|
Paragoge
Paragoge () is the addition of a sound to the end of a word. It is a type of epenthesis. Paragoge is most often linked with the nativization of loanwords. It is particularly common in Brazilian Portuguese, not only in loanwords but also in word derivation. It is also present in the accents of many Brazilians while speaking foreign languages such as English. Some languages have undergone paragoge as a sound change, and modern forms are longer than the historical forms they are derived from. Italian ''sono'' 'I am', from Latin ''sum'', is an example. Sometimes, as above, the paragogic vowel is an echo vowel, such as Proto-Oceanic ''*saqat'' "bad" > Uneapa ''zaɣata''. Etymology The word ''paragoge'' is taken from 'deviation; language alteration': from παρα- prefix ''para-'' 'beside' and ἀγωγή ''agogē'' 'bringing in'. In loanwords Some languages add a sound to the end of a loanword when it would otherwise end in a forbidden sound. Some languages add a grammatical en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echo Vowel
An echo vowel, also known as a synharmonic vowel, is a paragogic vowel that repeats the final vowel in a word in speech. For example, in Chumash, when a word ends with a glottal stop and comes at the end of an intonation unit, the final vowel is repeated after the glottal stop but is whispered and faint, as in for "arrow" (written ''ya).'' Languages In modern Sanskrit, echo vowels are often added in pronunciation to the visarga. In Rukai, an Austronesian language, vowels are pronounced as full vowels but are predictable and disappear when they are under reduplication or when a suffix beginning with /a/ is added to the word: Similarly, in the related Uneapa, echo vowels are added after a Proto-Oceanic final consonant, such as ''*Rumaq'' "house" > ''rumaka''. The Makassaric languages also occurs the echo vowels with stems ending in final /r/, /l/ or /s/. E.g. /botol/ "bottle" is realized as ''bótolo'' in Selayar and Coastal Konjo, and as ''bótoloʔ'' in Makassares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epenthesis
In phonology, epenthesis (; Greek ) means the addition of one or more sounds to a word, especially in the first syllable ('' prothesis''), the last syllable ('' paragoge''), or between two syllabic sounds in a word. The opposite process in which one or more sounds are removed is referred to as syncope or elision. Etymology The word ''epenthesis'' comes from and ''en-'' and ''thesis'' . Epenthesis may be divided into two types: excrescence for the addition of a consonant, and for the addition of a vowel, svarabhakti (in Sanskrit) or alternatively anaptyxis (). Uses Epenthesis arises for a variety of reasons. The phonotactics of a given language may discourage vowels in hiatus or consonant clusters, and a consonant or vowel may be added to help pronunciation. Epenthesis may be represented in writing, or it may be a feature only of the spoken language. Separating vowels A consonant may be added to separate vowels in hiatus, as is the case with linking and intrusive R in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latvian Language
Latvian (, ), also known as Lettish, is an East Baltic languages, East Baltic language belonging to the Indo-European language family. It is spoken in the Baltic region, and is the language of the Latvians. It is the official language of Latvia as well as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 1.5 million native Latvian speakers in Latvia and 100,000 abroad. Altogether, 2 million, or 80% of the population of Latvia, spoke Latvian in the 2000s, before the total number of inhabitants of Latvia slipped to 1.8 million in 2022. Of those, around 1.16 million or 62% of Latvia's population used it as their primary language at home, though excluding the Latgale Planning Region, Latgale and Riga Planning Region, Riga regions it is spoken as a native language in villages and towns by over 90% of the population. As a Baltic languages, Baltic language, Latvian is most closely related to neighboring Lithuanian language, Lithuanian (as well as Old Prussian language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalan Language
Catalan () is a Western Romance languages, Western Romance language and is the official language of Andorra, and the official language of three autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous communities in eastern Spain: Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and the Valencian Community, where it is called ''Valencian language, Valencian'' (). It has semi-official status in the Italy, Italian ''comune'' of Alghero, and it is spoken in the Pyrénées-Orientales department of France and in two further areas in eastern Spain: the La Franja, eastern strip of Aragon and the Carche area in the Region of Murcia. The Catalan-speaking territories are often called the or "Països Catalans". The language evolved from Vulgar Latin in the Middle Ages around the eastern Pyrenees. It became the language of the Principality of Catalonia and the kingdoms of kingdom of Valencia, Valencia and Kingdom of Majorca, Mallorca, being present throughout the Mediterranean. Replaced by Spanish as a language of gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Language
Italian (, , or , ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family. It evolved from the colloquial Latin of the Roman Empire. Italian is the least divergent language from Latin, together with Sardinian language, Sardinian. It is spoken by about 68 million people, including 64 million native speakers as of 2024. Italian is an official language in Languages of Italy, Italy, Languages of San Marino, San Marino, Languages of Switzerland, Switzerland (Ticino and the Grisons), and Languages of Vatican City, Vatican City; it has official Minority language, minority status in Minority languages of Croatia, Croatia, Slovene Istria, Romania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and the municipalities of Santa Teresa, Espírito Santo, Santa Tereza, Encantado, Rio Grande do Sul, Encantado, and Venda Nova do Imigrante in Languages of Brazil#Language co-officialization, Brazil. Italian is also spoken by large Italian diaspora, immigrant and expatriate communities in the Americas and Austral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austronesian Languages
The Austronesian languages ( ) are a language family widely spoken throughout Maritime Southeast Asia, parts of Mainland Southeast Asia, Madagascar, the islands of the Pacific Ocean and Taiwan (by Taiwanese indigenous peoples). They are spoken by about 328 million people (4.4% of the world population). This makes it the fifth-largest language family by number of speakers. Major Austronesian languages include Malay (around 250–270 million in Indonesia alone in its own literary standard named " Indonesian"), Javanese, Sundanese, Tagalog (standardized as Filipino), Malagasy and Cebuano. According to some estimates, the family contains 1,257 languages, which is the second most of any language family. In 1706, the Dutch scholar Adriaan Reland first observed similarities between the languages spoken in the Malay Archipelago and by peoples on islands in the Pacific Ocean. In the 19th century, researchers (e.g. Wilhelm von Humboldt, Herman van der Tuuk) started to apply the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
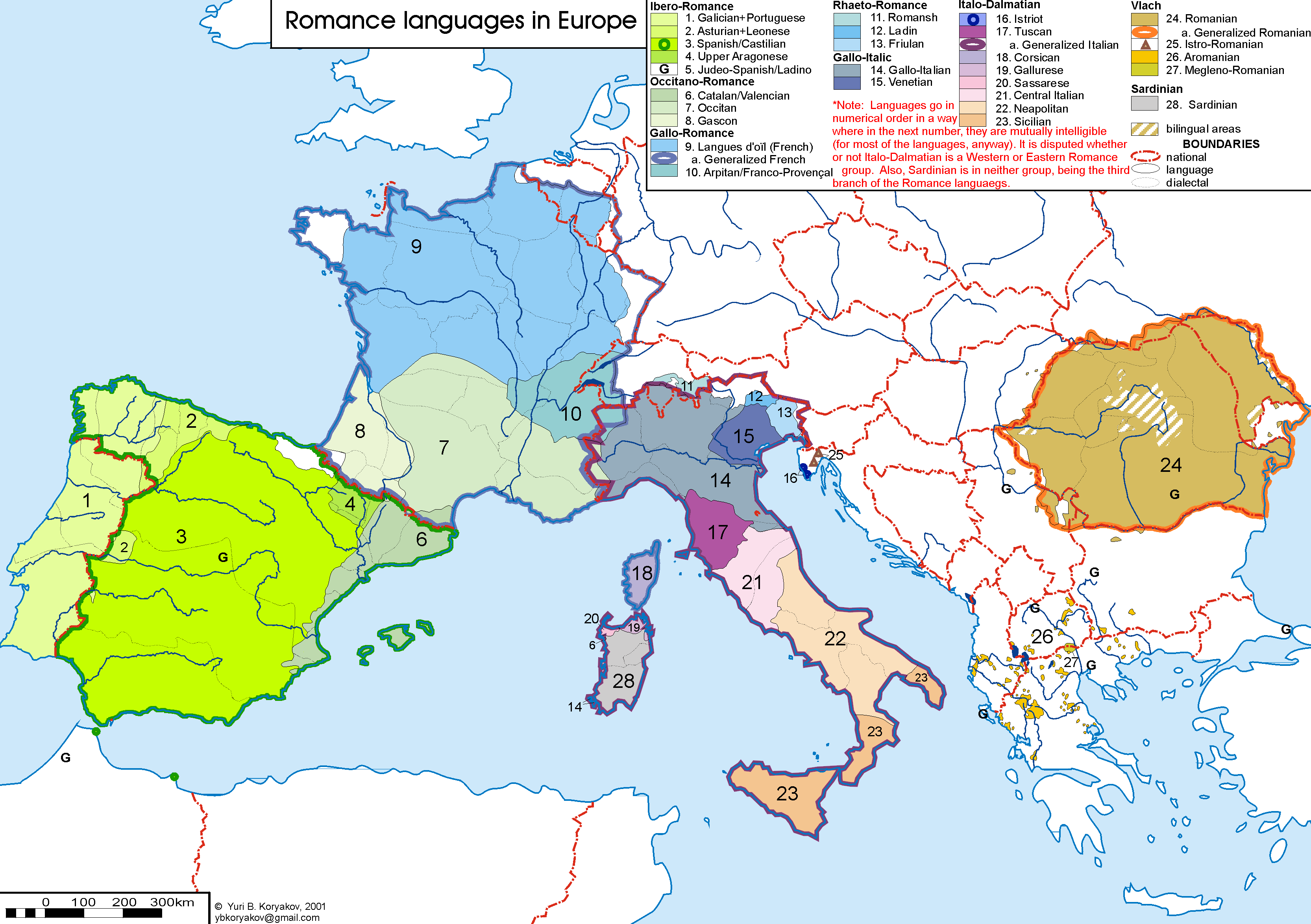
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierogi
Pierogi ( ; ) are filled dumplings made by wrapping Leavening, unleavened dough around a Stuffing, filling and cooked in boiling water. They are occasionally flavored with a savory or sweet garnish. Typical fillings include potato, cheese, Quark (dairy product), quark, sauerkraut, ground meat, Edible mushroom, mushrooms, fruits, or Berry, berries. Savory pierogi are often served with a topping of sour cream, fried onions, or both. Pierogi varieties are associated with the cuisines of Central European cuisine, Central, Eastern European cuisine, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. Dumplings most likely originated in Asia and came to Europe via trade in the Middle Ages. However, the dish itself dates back to at least 1682, when Poland's first cookbook, ''Compendium ferculorum, albo Zebranie potraw'', was published. The widely used English name pierogi was derived from Polish language, Polish. In Ukraine and parts of Canadian cuisine, Canada they are known under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Plural
A double plural is a plural form to which an extra suffix has been added, mainly because the original plural suffix (or other variation) had become unproductive and therefore irregular. So the form as a whole was no longer seen as a plural, an instance of morphological leveling. For example, if "geese" (the plural) became the word for "goose" (the singular) in a future version of English, a word ''geeses'' might become the licit plural form. Likewise, "peoples" in English currently means "nations or ethnic groups" but is sometimes used informally as a plural of "person" (eg, "these peoples standing here"). Examples English and Dutch Examples of this can be seen in the history of English and Dutch. Historically, the general English plural markers were not only ''-s'' or ''-en'' but also (in certain specific declensions) ''-ra'' and ''-ru'' (which is still rather general today in German under the form ''-er''). The ancient plural of ''child'' was "cildra/cildru", to which an ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (, , or simply , ) is a West Slavic languages, West Slavic language of the Lechitic languages, Lechitic subgroup, within the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is written in the Latin script. It is primarily spoken in Poland and serves as the official language of the country, as well as the language of the Polish diaspora around the world. In 2024, there were over 39.7 million Polish native speakers. It ranks as the sixth-most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional Dialects of Polish, dialects. It maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, Honorifics (linguistics), honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (, , , , , , , , ) to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet. The traditional set compri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potato Chip
Potato chips (North American English and Australian English; often just chip) or crisp (British English and Hiberno-English) are thin slices of potato (or a thin deposit of potato paste) that has been deep frying, deep fried, baking, baked, or air frying, air fried until crunchy. They are commonly served as a snack, side dish, or appetizer. The basic chips are cooked and Edible salt, salted; additional varieties are manufactured using various flavorings and ingredients including herbs, spices, cheeses, other natural flavors, artificial flavours, artificial flavors, and Food additive, additives. Potato chips form a large part of the snack food and convenience food market in Western countries. The global potato chip market generated total revenue of US$16.49 billion in 2005. This accounted for 35.5% of the total savory snacks market in that year (which was $46.1 billion overall). History The earliest known recipe for potato chips is in the English cook William Kitchiner's b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |