|
Palmitoyl Chain
In molecular biology, palmitoylation is the covalent attachment of fatty acids, such as palmitic acid, to cysteine (''S''-palmitoylation) and less frequently to serine and threonine (''O''-palmitoylation) residues of proteins, which are typically membrane proteins. The precise function of palmitoylation depends on the particular protein being considered. Palmitoylation enhances the hydrophobicity of proteins and contributes to their membrane association. Palmitoylation also appears to play a significant role in subcellular trafficking of proteins between membrane compartments, as well as in modulating protein–protein interactions. In contrast to prenylation and myristoylation, palmitoylation is usually reversible (because the bond between palmitic acid and protein is often a thioester bond). The reverse reaction in mammalian cells is catalyzed by acyl-protein thioesterases (APTs) in the cytosol and palmitoyl protein thioesterases in lysosomes. Because palmitoylation is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmitic Acid
Palmitic acid (hexadecanoic acid in IUPAC nomenclature) is a fatty acid with a 16-carbon chain. It is the most common saturated fatty acid found in animals, plants and microorganisms.Gunstone, F. D., John L. Harwood, and Albert J. Dijkstra. The Lipid Handbook, 3rd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2007. , Its chemical formula is , and its C:D ratio (the total number of carbon atoms to the number of carbon-carbon double bonds) is 16:0. It is a major component of palm oil from the fruit of '' Elaeis guineensis'' ( oil palms), making up to 44% of total fats. Meats, cheeses, butter, and other dairy products also contain palmitic acid, amounting to 50–60% of total fats. Palmitates are the salts and esters of palmitic acid. The palmitate anion is the observed form of palmitic acid at physiologic pH (7.4). Major sources of C16:0 are palm oil, palm kernel oil, coconut oil, and milk fat. Occurrence and production Palmitic acid was discovered by saponification of palm oil, which process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
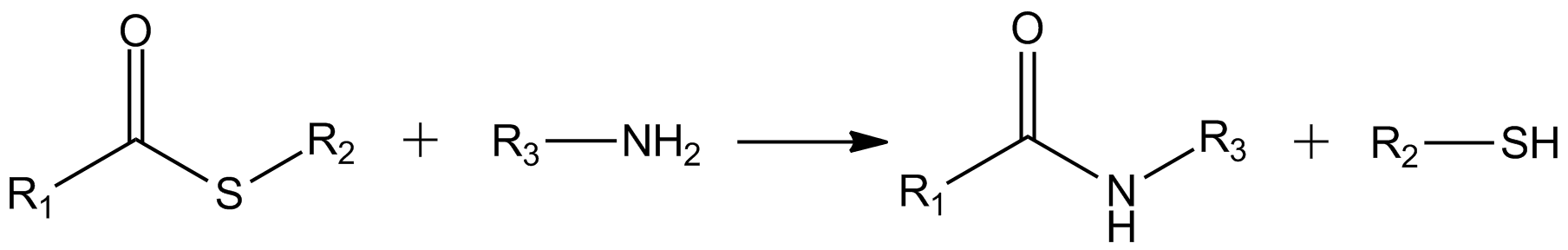
Thioester
In organic chemistry, thioesters are organosulfur compounds with the molecular structure . They are analogous to carboxylate esters () with the sulfur in the thioester replacing oxygen in the carboxylate ester, as implied by the thio- prefix. They are the product of esterification of a carboxylic acid () with a thiol (). In biochemistry, the best-known thioesters are derivatives of coenzyme A, e.g., acetyl-CoA.Matthys J. Janssen "Carboxylic Acids and Esters" in PATAI's Chemistry of Functional Groups: Carboxylic Acids and Esters, Saul Patai, Ed. John Wiley, 1969, New York: pp. 705–764. The R and R' represent organyl groups, or H in the case of R. Synthesis One route to thioesters involves the reaction of an acid chloride with an alkali metal salt of a thiol: : Another common route entails the displacement of halides by the alkali metal salt of a thiocarboxylic acid. For example, thioacetate esters are commonly prepared by alkylation of potassium thioacetate: : Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelium
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. Endothelial cells in direct contact with blood are called vascular endothelial cells whereas those in direct contact with lymph are known as lymphatic endothelial cells. Vascular endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart to the smallest capillaries. These cells have unique functions that include fluid filtration, such as in the glomerulus of the kidney, blood vessel tone, hemostasis, neutrophil recruitment, and hormone trafficking. Endothelium of the interior surfaces of the heart chambers is called endocardium. An impaired function can lead to serious health issues throughout the body. Structure The endothelium is a thin layer of single flat (squamous) cells that line the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
β2-adrenergic Receptor
The beta-2 adrenergic receptor (β2 adrenoreceptor), also known as ADRB2, is a cell membrane-spanning beta-adrenergic receptor that binds epinephrine (adrenaline), a hormone and neurotransmitter whose signaling, via adenylate cyclase stimulation through trimeric Gs proteins, increases cAMP, and, via downstream L-type calcium channel interaction, mediates physiologic responses such as smooth muscle relaxation and bronchodilation. Robert Lefkowitz and Brian Kobilka's study of the beta-2 adrenergic receptor as a model system earned them the 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry "for studies of G-protein-coupled receptors". The official symbol for the human gene encoding the β2 adrenoreceptor is ''ADRB2''. Gene The gene is intronless. Different polymorphic forms, point mutations, and/or downregulation of this gene are associated with nocturnal asthma, obesity and type 2 diabetes. Structure The 3D crystallographic structure (see figure and links to the right) of the β2-adrenergic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gsα
The Gs alpha subunit (Gαs, Gsα) is a subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein Gs that stimulates the cAMP-dependent pathway by activating adenylyl cyclase. Gsα is a GTPase that functions as a cellular signaling protein. Gsα is the founding member of one of the four families of heterotrimeric G proteins, defined by the alpha subunits they contain: the Gαs family, Gαi/Gαo family, Gαq family, and Gα12/Gα13 family. The Gs-family has only two members: the other member is Golf, named for its predominant expression in the olfactory system. In humans, Gsα is encoded by the GNAS complex locus, while Golfα is encoded by the GNAL gene. Function The general function of Gs is to activate intracellular signaling pathways in response to activation of cell surface G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). GPCRs function as part of a three-component system of receptor-transducer-effector. The transducer in this system is a heterotrimeric G protein, composed of three subunits: a Gα ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-Ras
GTPase HRas, from "Harvey Rat sarcoma virus", also known as transforming protein p21 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the gene. The ''HRAS'' gene is located on the short (p) arm of chromosome 11 at position 15.5, from base pair 522,241 to base pair 525,549. HRas is a small G protein in the Ras subfamily of the Ras superfamily of small GTPases. Once bound to Guanosine triphosphate, H-Ras will activate a Raf kinase like c-Raf, the next step in the MAPK/ERK pathway. Function GTPase HRas is involved in regulating cell division in response to growth factor stimulation. Growth factors act by binding cell surface receptors that span the cell's plasma membrane. Once activated, receptors stimulate signal transduction events in the cytoplasm, a process by which proteins and second messengers relay signals from outside the cell to the cell nucleus and instructs the cell to grow or divide. The HRAS protein is a GTPase and is an early player in many signal transduction pathways ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms begin one to four (typically two) days after exposure to the virus and last for about two to eight days. Diarrhea and vomiting can occur, particularly in children. Influenza may progress to pneumonia from the virus or a subsequent bacterial infection. Other complications include acute respiratory distress syndrome, meningitis, encephalitis, and worsening of pre-existing health problems such as asthma and cardiovascular disease. There are four types of influenza virus: types A, B, C, and D. Aquatic birds are the primary source of influenza A virus (IAV), which is also widespread in various mammals, including humans and pigs. Influenza B virus (IBV) and influenza C virus (ICV) primarily infect humans, and influenza D virus (IDV) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemagglutinin
The term hemagglutinin (alternatively spelt ''haemagglutinin'', from the Greek , 'blood' + Latin , 'glue') refers to any protein that can cause red blood cells (erythrocytes) to clump together (" agglutinate") ''in vitro''. They do this by binding to the sugar residues on a red blood cell; when a single hemagglutinin molecule binds sugars from multiple red blood cells, it "glues" these cells together. As a result, they are carbohydrate-binding proteins (lectins). The ability to bind red blood cell sugars have independently appeared several times, and as a result hemaglutinins do not all bind using the same mechanism. The ability to bind red blood sugars is also not necessarily related to the ''in vivo'' function of the protein. The term ''hemagglutinin'' is most commonly applied to plant and viral lectins. Natural proteins that clump together red blood cells were known since the turn of the 19th century. Virologist George K. Hirst is also credited for "discovering agglutination a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-translational Modification
In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translation (biology), translate mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then change to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signal transduction, signalling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones. Post-translational modifications can occur on the amino acid side chains or at the protein's C-terminus, C- or N-terminus, N- termini. They can expand the chemical set of the 22 proteinogenic amino acid, amino acids by changing an existing functional group or adding a new one such as phosphate. Phosphorylation is highly effective for controlling the enzyme activity and is the most common change after translation. Many eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins also have carbohydrate molecules attached to them in a pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysosomes
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation center. Their primary responsibility is catabolic degradation of proteins, polysaccharides and lipids into their respective building-block molecules: amino acids, monosaccharides, and free fatty acids. The breakdown is done by various enzymes, for example proteases, glycosidases and lipases. With an acidic lumen limited by a single-bilayer lipid membrane, the lysosome holds an environment isolated from the rest of the cell. The lower pH creates optimal conditions for the over 60 different hydrolases inside. Lysosomes receive extracellular particles through endocytosis, and intracellular components through autophagy. They can also fuse with the plasma membrane and secrete their contents, a process called lysosomal exocytosis. After degradation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmitoyl Protein Thioesterase
Palmitoyl protein hydrolase/thioesterases is an enzyme (EC 3.1.2.22) that removes thioester-linked fatty acyl groups such as palmitate from modified cysteine residues in proteins or peptides during lysosomal degradation. It catalyzes the reaction :palmitoyl rotein+ H2O \rightleftharpoons palmitate + protein This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on thioester bonds. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature. A semisystematic name or semitrivi ... is palmitoyl roteinhydrolase. Other names in common use include palmitoyl-protein thioesterase, and palmitoyl-(protein) hydrolase. This enzyme participates in fatty acid elongation in mitochondria. Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (NCL) represent a group of encephalopathies that occur in 1 in 12,500 childre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |