|
Oxazoline
Oxazoline is a five-membered heterocyclic organic compound with the formula . It is the parent of a family of compounds called oxazolines (emphasis on plural), which contain non-hydrogenic substituents on carbon and/or nitrogen. Oxazolines are the unsaturated analogues of oxazolidines, and they are isomeric with isoxazolines, where the N and O are directly bonded. Two isomers of oxazoline are known, depending on the location of the double bond. Oxazoline itself has no applications however oxazolines have been widely investigated for potential applications. These applications include use as ligands in asymmetric catalysis, as protecting groups for carboxylic acids and increasingly as monomers for the production of polymers. Isomers Synthesis The synthesis of 2-oxazoline rings is well established and in general proceeds via the cyclisation of a 2-amino alcohol (typically obtained by the reduction of an amino acid) with a suitable functional group. The overall mechanism is usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocyclic
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of these heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan are quino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxazolidine
An oxazolidine is a five-membered ring compound consisting of three carbon atoms, a nitrogen atom and an oxygen atom. The O atom and NH group are the 1 and 3 positions, respectively. In oxazolidine derivatives, there is always a carbon atom between the O and N atoms (or it would be an ''isoxazolidine''). All of the carbon atoms in oxazolidines are reduced (compare to oxazole and oxazoline). Some of their derivatives, the 2,4-Oxazolidinedione, oxazolidinediones, are used as anticonvulsants. Oxazolidines were first synthesized over 100 years ago. Monooxazolidines Oxazolidines that are the precursor to bisoxazolidines are in effect mono-oxazolidines. They are also used as moisture scavengers in polyurethane and other systems. Dioxooxazolidines Oxazolidines where the carbon centers at the 1 and 3 positions are carbonyl group, carbonyls are called dioxooxazolidines. Some of these are commercial fungicides including chlozolinate, vinclozolin, and famoxadone. Bisoxazolidines Bisoxazol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protecting Group
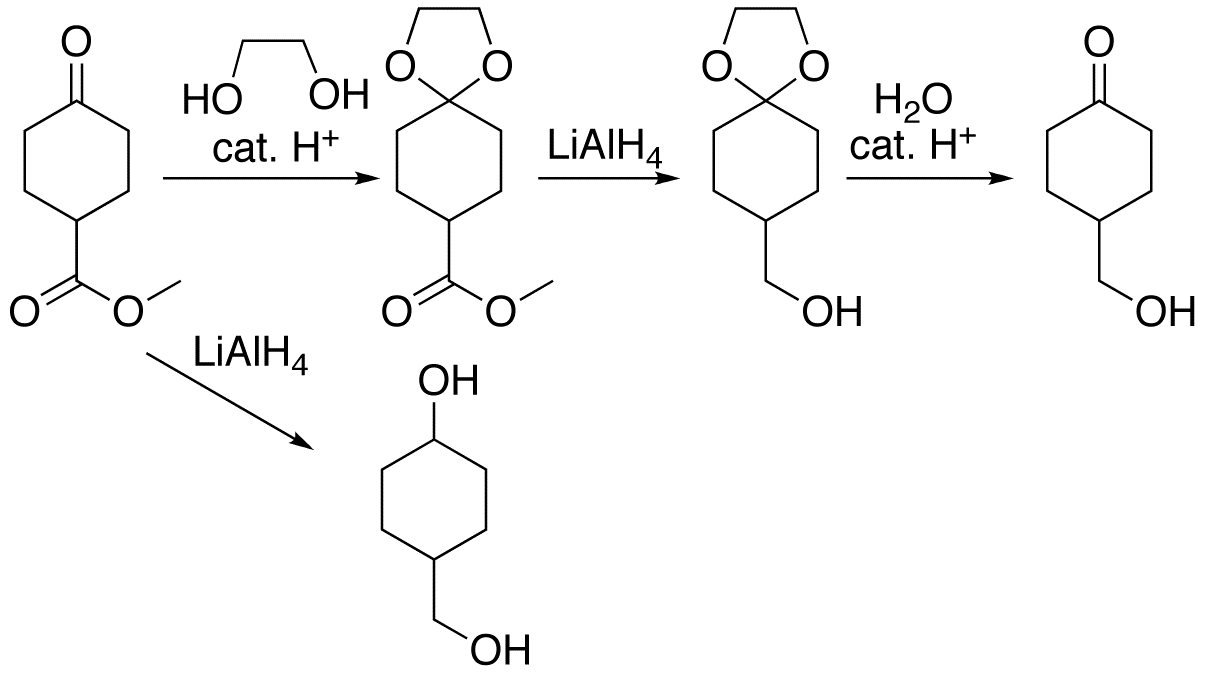
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, some specific parts of their molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. Then, these parts, or groups, must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive but useful reagent capable of reducing esters to alcohols. It will always react with carbonyl groups, and this cannot be discouraged by any means. When a reduction of an ester is required in the presence of a carbonyl, the attack of the hydride on the carbonyl has to be prevented. For example, the carbonyl is converted into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the step involving the hydride is complete, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baldwin's Rules
Baldwin's rules in organic chemistry are a series of guidelines outlining the relative favorabilities of ring closure reactions in alicyclic compounds. They were first proposed by Jack Baldwin in 1976. Baldwin's rules discuss the relative rates of ring closures of these various types. These terms are not meant to describe the absolute probability that a reaction will or will not take place, rather they are used in a relative sense. A reaction that is disfavoured (slow) does not have a rate that is able to compete effectively with an alternative reaction that is favoured (fast). However, the disfavoured product may be observed, if no alternate reactions are more favoured. The rules classify ring closures in three ways: *the number of atoms in the newly formed ring *into ''exo'' and ''endo'' ring closures, depending whether the bond broken during the ring closure is inside (''endo'') or outside (''exo'') the ring that is being formed *into ''tet'', ''trig'' and ''dig'' geometry o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montreal Protocol
The Montreal Protocol is an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of numerous substances that are responsible for ozone depletion. It was agreed on 16 September 1987, and entered into force on 1 January 1989. Since then, it has undergone nine revisions, in 1990 (London), 1991 (Nairobi), 1992 (Copenhagen), 1993 (Bangkok), 1995 (Vienna), 1997 (Montreal), 1998 ( Australia), 1999 (Beijing) and 2016 ( Kigali) As a result of the international agreement, the ozone hole in Antarctica is slowly recovering. Climate projections indicate that the ozone layer will return to 1980 levels between 2050 and 2070. Due to its widespread adoption and implementation, it has been hailed as an example of successful international co-operation. Former UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan stated that "perhaps the single most successful international agreement to date has been the Montreal Protocol". In comparison, effective burden-sharing and solution proposa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names (such as tetrachloromethane, also recognised by the IUPAC, carbon tet in the cleaning industry, Halon-104 in firefighting, and Refrigerant-10 in HVACR) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CCl4. It is a colourless liquid with a "sweet" smell that can be detected at low levels. It is practically incombustible at lower temperatures. It was formerly widely used in fire extinguishers, as a precursor to refrigerants and as a cleaning agent, but has since been phased out because of environmental and safety concerns. Exposure to high concentrations of carbon tetrachloride (including vapor) can affect the central nervous system and degenerate the liver and kidneys. Prolonged exposure can be fatal. Properties In the carbon tetrachloride molecule, four chlorine atoms are positioned symmetrically as corners in a tetrahedral configuration joined to a central carbon atom by single covalent bonds. Because of this symmetri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylphosphine Oxide
Triphenylphosphine oxide (often abbreviated TPPO) is the organophosphorus compound with the formula OP(C6H5)3, also written as Ph3PO or PPh3O (Ph = C6H5). This colourless crystalline compound is a common but potentially useful waste product in reactions involving triphenylphosphine. It is a popular reagent to induce the crystallizing of chemical compounds. Structure and properties Ph3PO is a tetrahedral molecule related to POCl3. The oxygen center is relatively basic. The rigidity of the backbone and the basicity of the oxygen center make this species a popular agent to crystallize otherwise difficult to crystallize molecules. This trick is applicable to molecules that have acidic hydrogen atoms, e.g. phenols. Up to now, several modifications of Ph3PO have been found: For example, a monoclinic form crystalizes in the space group ''P''21/''c'' with Z = 4 and a = 15.066(1) Å, b = 9.037(2) Å, c = 11.296(3) Å, and β = 98.47(1)°. The orthorhombic modification crystallizes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appel Reaction
The Appel reaction is an organic reaction that converts an alcohol into an alkyl chloride using triphenylphosphine and carbon tetrachloride. The use of carbon tetrabromide or bromine as a halide source will yield alkyl bromides, whereas using carbon tetraiodide, methyl iodide or iodine gives alkyl iodides. The reaction is credited to and named after Rolf Appel, it had however been described earlier. The use of this reaction is becoming less common, due to carbon tetrachloride being restricted under the Montreal protocol. Drawbacks to the reaction are the use of toxic halogenating agents and the coproduction of organophosphorus product that must be separated from the organic product. The phosphorus reagent can be used in catalytic quantities. The corresponding alkyl bromide can also be synthesised by addition of lithium bromide as a source of bromide ions. A greener, more sustainable catalytic Appel reaction, free from chlorinated solvents, has also been reported. Mechanism T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminomethyl Propanol
Aminomethyl propanol is an organic compound with the formula H2NC(CH3)2CH2OH. It is colorless liquid that is classified as an alkanolamine. It is a useful buffer and a precursor to numerous other organic compounds. Synthesis Aminomethyl propanol can be produced by the hydrogenation of 2-aminoisobutyric acid or its esters. Properties Aminomethyl propanol is soluble in water and about the same density as water. Uses Aminomethyl propanol is used for the preparation of buffer solutions. It is a component of the drugs ambuphylline and pamabrom. It is also used in cosmetics. It is a precursor to oxazolines via its reaction with acyl chlorides. Via sulfation of the alcohol, the compound is also a precursor to 2,2-dimethylaziridine. It is used in the synthesis of Fepradinol & G-130 G-130 (GP-130, 2-Phenyl-5,5-dimethyltetrahydro-1,4-oxazine) is a drug with stimulant and anorectic effects, related to phenmetrazine. Structural analogs Compounds related to G-130 and radafaxin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalyl Chloride
Oxalyl chloride is an organic chemical compound with the formula (COCl)2. This colorless, sharp-smelling liquid, the diacyl chloride of oxalic acid, is a useful reagent in organic synthesis. Preparation Oxalyl chloride was first prepared in 1892 by the French chemist Adrien Fauconnier, who reacted diethyl oxalate with phosphorus pentachloride. It can also be prepared by treating oxalic acid with phosphorus pentachloride. Oxalyl chloride is produced commercially from ethylene carbonate. Photochlorination gives the tetrachloride, which is subsequently degraded: :C2H4O2CO + 4 Cl2 → C2Cl4O2CO + 4 HCl :C2Cl4O2CO → C2O2Cl2 + COCl2 Reactions Oxalyl chloride reacts with water giving off gaseous products only: hydrogen chloride (HCl), carbon dioxide (CO2), and carbon monoxide (CO). : In this, it is quite different from other acyl chlorides which hydrolyze with formation of hydrogen chloride and the original carboxylic acid. Applications in organic synthesis Oxidation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


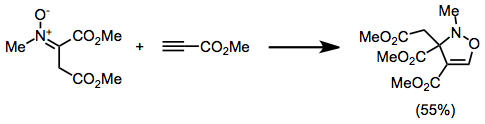

nickel(II)-from-xtal-3D-balls.png)
