|
POU Domain
POU (pronounced 'pow') is a family of eukaryotic transcription factors that have well-conserved homeodomains. The Pou domain is a bipartite DNA binding domain found in these proteins. Etymology The acronym POU is derived from the names of three transcription factors: * the Pituitary-specific Pit-1 * the Octamer transcription factor proteins Oct-1 and Oct-2 (octamer sequence is ATGCAAAT) * the neural Unc-86 transcription factor from ''Caenorhabditis elegans''. Diversity POU domain genes have been described in organisms as divergent as ''Caenorhabditis elegans'', ''Drosophila'', ''Xenopus'', zebrafish and human but have not been yet identified in plants and fungi. Comparisons of POU domain genes across the animals suggests that the family can be divided into six major classes (POU1-POU6). Pit-1 is part of the POU1 class, Oct-1 and Oct-2 are members of POU2, while Unc-86 is a member of POU4. The six classes diverged early in animal evolution: POU1, POU3, POU4, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Family
A protein family is a group of evolutionarily related proteins. In many cases, a protein family has a corresponding gene family, in which each gene encodes a corresponding protein with a 1:1 relationship. The term "protein family" should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy. Proteins in a family descend from a common ancestor and typically have similar three-dimensional structures, functions, and significant sequence similarity. Sequence similarity (usually amino-acid sequence) is one of the most common indicators of homology, or common evolutionary ancestry. Some frameworks for evaluating the significance of similarity between sequences use sequence alignment methods. Proteins that do not share a common ancestor are unlikely to show statistically significant sequence similarity, making sequence alignment a powerful tool for identifying the members of protein families. Families are sometimes grouped together into larger clades called superfamilies based on st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
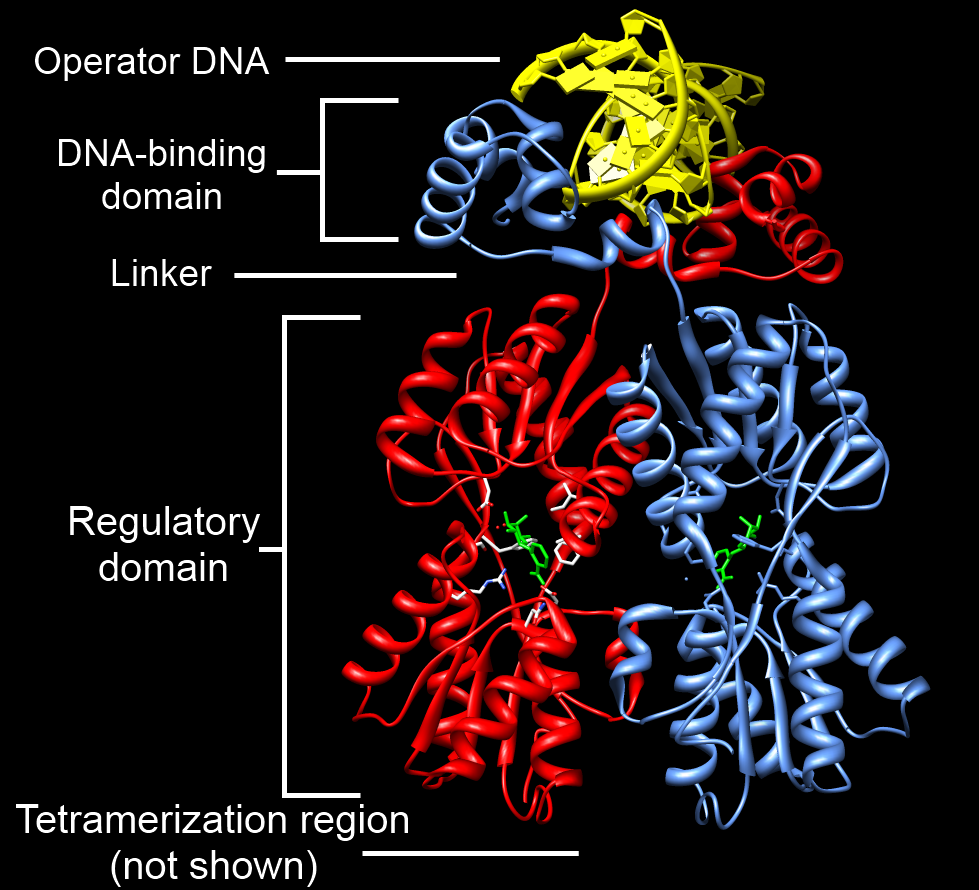
DNA Binding Domain
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence (a recognition sequence) or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure. Function One or more DNA-binding domains are often part of a larger protein consisting of further protein domains with differing function. The extra domains often regulate the activity of the DNA-binding domain. The function of DNA binding is either structural or involves transcription regulation, with the two roles sometimes overlapping. DNA-binding domains with functions involving DNA structure have biological roles in DNA replication, repair, storage, and modification, such as methylation. Many proteins involved in the regulation of gene expression contain DNA-binding domains. For example, proteins that regulate transcription by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are Gene expression, expressed in the desired Cell (biology), cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are approximately 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Competence
Genetic may refer to: *Genetics, in biology, the science of genes, heredity, and the variation of organisms **Genetic, used as an adjective, refers to genes ***Genetic disorder, any disorder caused by a genetic mutation, whether inherited or de novo ***Genetic mutation, a change in a gene ****Heredity, genes and their mutations being passed from parents to offspring **Genetic recombination, refers to the recombining of alleles resulting in a new molecule of DNA *Genetic relationship (linguistics), in linguistics, a relationship between two languages with a common ancestor language *Genetic algorithm In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to g ..., in computer science, a kind of search technique modeled on evolutionary biology See also * Genetic memory (other) {{disam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metazoans
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology, and the study of animal behaviour is known as ethology. The animal kingdom is divided into five major clades, namely Porifera, Ctenophora, Placozoa, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Subtilis
''Bacillus subtilis'' (), known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus ''Bacillus'', ''B. subtilis'' is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. ''B. subtilis'' has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. ''B. subtilis'' is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies. Description ''Bacillus subtilis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, rod-shaped and catalase-positive. It was originally named ''Vibrio subtilis'' by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'before', and (), meaning 'nut' or 'kernel'. In the earlier two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard Chatton, prokaryotes were classified within the empire Prokaryota. However, in the three-domain system, based upon molecular phylogenetics, prokaryotes are divided into two domain (biology), domains: Bacteria and Archaea. A third domain, Eukaryote, Eukaryota, consists of organisms with nuclei. Prokaryotes evolution, evolved before eukaryotes, and lack nuclei, mitochondria, and most of the other distinct organelles that characterize the eukaryotic cell. Some unicellular prokaryotes, such as cyanobacteria, form colony (biology), colonies held together by biofilms, and large colonies can create multilayered microbial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram Positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. The Gram stain is used by microbiologists to place bacteria into two main categories, gram-positive (+) and gram-negative (−). Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan within the cell wall, and gram-negative bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan. Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet stain used in the test, resulting in a purple color when observed through an optical microscope. The thick layer of peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it has been fixed in place by iodine. During the decolorization step, the decolorizer removes crystal violet from all other cells. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain. The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebrata with some 65,000 species, by far the largest ranked grouping in the phylum Chordata. The vertebrates include mammals, birds, amphibians, and various classes of fish and reptiles. The fish include the jawless Agnatha, and the jawed Gnathostomata. The jawed fish include both the Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish and the Osteichthyes, bony fish. Bony fish include the Sarcopterygii, lobe-finned fish, which gave rise to the tetrapods, the animals with four limbs. Despite their success, vertebrates still only make up less than five percent of all described animal species. The first vertebrates appeared in the Cambrian explosion some 518 million years ago. Jawed vertebrates evolved in the Ordovician, followed by bony fishes in the Devonian. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilateria
Bilateria () is a large clade of animals characterised by bilateral symmetry during embryonic development. This means their body plans are laid around a longitudinal axis with a front (or "head") and a rear (or "tail") end, as well as a left–right–symmetrical belly ( ventral) and back ( dorsal) surface. Nearly all bilaterians maintain a bilaterally symmetrical body as adults; the most notable exception is the echinoderms, which have pentaradial symmetry as adults, but bilateral symmetry as embryos. With few exceptions, bilaterian embryos are triploblastic, having three germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm, and have complete digestive tracts with a separate mouth and anus. Some bilaterians lack body cavities, while others have a primary body cavity derived from the blastocoel, or a secondary cavity, the coelom. Cephalization is a characteristic feature among most bilaterians, where the sense organs and central nerve ganglia become concentrated at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eumetazoa
Eumetazoa (), also known as Epitheliozoa or Histozoa, is a proposed basal animal subkingdom as a sister group of Porifera (sponges). The basal eumetazoan clades are the Ctenophora and the ParaHoxozoa. Placozoa is now also seen as a eumetazoan in the ParaHoxozoa. The competing hypothesis is the Myriazoa clade. The subkingdom Parazoa and Agnotozoa are the other taxa, and agnotozoa may be fake or even nonexistent at studies. Parazoa or Agnotozoa are a main sister group to eumetazoans, forming clade Blastozoa/Diploblastozoa. Alternatively, Parazoa was considered as a sister group to Agnotozoa(now considered polyphyletic). Several other extinct or obscure life forms, such as '' Iotuba'' and '' Thectardis'', appear to have emerged in the group. Characteristics of eumetazoans include true tissues organized into germ layers, the presence of neurons and muscles, and an embryo that goes through a gastrula stage. Some phylogenists once speculated the sponges and eumetazoans evolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |