|
Pacho Rodríguez
Pacho is a municipality and town of Colombia in the department of Cundinamarca. Pacho is part of the Rionegro Province and the urban centre is situated at a distance of from the capital Bogotá at an altitude of , while the altitude ranges from to . The municipality borders San Cayetano, Villagómez and Topaipí in the north, Supatá and Subachoque in the south, Vergara and El Peñón in the west and in the east Zipaquirá, Tausa and Cogua.Official website Pacho Etymology In the times before the , Pacho was called ''Guataque'' or ''Gotaque''; ''Gua''; "mountain", ''Tha''; "strong" and ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Colombia
The municipalities of Colombia are decentralized subdivisions of the Colombia, Republic of Colombia. Municipalities make up most of the departments of Colombia, with 1,104 municipality, municipalities (''municipios''). Each one of them is led by a mayor (''alcalde'') elected by popular vote and represents the maximum executive government official at a municipality level under the mandate of the governor of their department which is a representative of all municipalities in the department; municipalities are grouped to form departments. The municipalities of Colombia are also grouped in an association called the ''Federación Colombiana de Municipios'' (Colombian Federation of Municipalities), which functions as a union under the private law and under the Colombian Constitution of 1991, constitutional Freedom of association, right to free association to defend their common interests. Categories Conforming to the law 1551/12 that modified the sixth article of the law 136/94 Art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
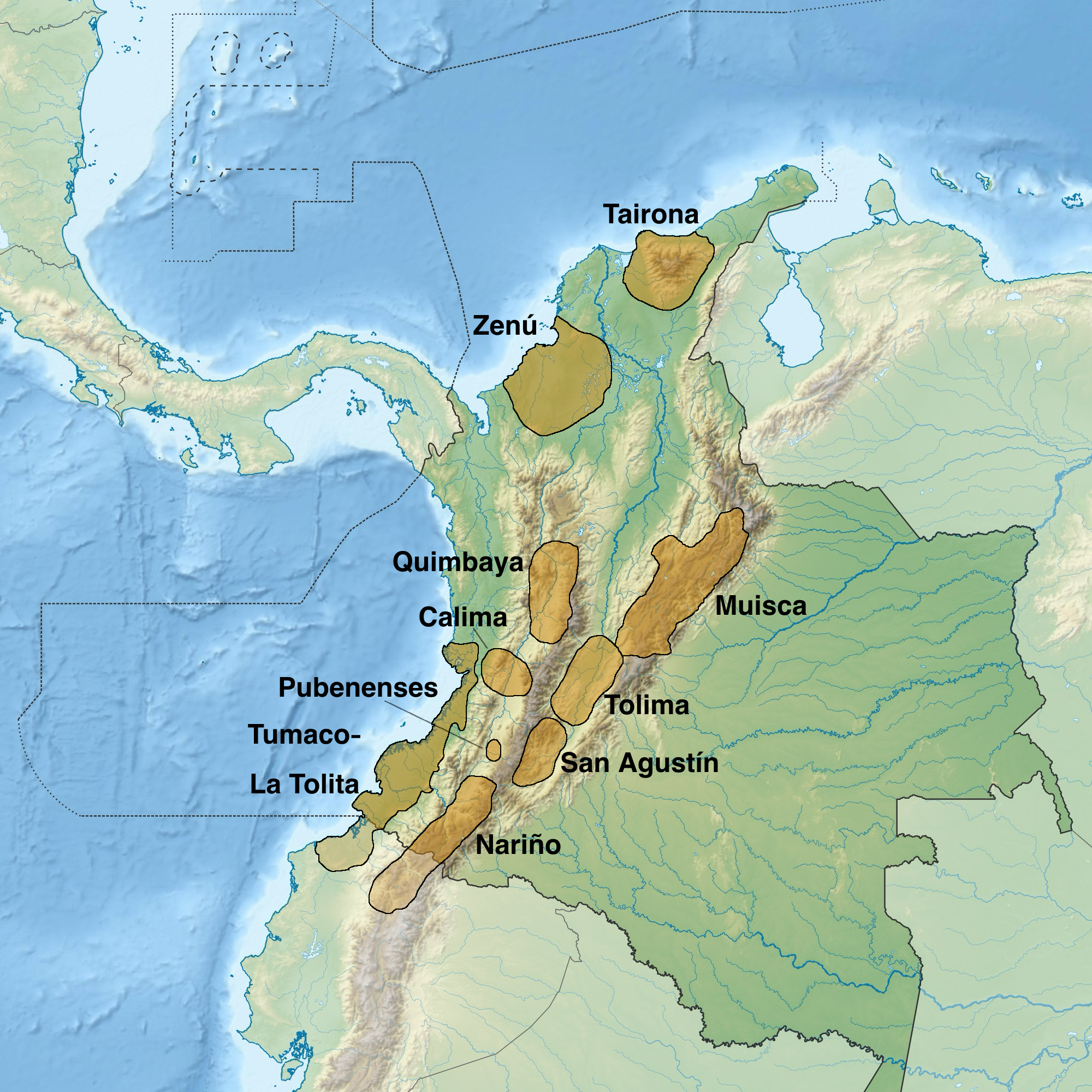
Spanish Conquest Of The Muisca
The Spanish conquest of the Muisca took place from 1537 to 1540. The Muisca people, Muisca were the inhabitants of the central Andes, Andean highlands of Colombia before the arrival of the Spanish conquistadors. They were organised in a loose Muisca Confederation, confederation of different Muisca rulers, rulers; the ''zipa, psihipqua'' of Bacatá, Muyquytá, with his headquarters in Funza, the ''zaque, hoa'' of Tunja, Hunza, the ''iraca'' of the sacred City of the Sun Sogamoso, Sugamuxi, the Tundama of Duitama, Tundama, and several other independent ''caciques''. The most important rulers at the time of the conquest were ''psihipqua'' Tisquesusa, ''hoa'' Quemuenchatocha, Eucaneme, ''iraca'' Sugamuxi and Tundama in the northernmost portion of their territories. The Muisca were organised in small communities of circular enclosures (''ca'' in their language Chibcha language, Muysccubbun; literally "language of the people"), with a central square where the ''Muisca architecture, boh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strawberry
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown Hybrid (biology), hybrid plant cultivated worldwide for its fruit. The genus ''Fragaria'', the strawberries, is in the rose family, Rosaceae. The fruit is appreciated for its aroma, bright red colour, juicy texture, and sweetness. It is eaten either fresh or in prepared foods such as fruit preserves, jam, ice cream, and chocolates. Artificial strawberry flavourings and aromas are widely used in commercial products. Botanically, the strawberry is not a berry (botany), berry, but an aggregate fruit, aggregate accessory fruit, accessory fruit. Each apparent 'seed' on the outside of the strawberry is actually an achene, a botanical fruit with a seed inside it. The garden strawberry was first bred in Brittany, France, in the 1750s via a cross of ''Virginia strawberry, F. virginiana'' from eastern North America and ''Fragaria chiloensis, F. chiloensis'', which was brought from Chile by Amédé ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orange (fruit)
The orange, also called sweet orange to distinguish it from the bitter orange (''Citrus × aurantium''), is the fruit of a tree in the family (biology), family Rutaceae. Botanically, this is the hybrid Citrus × sinensis, ''Citrus'' × ''sinensis'', between the pomelo (''Citrus maxima'') and the mandarin orange (''Citrus reticulata''). The chloroplast genome, and therefore the maternal line, is that of pomelo. There are many related hybrids including of mandarins and sweet orange. The sweet orange has had its full Whole genome sequencing, genome sequenced. The orange originated in a region encompassing Northern and southern China, Southern China, Northeast India, and Myanmar; the earliest mention of the sweet orange was in Chinese literature in 314 BC. Orange trees are widely grown in tropical and subtropical areas for their sweet fruit. The fruit of the Citrus × sinensis, orange tree can be eaten fresh or processed for its juice or fragrant peel (fruit), peel. In 2022, 76 mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
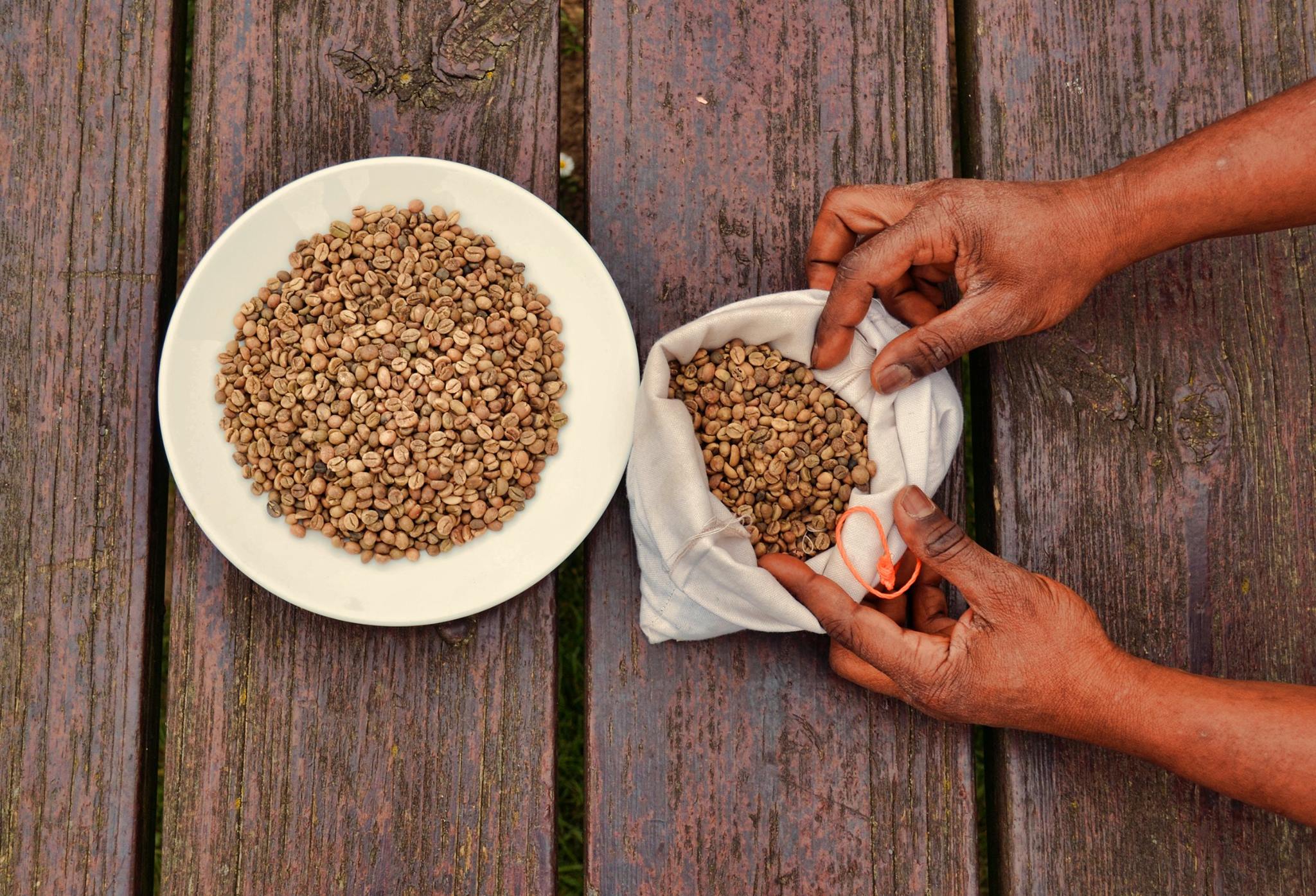
Coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially available. There are also various coffee substitutes. Typically served hot, coffee has the highest sales in the world market for hot drinks. Coffee production begins when the seeds from coffee cherries (the '' Coffea'' plant's fruits) are separated to produce unroasted green coffee beans. The "beans" are roasted and then ground into fine particles. Coffee is brewed from the ground roasted beans, which are typically steeped in hot water before being filtered out. It is usually served hot, although chilled or iced coffee is common. Coffee can be prepared and presented in a variety of ways (e.g., espresso, French press, caffè latte, or already-brewed canned coffee). Sugar, sugar substitutes, milk, and cream are often added to mask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muisca Agriculture
The Muisca agriculture describes the agriculture of the Muisca people, Muisca, the advanced civilisation that was present in the times before the Spanish conquest of the Muisca, Spanish conquest on the high plateau in the Colombian Andes; the Altiplano Cundiboyacense. The Muisca were a predominantly agricultural society with small-scale farmfields, part of more extensive terrains. To diversify their diet, they traded mantles, gold, emeralds and halite, salt for fruits, vegetables, coca, Anadenanthera peregrina, yopo and cotton cultivated in lower altitude warmer terrains populated by their neighbours, the Muzo people, Muzo, Panche people, Panche, Guane people, Guane, Guayupe people, Guayupe, Lache people, Lache, Sutagao people, Sutagao and U'wa people, U'wa. Trade of products grown farther away happened with the Calima culture, Calima, Pijao people, Pijao and Caribbean coastal communities around the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta. Important List of Muisca scholars, scholars w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Hydrology, Meteorology And Environmental Studies (Colombia)
The Institute of Hydrology, Meteorology and Environmental Studies (), also known by its acronym in Spanish, IDEAM, is a government agency of the Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development (Colombia), Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development of Colombia. It is in charge of producing and managing the scientific and technical information on the environment of Colombia, and its territorial composition. The IDEAM also serves as the Colombian meteorology, institute of meteorology and studies the climate of Colombia. The agency is currently led by the Director General, forestry engineer Yolanda González Hernandez. González Hernández is a specialist in Geographic information system, Geographic Information Systems with a Masters in Meteorology Sciences from the National University of Colombia, and is the first woman to lead the agency. Creation It was created on December 22, 1993, when Congress of Colombia, Congress passed ''Law 99 of 1993'', replacing the Colombia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtropical Highland Climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool to warm summers and cool to mild winters (for their latitude), with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 40 and 60 degrees latitude, with subpolar versions extending to 70 degrees latitude in some coastal areas. Other varieties of climates usually classified together with these include subtropical highland climates, represented as ''Cwb'' or ''Cfb'', and subpolar oceanic or cold subtropical highland climates, represented as ''Cfc'' or ''Cwc''. Subtropical highland climates occur in some mountainous parts of the subtropics or tropics, some of which have monsoon influence, while their cold variants and subpolar oceanic climates occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panche People
The Panche or Tolima are an indigenous peoples of Colombia, indigenous group of people that lived in what is now Colombia. They inhabited the southwestern parts of the Departments of Colombia, department of Cundinamarca Department, Cundinamarca and the northeastern areas of the department of Tolima Department, Tolima, close to the Magdalena River. At the time of the Spanish conquest of the Muisca, Spanish conquest, more than 30,000 Panche were living in what would become the New Kingdom of Granada. Early knowledge about the Panche has been compiled by List of Muisca scholars, scholar Pedro Simón. Panche territory The Panche were inhabiting the lower altitude southwestern areas of the Cundinamarca department, close to the Magdalena River. Their northern neighbours were the Muzo people, Muzo in the northeast and the Pantágora people, Pantágora in the northwest, in the east the Muisca people, Muisca, in the southeast the Sutagao people, Sutagao and to the south and southwest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muzo People
The Muzo people are a Cariban languages, Cariban-speaking Indigenous group who inhabited the western slopes of the eastern Colombian Andes. They were a highly war-like tribe who frequently clashed with their neighbouring Indigenous groups, especially the Muisca. The Muzo inhabited the right banks of the Magdalena River in the lower elevations of western Boyacá Department, Boyacá and Cundinamarca Department, Cundinamarca and were known as the Emerald People, thanks to their exploitation of the gemstone in Muzo. During the time of Spanish conquest of the Muisca, conquest, they resisted heavily against the Spanish invaders taking twenty years to submit the Muzo. Knowledge about the Muzo people has been provided by List of Muisca and pre-Muisca scholars, chroniclers Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada, Pedro Simón, Juan de Castellanos, Lucas Fernández de Piedrahita and others. Muzo territory The Muzo were inhabiting the lower-elevation northwestern areas of the Cundinamarca departmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muisca Confederation
The Muisca Confederation was a loose confederation of different Muisca rulers (''zaques'', ''zipas'', ''iraca'', and ''tundama'') in the central Andes, Andean highlands of what is today Colombia before the Spanish conquest of the Americas, Spanish conquest of northern South America. The area, presently called Altiplano Cundiboyacense, comprised the current departments of Colombia, departments of Boyacá Department, Boyacá, Cundinamarca Department, Cundinamarca and minor parts of Santander Department, Santander. According to some List of Muisca scholars, Muisca scholars the Muisca Confederation was one of the best-organized confederations of tribes on the South American continent. Other Historian, historians and anthropologists, however, such as Jorge Gamboa Mendoza, attribute the present-day knowledge about the confederation and its organization more to a reflection by Spanish chroniclers who predominantly wrote about it a century or more after the Muisca were conquered and propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |