, ten cohorts (about 5,000 men total) made up a legion. Cohorts were named "first cohort", "second cohort", etc. The first cohort consisted of experienced legionaries, while the legionaries in the tenth cohort were less experienced. Legionary cohort A legionary cohort of the early empire consisted of six '' centuriae'', or centurie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard-bearer
A standard-bearer, also known as a colour-bearer or flag-bearer, is a person who bears an emblem known as a standard or military colours, i.e. either a type of flag or an inflexible but mobile image, which is used (and often honoured) as a formal, visual symbol of a state, prince, military unit, etc. This can either be an occasional duty, often seen as an honour (especially on parade), or a permanent charge (also on the battlefield); the second type has even led in certain cases to this task being reflected in official rank titles such as Chorąży, Ensign, Cornet, Fähnrich and Alferes/ Alférez. Role In the context of the Olympic Games, a flagbearer is the athlete who carries the flag of their country during the opening and closing ceremonies. While at present a purely ceremonial function, as far back as Roman warfare and medieval warfare bearing the standard had an important role on the battlefield. The standard-bearer acted as an indicator of where the position of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thraex
The Thraex (: Thraeces), or Thracian, was a type of Roman gladiator A gladiator ( , ) was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gladiators were volunteers who risked their ... armed in Thracians, Thracian style. His equipment included a ''Parma (shield), parmula'', a small shield (about 60 × 65 cm) that might be rectangular, square or circular; and a sica, a short sword with a curved blade like a small version of the Dacian falx, intended to maim an opponent's unarmoured back. His other armour included greaves, a protective belt above a loincloth, and a helmet with a side plume, visor and high crest. Fighting style and techniques A passage in Petronius indicates that "Thracian" was a style of gladiatorial fighting taught in training schools. An inscription records a ''doctor thraecum'', a teacher of would-be Thracians. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
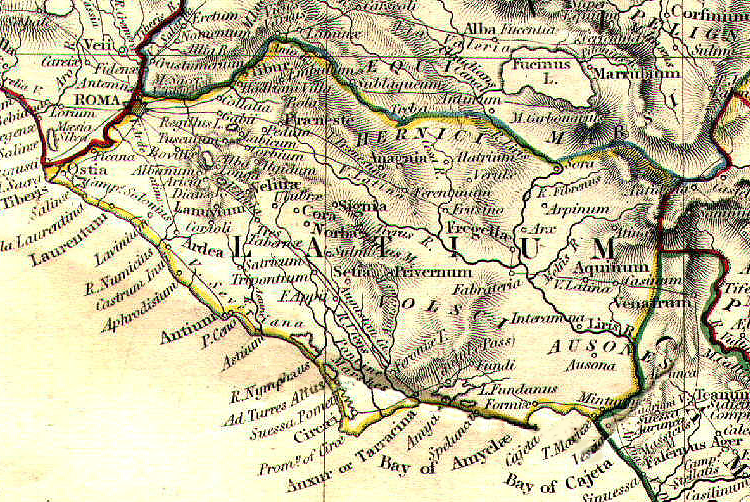
Rutuli
The Rutuli or Rutulians were an ancient people in Italy. The Rutuli were located in a territory whose capital was the ancient town of Ardea, located about 35 km southeast of Rome. Thought to have been descended from the Umbri and the Pelasgians, according to modern scholars they were more probably connected with the Etruscan or Ligurian peoples. Mythological history In Virgil's ''Aeneid'', and also according to Livy, the Rutuli are led by Turnus, a young prince to whom Latinus, king of the Latins, had promised the hand of his daughter Lavinia in marriage. When the Trojans arrived in Italy, Latinus decided to give his daughter to Aeneas instead because of instructions he had received from the gods to marry his daughter to a foreigner. Turnus was outraged and led his people as well as several other Italian tribes against the Trojans in war. Virgil's text ends when Aeneas defeats Turnus in single combat and therefore confirms his right to marry Lavinia. In some other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trojan War
The Trojan War was a legendary conflict in Greek mythology that took place around the twelfth or thirteenth century BC. The war was waged by the Achaeans (Homer), Achaeans (Ancient Greece, Greeks) against the city of Troy after Paris (mythology), Paris of Troy took Helen of Troy, Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology, and it has been Epic Cycle, narrated through many works of ancient Greek literature, Greek literature, most notably Homer's ''Iliad''. The core of the ''Iliad'' (Books II – XXIII) describes a period of four days and two nights in the tenth year of the decade-long siege of Troy; the ''Odyssey'' describes the journey home of Odysseus, one of the war's heroes. Other parts of the war are described in a Epic Cycle, cycle of epic poems, which have survived through fragments. Episodes from the war provided material for Greek tragedy and other works of Greek literature, and for Latin literature, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |