|
Paraneoplastic
A paraneoplastic syndrome is a syndrome (a set of signs and symptoms) that is the consequence of a tumor in the body (usually a cancerous one), specifically due to the production of chemical signaling molecules (such as hormones or cytokines) by tumor cells or by an immune response against the tumor. Unlike a mass effect, it is not due to the local presence of cancer cells. Paraneoplastic syndromes are typical among middle-aged to older patients, and they most commonly present with cancers of the lung, breast, ovaries or lymphatic system (a lymphoma). Sometimes, the symptoms of paraneoplastic syndromes show before the diagnosis of a malignancy, which has been hypothesized to relate to the disease pathogenesis. In this paradigm, tumor cells express tissue-restricted antigens (e.g., neuronal proteins), triggering an anti-tumor immune response which may be partially or, rarely, completely effective in suppressing tumor growth and symptoms. Patients then come to clinical attention whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Degeneration
Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration (PCD) is a paraneoplastic syndrome associated with a broad variety of tumors including lung cancer, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, Hodgkin’s lymphoma and others. PCD is a rare condition that occurs in less than 1% of cancer patients. As is the case with other paraneoplastic syndromes, PCD is believed to be due to an autoimmune reaction targeted against components of the central nervous system, mostly to Purkinje cells.S. Jarius, B. Wildemann: ''‘Medusa head ataxia’: the expanding spectrum of Purkinje cell antibodies in autoimmune cerebellar ataxia. Part 1: Anti-mGluR1, anti-Homer-3, anti-Sj/ITPR1 and anti-CARP VIII'' 2015; 12, 16(free)/ref>S. Jarius, B. Wildemann: ''‘Medusa head ataxia’: the expanding spectrum of Purkinje cell antibodies in autoimmune cerebellar ataxia. Part 2: Anti-PKC-gamma, anti-GluR-delta2, anti-Ca/ARHGAP26 and anti-VGCC'' 2015; 12, 16(free)/ref>S. Jarius, B. Wildemann: ''‘Medusa head ataxia’: the expa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
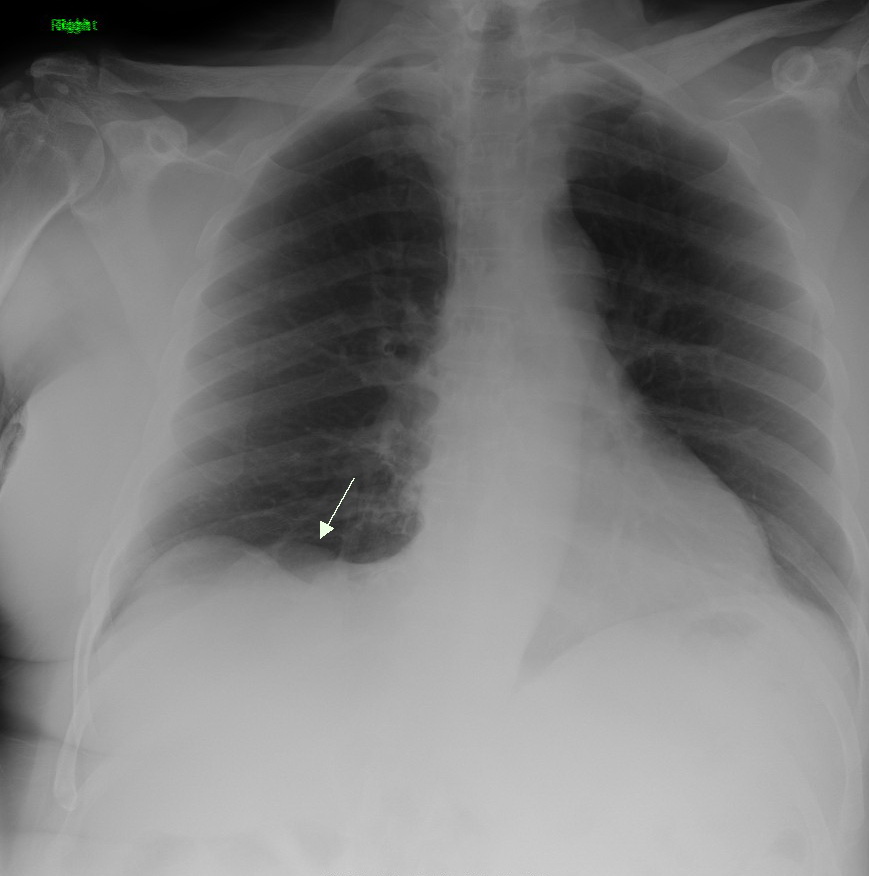
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malignant cells that originate as epithelial cells, or from tissues composed of epithelial cells. Other lung cancers, such as the rare sarcomas of the lung, are generated by the malignant transformation of connective tissues (i.e. nerve, fat, muscle, bone), which arise from mesenchymal cells. Lymphomas and melanomas (from lymphoid and melanocyte cell lineages) can also rarely result in lung cancer. In time, this uncontrolled growth can metastasize (spreading beyond the lung) either by direct extension, by entering the lymphatic circulation, or via hematogenous, bloodborne spread – into nearby tissue or other, more distant parts of the body. Most cancers that originate from within the lungs, known as primary lung cancers, are carcinomas. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambert–Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome
Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a rare autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle weakness of the limbs. Around 60% of those with LEMS have an underlying malignancy, most commonly small-cell lung cancer; it is therefore regarded as a paraneoplastic syndrome (a condition that arises as a result of cancer elsewhere in the body). It is the result of antibodies against presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels, and likely other nerve terminal proteins, in the neuromuscular junction (the connection between nerves and the muscle that they supply). The diagnosis is usually confirmed with electromyography and blood tests; these also distinguish it from myasthenia gravis, a related autoimmune neuromuscular disease. If the disease is associated with cancer, direct treatment of the cancer often relieves the symptoms of LEMS. Other treatments often used are steroids, azathioprine, which suppress the immune system, intravenous immunoglobulin, which outcompetes autoreactive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
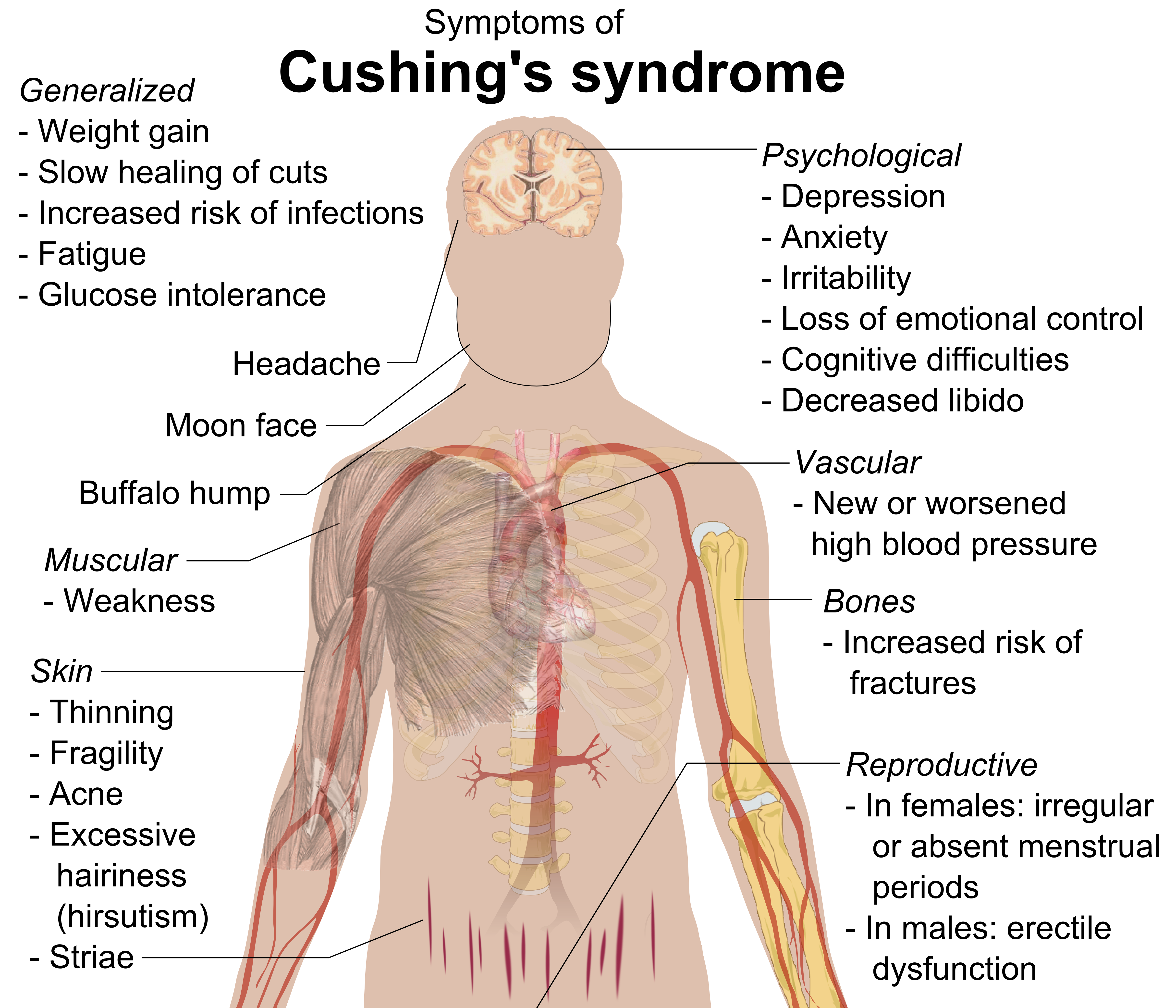
Cushing Syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a round red face, a fat lump between the shoulders, weak muscles, weak bones, acne, and fragile skin that heals poorly. Women may have more hair and irregular menstruation. Occasionally there may be changes in mood, headaches, and a chronic feeling of tiredness. Cushing's syndrome is caused by either excessive cortisol-like medication, such as prednisone, or a tumor that either produces or results in the production of excessive cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cases due to a pituitary adenoma are known as Cushing's disease, which is the second most common cause of Cushing's syndrome after medication. A number of other tumors, often referred to as ectopic due to their placement outside the pituitary, may also cause Cushing's. Some of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as '' Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinoid Syndrome
Carcinoid syndrome is a paraneoplastic syndrome comprising the signs and symptoms that occur secondary to carcinoid tumors. The syndrome includes flushing and diarrhea, and less frequently, heart failure, vomiting and bronchoconstriction. It is caused by endogenous secretion of mainly serotonin and kallikrein. Signs and symptoms The carcinoid syndrome occurs in approximately 5% of carcinoid tumors and becomes manifest when vasoactive substances from the tumors enter the systemic circulation escaping hepatic degradation. If the primary tumor is from the gastrointestinal tract (hence releasing serotonin into the hepatic portal circulation), carcinoid syndrome generally does not occur until the disease is so advanced that it overwhelms the liver's ability to metabolize the released serotonin. * Flushing: The most important clinical finding is flushing of the skin, usually of the head and the upper part of thorax. * Diarrhea: It may be associated with abdominal cramping. This sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous tumor of an ovary. It may originate from the ovary itself or more commonly from communicating nearby structures such as fallopian tubes or the inner lining of the abdomen. The ovary is made up of three different cell types including epithelial cells, germ cells, and stromal cells. When these cells become abnormal, they have the ability to divide and form tumors. These cells can also invade or spread to other parts of the body. When this process begins, there may be no or only vague symptoms. Symptoms become more noticeable as the cancer progresses. These symptoms may include bloating, vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, abdominal swelling, constipation, and loss of appetite, among others. Common areas to which the cancer may spread include the lining of the abdomen, lymph nodes, lungs, and liver. The risk of ovarian cancer increases with age. Most cases of ovarian cancer develop after menopause. It is also more common in women who have ovulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ónkos''), meaning "tumor", "volume" or "mass". Oncology is concerned with: * The diagnosis of any cancer in a person (pathology) * Therapy (e.g. surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other modalities) * Follow-up of cancer patients after successful treatment * Palliative care of patients with terminal malignancies * Ethics, Ethical questions surrounding cancer care * Screening (medicine), Screening efforts: ** of populations, or ** of the relatives of patients (in types of cancer that are thought to have a hereditary basis, such as breast cancer) Diagnosis Medical histories remain an important screening tool: the character of the complaints and nonspecific symptoms (such as Fatigue (physical), fatigue, weight loss, unexplained anemia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune Response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which could cause serious problems to the health of the host organism if not cleared from the body. There are two distinct aspects of the immune response, the innate and the adaptive, which work together to protect against pathogens. The innate branch—the body's first reaction to an invader—is known to be a non-specific and quick response to any sort of pathogen. Components of the innate immune response include physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes, immune cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, and monocytes, and soluble factors including cytokines and complement. On the other hand, the adaptive branch is the body's immune response which is catered against specific antigens and thus, it takes longer to activate the components in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using values between in humans. The increase in set point triggers increased muscle contractions and causes a feeling of cold or chills. This results in greater heat production and efforts to conserve heat. When the set point temperature returns to normal, a person feels hot, becomes flushed, and may begin to sweat. Rarely a fever may trigger a febrile seizure, with this being more common in young children. Fevers do not typically go higher than . A fever can be caused by many medical conditions ranging from non-serious to life-threatening. This includes viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections—such as influenza, the common cold, meningitis, urinary tract infections, appendicitis, Lassa, COVID-19, and malaria. Non-infectious cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Sign
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pain or pains in the body. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or abnormal physiological state that may be detected during a physical examination, examining the patient history, or diagnostic procedure. These signs are visible or otherwise detectable such as a rash or bruise. Medical signs, along with symptoms, assist in formulating diagnostic hypothesis. Examples of signs include elevated blood pressure, nail clubbing of the fingernails or toenails, staggering gait, and arcus senilis and arcus juvenilis of the eyes. Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperaldosteronism
Hyperaldosteronism is a medical condition wherein too much aldosterone is produced by the adrenal glands, which can lead to lowered levels of potassium in the blood (hypokalemia) and increased hydrogen ion excretion ( alkalosis). This cause of mineralocorticoid excess is primary hyperaldosteronism reflecting excess production of aldosterone by adrenal zona glomerulosa. Bilateral micronodular hyperplasia is more common than unilateral adrenal adenoma. Signs and symptoms It can be asymptomatic, but these symptoms may be present: * Fatigue * Headache * High blood pressure * Hypokalemia * Hypernatraemia * Hypomagnesemia * Intermittent or temporary paralysis * Muscle spasms * Muscle weakness * Numbness * Polyuria * Polydipsia * Tingling * Metabolic alkalosis * Nocturia * Blurry Vision * Dizziness/Vertigo Cause The causes of primary hyperaldosteronism are adrenal hyperplasia and adrenal adenoma ( Conn's syndrome). These cause hyperplasia of aldosterone-producing cells of the adre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |