|
Palokkajärvi
Palokkajärvi () is a lake in Jyväskylä, Finland, covering an area of . The lake is mostly open in shape, with the exception of the Tyyppälänlahti bay in its eastern part extending towards Seppälänkangas. There is also a single island called Palosaari in its mid-western part. Palokkajärvi is surrounded by urban area, including the districts of Palokka in the north and Lohikoski in the south. The district of Mannila, Jyväskylä, Mannila is located to its west, however, its buildings are separated from the lake by the Finnish national road 4, national road 4, the longest highway in the country. Etymology The names of Palokkajärvi and Palokka are clearly connected, but whether the settlement was named after the lake or vice versa is unclear. In either case, the name is taken to refer to slash-and-burn agriculture (cf. "to burn"), and may have been given either by early settlers or hunters preceding permanent settlement in the area. Palokka was first mentioned as a villag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuomiojärvi
Tuomiojärvi is a lake in the city of Jyväskylä, Central Finland. The 298-hectare lake has 7 islands. The average depth of the lake is 3.5 metres and the maximum depth is 13.1 metres. The lake has five official beach areas. Residential areas by the lake include Kortepohja, Viitaniemi, Taulumäki, Mannila and Haukkala. There are two similarly named lakes within the catchment area of Tuomiojärvi: Ylä-Tuomiojärvi and Vähä Tuomiojärvi, both of which are located near Saarenmaa. Etymology The name of Tuomiojärvi appears to contain the word , meaning 'sentence' or 'judgment'. According to linguist Viljo Nissilä, the name of the lake may refer to local court hearings regarding hunting grounds, as minor conflicts such as theft were often settled by the place where they had happened. Geography Tuomiojärvi is located in the Kymijoki main catchment area and is part of its second-order Päijänne basin. The catchment area of Tuomiojärvi covers an area of , of which 57. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palokka
Palokka is a district of Jyväskylä and the largest area by population in the Palokka-Puuppola ward. Until 31 December 2008, it was a part of Jyväskylän maalaiskunta. The greater Palokka area has a population of ~14000. Palokka is approximately 5 km to the north of central Jyväskylä. The national road 4 goes through Palokka. Palokka is one of the fastest-growing parts of Jyväskylä. Geography Residential areas Officially, Palokka includes the following residential areas: The exact borders of Palokka are not well-defined. More commonly Palokka refers to the urbanized area and does not include the settlements on its outskirts, such as Saarenmaa. Lakes Palokka is located by the Alvajärvi and Palokkajärvi. The river Pappilanjoki connects the two lakes. The river Karjujoki connects Tyyppälänjärvi to Palokkajärvi. History Name The name ''Palokka'' refers to slash-and-burn agriculture (''palaa'' = to burn). Similar toponyms exist elsewhere in Finland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jyväskylä
Jyväskylä () is a city in Finland and the regional capital of Central Finland. It is located in the Finnish Lakeland. The population of Jyväskylä is approximately , while the Jyväskylä sub-region, sub-region has a population of approximately . It is Finland's most populous Municipalities of Finland, municipality, and fifth most populous List of urban areas in Finland by population, urban area. Jyväskylä is located about northeast of Tampere, the third largest city in Finland; and about north of Helsinki, the national capital. The Jyväskylä sub-region includes Jyväskylä, Hankasalmi, Laukaa, Muurame, Petäjävesi, Toivakka, and Uurainen. Other neighbouring municipalities of Jyväskylä are Joutsa, Jämsä and Luhanka. Jyväskylä is the largest city in the Central Finland and Finnish Lakeland region. Jyväskylä was one of the fastest growing cities in Finland during the 20th century; in 1940, there were only 8,000 inhabitants in Jyväskylä. Elias Lönnrot, the auth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jyväsjärvi
Lake Jyväsjärvi () is a lake situated in the centre of Jyväskylä in Finland. The lake is sometimes seen as a part of the Päijänne, as both lakes are on the same level ( from sea level) and are connected by the Äijälänsalmi strait. Parts of Jyväsjärvi have been filled many times to gain more land for the growing city of Jyväskylä. Mattilanniemi and Ylistö, two campuses of the University of Jyväskylä, are situated on the western shores of the lake. Two bridges cross the lake, connecting Ylistönrinne and Kuokkala to the city centre. The harbour of Jyväskylä is located in Lutakko, near the Kuokkala bridge. During winter, a long ice skating track is created on the surface of the lake. There is also a path, popular among pedestrians, cyclists, joggers and rollerbladers, going around the lake. Naming and etymology The name of Jyväsjärvi is connected to that of Jyväskylä itself, as well as to that of ''Jyväsjoki'', a historical name for a watercourse begin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutrophic Lake
The Trophic State Index (TSI) is a classification system designed to rate water bodies based on the amount of biological productivity they sustain. Although the term "trophic index" is commonly applied to lakes, any surface water body may be indexed. The TSI of a water body is rated on a scale from zero to one hundred. Under the TSI scale, water bodies may be defined as: * oligotrophic (TSI 0–40, having the least amount of biological productivity, "good" water quality); * mesotrophic (TSI 40–60, having a moderate level of biological productivity, "fair" water quality); or * eutrophic to hypereutrophic (TSI 60–100, having the highest amount of biological productivity, "poor" water quality). The quantities of nitrogen, phosphorus, and other biologically useful nutrients are the primary determinants of a water body's TSI. Nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus tend to be limiting resources in standing water bodies, so increased concentrations tend to result in increased p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Pike
The northern pike (''Esox lucius'') is a species of carnivorous fish of the genus ''Esox'' (pikes). They are commonly found in brackish water, moderately salty and fresh waters of the Northern Hemisphere (''i.e.'' holarctic in distribution). They are known simply as a pike (Plural, : pike) in Great Britain, Ireland, most of Eastern Europe, Canada and the United States, U.S., although in the Midwestern United States, they may just be called a Northern. Pike can grow to a relatively large size. Their average length is about , with maximum recorded lengths of up to and maximum weights of . The International Game Fish Association, IGFA currently recognises a pike caught by Lothar Louis on Greffern Lake, Germany, on 16 October 1986, as the all-tackle world-record holding northern pike. Northern pike grow to larger sizes in Eurasia than in North America, and in coastal Eurasian regions than inland ones. Etymology The northern pike gets its common name from its resemblance to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zander
The zander (''Sander lucioperca''), sander or pikeperch, is a species of ray-finned fish from the Family (biology), family Percidae, which also includes perch, Gymnocephalus, ruffe and Darter (fish), darter. It is found in freshwater and brackish habitats in western Eurasia. It is a popular game fish and has been introduced to a variety of localities outside its native range. It is the type species of the genus ''Sander''. Taxonomy The zander was first formally Species description, described in 1758 as ''Perca lucioperca'' by Carolus Linnaeus in volume 1 of the tenth edition of ''Systema Naturae'' and he gave the Type locality (biology), type locality as "European lakes". When Lorenz Oken (1779–1851) created the genus ''Sander (fish), Sander'' he made ''Perca lucioperca'' its type species. The zander is part of the European clade within the genus ''Sander'' which split from a common ancestor with the North American clade, which the walleye (''S. vitreus'') and the sauger (''S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Perch
The European perch (''Perca fluviatilis''), also known as the common perch, redfin perch, big-scaled redfin, English perch, Euro perch, Eurasian perch, Eurasian river perch, Hatch, poor man's rockfish or in Anglophone parts of Europe, simply the perch, is a predatory freshwater fish native to Europe and North Asia. It is the type species of the genus '' Perca''. The perch is a popular game fish for recreational anglers, and has been widely introduced beyond its native Eurasian habitats into Australia, New Zealand and South Africa. Known locally simply as "redfin", they have caused substantial damage to native fish populations in Australia and have been proclaimed a noxious species in New South Wales. Taxonomy The first scientific description of the river perch was made by Peter Artedi in 1730. He defined the basic morphological signs of this species after studying perch from Swedish lakes. Artedi described its features, counting the fin rays scales and vertebrae of the typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
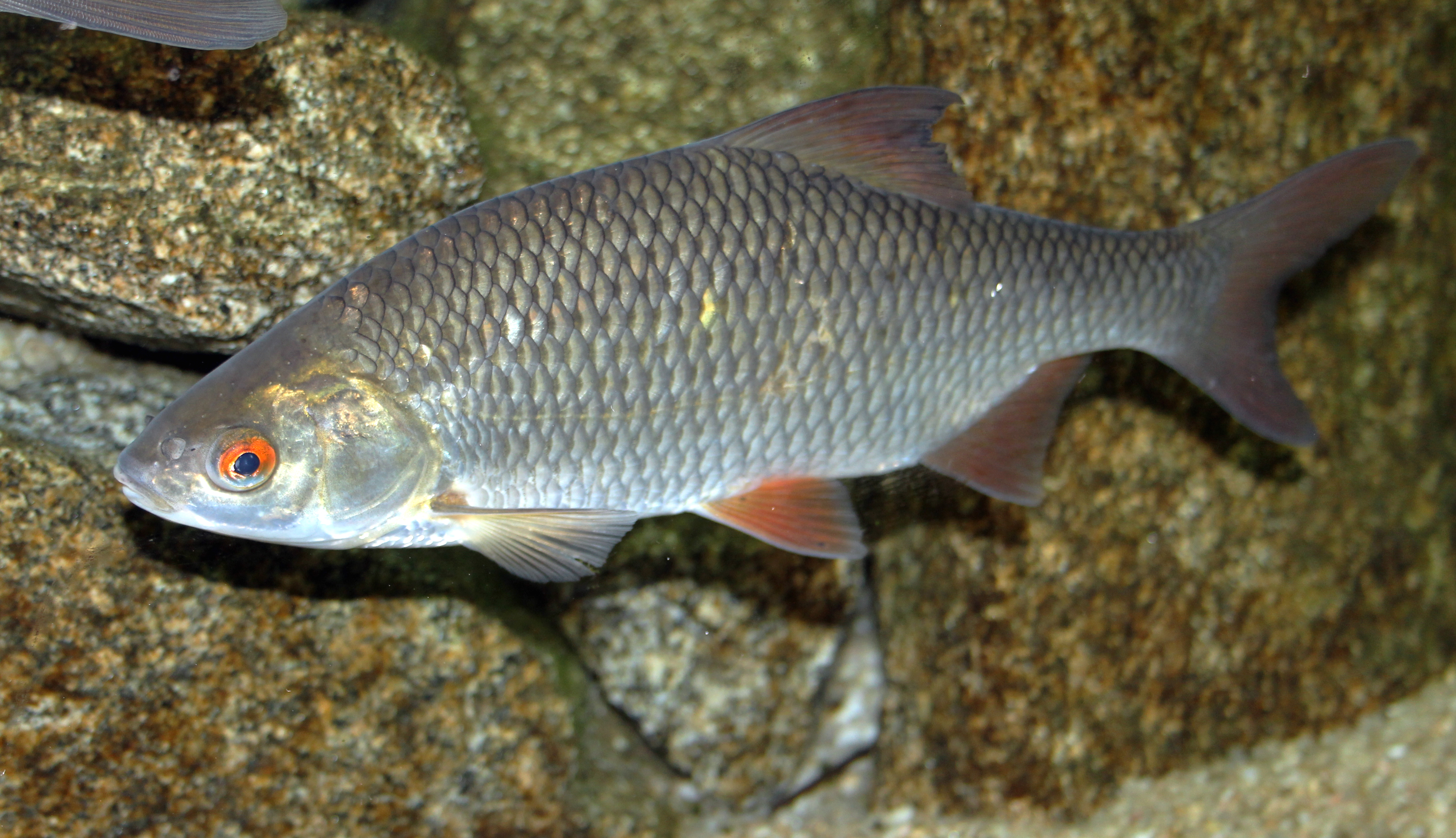
Common Roach
The roach, or rutilus roach (''Rutilus rutilus''), also known as the common roach, is a fresh- and brackish-water fish of the family Cyprinidae, native to most of Europe and western Asia. Fish called roach can be any species of the genera ''Rutilus'', '' Leucos'' and ''Hesperoleucus'', depending on locality. The plural of the term is also roach. Description The roach is a small fish, often reaching no more than about ; maximum length is . Its body has a bluish-silvery colour and becomes white at the belly. The fins are red. The number of scales along the lateral line is 39–48. The dorsal and anal fins have 12–14 rays. Young specimens have a slender build; older specimens acquire a higher and broader body shape. The roach can often be recognized by the big red spot in the iris above and beside the pupil. Colours of the eye and fins can be very pale, however, in some environments. In Central and Northern Europe, the common roach can most easily be confused with the common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Bream
The common bream (''Abramis brama''), also known as the freshwater bream, bream, bronze bream, carp bream or sweaty bream, is a European species of freshwater fish in the family Leuciscidae. It is now considered to be the monotypic, only species in the genus ''Abramis''. Taxonomy The common bream was first formally Species description, described as ''Cyprinus brama'' in the 10th edition of Systema Naturae, 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' published in 1758 by Carl Linnaeus with its Type locality (biology), type locality given as European lakes. In 1816 Georges Cuvier proposed the gneus ''Abramis'', designating ''Cyprinus brama'' as its type species. This taxon is classified within the subfamily Leuciscinae of the family Leuciscidae. Etymology The common bream is the only species in the genus ''Abramis'', this name is an Ancient Greek name for a bream or mullet. The Specific name (zoology), specific name is derived from ''Abramis''. Range and habitat The common bream's home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
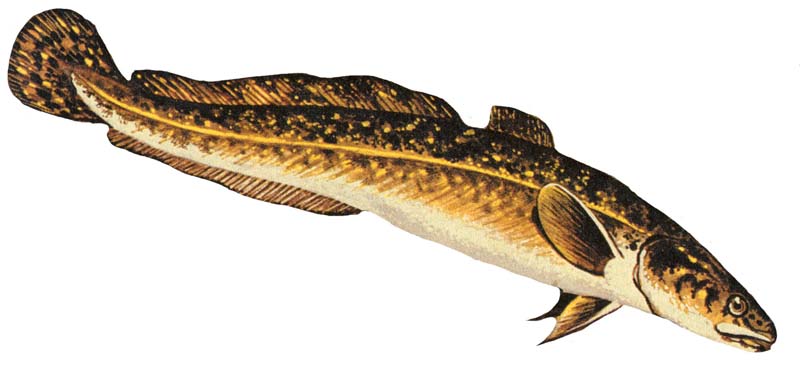
Burbot
The burbot (''Lota lota''), also known as bubbot, mariah, loche, cusk, freshwater cod, freshwater ling, freshwater cusk, the lawyer, coney-fish, lingcod, or eelpout, is a species of coldwater ray-finned fish native to the subarctic regions of the Northern hemisphere. It is the only member of the genus ''Lota'', and is the only freshwater species of the order Gadiformes. The species is closely related to marine fish such as the common ling and cusk, all of which belong to the family Lotidae (rocklings). Etymology The name burbot comes from the Latin word ''barba'', meaning beard, referring to its single chin whisker, or barbel. Its generic and specific names, ''Lota lota'', comes from the old French ''lotte'' fish, which is also named "barbot" in Old French. Description With an appearance like a cross between a catfish and an eel, the burbot has a serpent-like body, but is easily distinguished by a single barbel on the chin. The body is elongated and laterally compress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |