|
Paracosm
A paracosm is a detailed imaginary world thought generally to originate in childhood. The creator of a paracosm has a complex and deeply felt relationship with this subjective universe, which may incorporate real-world or imaginary characters and conventions. Commonly having its own geography, history, and language, it is an experience that is often developed during childhood and continues over a long period of time, months or even years, as a sophisticated reality that can last into adulthood. Origin and usage The concept was first described by Robert Silvey, with later research by British psychiatrist Stephen A. MacKeith and British psychologist David Cohen. The term "paracosm" was coined by Ben Vincent, a participant in Silvey's 1976 study and a self-professed paracosmist. Psychiatrists Delmont Morrison and Shirley Morrison mention paracosms and "paracosmic fantasy" in their book ''Memories of Loss and Dreams of Perfection'', in the context of people who have suffered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imaginary Friend
Imaginary friends (also known as pretend friends, invisible friends or made-up friends) are a psychological and a social phenomenon where a friendship or other interpersonal relationship takes place in the imagination rather than physical reality. Although they may seem real to their creators, children usually understand that their imaginary friends are not real. The first studies focusing on imaginary friends are believed to have been conducted during the 1890s. There is little research about the concept of imaginary friends in children's imaginations. Klausen and Passman (2007) report that imaginary companions were originally described as being supernatural creatures and spirits that were thought to connect people with their past lives. Adults in history have had entities such as household gods, guardian angels, and muses that functioned as imaginary companions to provide comfort, guidance and inspiration for creative work. It is possible the phenomenon appeared among childre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
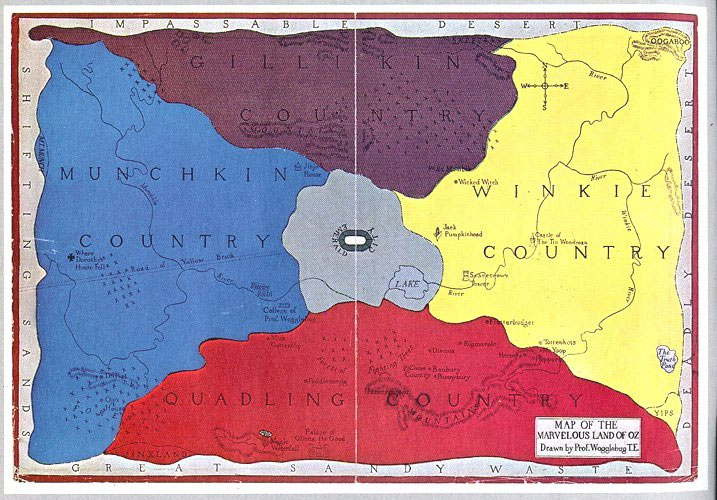
Fictional Universe
A fictional universe, also known as an imagined universe or a constructed universe, is the internally consistent fictional setting used in a narrative or a work of art. This concept is most commonly associated with works of fantasy and science fiction, and can be found in various forms such as novels, comics, films, television shows, video games, and other creative works. In science fiction, a fictional universe may be a remote alien planet or galaxy with little apparent relationship to the real world (as in '' Star Wars''). In fantasy, it may be a greatly fictionalized or invented version of Earth's distant past or future (as in ''The Lord of the Rings''). Fictional continuity In a 1970 article in '' CAPA-alpha'', comics historian Don Markstein defined the fictional ''universe'' as meant to clarify the concept of fictional continuities. According to the criteria he imagined: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agency (sociology)
In social science, agency is the capacity of individuals to have the power and resources to fulfill their potential. Social structure consists of those factors of influence (such as social class, religion, gender, ethnicity, ability, customs, etc.) that determine or limit agents and their decisions. The influences from structure and agency are debated—it is unclear to what extent a person's actions are constrained by social systems. One's agency is one's independent capability or ability to act on one's will. This ability is affected by the cognitive belief structure which one has formed through one's experiences, and the perceptions held by the society and the individual, of the structures and circumstances of the environment one is in and the position one is born into. Disagreement on the extent of one's agency often causes conflict between parties, e.g. parents and children. History The overall concept of agency has existed since the Enlightenment where there was debat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Trollope
Anthony Trollope ( ; 24 April 1815 – 6 December 1882) was an English novelist and civil servant of the Victorian era. Among the best-known of his 47 novels are two series of six novels each collectively known as the ''Chronicles of Barsetshire'' and the Palliser novels, as well as his longest novel, ''The Way We Live Now''. His novels address political, social, and gender issues and other topical matters. Trollope's literary reputation dipped during the last years of his life, but he regained somewhat of a following by the mid-20th century. Biography Anthony Trollope was the son of barrister Thomas Anthony Trollope and the novelist and travel writer Frances Milton Trollope. Though a clever and well-educated man and a Fellow of New College, Oxford, Thomas Trollope failed at the Bar due to his bad temper. Ventures into farming proved unprofitable, and his expectations of inheritance were dashed when an elderly, childless uncle remarried and fathered children. Thomas Trollope was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Child Prodigy
A child prodigy is, technically, a child under the age of 10 who produces meaningful work in some domain at the level of an adult expert. The term is also applied more broadly to describe young people who are extraordinarily talented in some field. The term ''wunderkind'' (from German ''Wunderkind''; literally "wonder child") is sometimes used as a synonym for child prodigy, particularly in media accounts. ''Wunderkind'' also is used to recognise those who achieve success and acclaim early in their adult careers. Generally, prodigies in all domains are suggested to have relatively elevated Intelligence quotient, IQ, extraordinary memory, and exceptional attention to detail. Significantly, while math and physics prodigies may have higher IQs, this may be an impediment to art prodigies. Examples Chess prodigies Deliberate practice K. Anders Ericsson emphasised the contribution of deliberate practice over their innate talent to prodigies' exceptional performance in chess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbara Newhall Follett
Barbara Newhall Follett . Columbia University Archive Collection. Retrieved February 17, 2012. (March 4, 1914 – disappeared December 7, 1939) was an American novelist. Her , '' The House Without Windows'', was published in January 1927, when she was twelve years old. Her next novel, ''The Voyage of the Norman D.'', received critical acclaim when she was fourteen. In December 1939, aged 25, Follet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Jameson
Anna Brownell Jameson (17 May 179417 March 1860) was an Anglo-Irish art historian whose work spanned art and literary criticism, philosophy, travel writing, and feminism. She became very well known for her extensive writings. Jameson was connected to some of the most prominent names of the period including Joanna Baillie, Fanny Kemble, Elizabeth Barrett-Browning and Robert Browning, Harriet Martineau, Ottilie von Goethe (the daughter-in-law of Goethe), Lady Byron, Harriet Hosmer, Ada Lovelace, Charles and Elizabeth Eastlake, and Barbara Leigh Smith Bodichon. Biography Anna Murphy was born in Dublin, 17 May 1794. Her father, Denis Brownell Murphy (died 1842), was a miniaturist and enamel painter. He moved to England in 1798 with his wife Johanna and four daughters (of whom Anna was the eldest) and eventually settled at Hanwell, London. At sixteen years of age, she became governess in the family of Charles Paulet, 13th Marquess of Winchester. In 1821 she was en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Heath Malkin
Benjamin Heath Malkin ( – ) was a British scholar and writer notable for his connection to the artist and poet William Blake. Career and education Malkin was born in London, the son of Thomas Malkin of the parish of St Mary-le-Bow and his wife Mary Heath, daughter of Holland Heath. He was educated at Harrow School, and became a pensioner at Trinity College, Cambridge in 1788. He matriculated there in 1792, graduating B.A. the same year; he graduated M.A. in 1802. He was incorporated at St Mary Hall, Oxford in 1810, where he was awarded the degrees of B.C.L. and D.C.L. that year. In 1795 he published ''Essays on Subjects connected with Civilization'' (C. Dilly, London). From 1809 to 1828 he was headmaster of Bury St Edmunds Free School, where he taught a number of pupils who would later go on to become Cambridge Apostles. In 1829, Malkin became the first professor of history in the newly formed London University. During his scholarly career he published both historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondal Poems
Gondal may refer to: Places * Gondal, India, a city in Gujarat, India ** Gondal Assembly constituency ** Gondal railway station * Gondal State, a princely state of the Bombay Presidency in colonial India * Gondal, Attock, a town in Pakistan * Gondal Bar, a region in Punjab, Pakistan * Gondal, Somalia, an ancient town in Somalia * Gondal (fictional country) Gondal is an imaginary world or paracosm created by Emily Brontë and Anne Brontë that is found in their juvenilia. Gondal is an island in the North Pacific, just north of the island Gaaldine. It included at least four kingdoms: Gondal, An ..., a fictional country created by Emily and Anne Brontë People * Gondal (clan), a clan of Jats and a surname in Pakistan * Nazar Muhammad Gondal (born 1950), Pakistani politician * Usman Gondal (born 1987), Pakistani footballer * Vishal Gondal (born 1976), Indian entrepreneur See also * Gondal Gilan, a village in Iran * Gondalpara, a town in West Bengal, India * Gunda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hartley Coleridge
Hartley Coleridge, possibly David Hartley Coleridge (19 September 1796 – 6 January 1849), was an English poet, biographer, essayist, and teacher. He was the eldest son of the poet Samuel Taylor Coleridge. His sister Sara Coleridge was a poet and translator, and his brother Derwent Coleridge was a scholar and author. Hartley was named after the philosopher David Hartley. Biography Early life Hartley was born in Clevedon, a small village near Bristol. His father mentions Hartley in several poems, including the well-known '' Frost at Midnight'', where he addresses him as his "babe so beautiful", and in his '' The Nightingale: A Conversation Poem'', both of which are concerned with young Hartley's future. In the autumn of 1800 Samuel Taylor Coleridge moved his wife and young son Hartley to the Lake District. They took a home in the vale of Derwentwater, on the bank of the Greta River, about a mile away from Greta Hall, Keswick, the future home of the poet Robert Southey, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avatar (2009 Film)
''Avatar'' is a 2009 Epic film, epic science fiction film co-produced, co-edited, written, and directed by James Cameron. It features an ensemble cast including Sam Worthington, Zoe Saldaña, Zoe Saldana, Stephen Lang, Michelle Rodriguez, and Sigourney Weaver. The first installment in the Avatar (franchise), ''Avatar'' film series, it is set in the mid-22nd century, when humans are colonizing Fictional universe of Avatar#Astronomy and geology, Pandora, a lush habitable moon of a gas giant in the Alpha Centauri star system, in order to mine the valuable Unobtainium, unobtanium, a room-temperature superconductor mineral. The expansion of the mining colony threatens the continued existence of a local tribe of Fictional universe of Avatar#Na'vi, Na'vi, a humanoid species indigenous to Pandora. The title of the film refers to a Genetic engineering, genetically engineered Na'vi body Brain–computer interface, operated from the brain of a remotely located human that is used to Telep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |