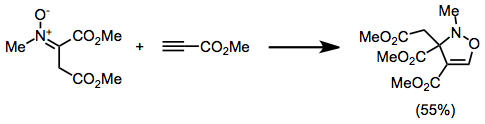|
Oxazolidinone
2-Oxazolidone is a heterocyclic organic compound containing both nitrogen and oxygen in a 5-membered ring. Oxazolidinones Evans auxiliaries Oxazolidinones are a class of compounds containing 2-oxazolidone in the structure. In chemistry, they are useful as Evans auxiliaries, which are used for chiral synthesis. Usually, the acid chloride substrate reacts with the oxazolidinone to form an imide. Substituents at the 4 and 5 position of the oxazolidinone direct any aldol reaction to the alpha position of the carbonyl of the substrate. Pharmaceuticals Oxazolidinones are mainly used as antimicrobials. The antibacterial effect of oxazolidinones is by working as protein synthesis inhibitors, targeting an early step involving the binding of N-formylmethionyl-tRNA to the ribosome. (See Linezolid#Pharmacodynamics) Some of the most important oxazolidinones are antibiotics. Examples of antibiotic oxazolidinones include: *Linezolid (Zyvox), which is available for intravenous administrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linezolid
Linezolid is an antibiotic used for the treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics. Linezolid is active against most Gram-positive bacteria that cause disease, including streptococci, vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), and methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA). The main uses are infections of the skin and pneumonia although it may be used for a variety of other infections including drug-resistant tuberculosis. It is used either by injection into a vein or by mouth. When given for short periods, linezolid is a relatively safe antibiotic. It can be used in people of all ages and in people with liver disease or poor kidney function. Common side effects with short-term use include headache, diarrhea, rash, and nausea. Serious side effects may include serotonin syndrome, bone marrow suppression, and high blood lactate levels, particularly when used for more than two weeks. If used for longer perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linezolid
Linezolid is an antibiotic used for the treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics. Linezolid is active against most Gram-positive bacteria that cause disease, including streptococci, vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), and methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA). The main uses are infections of the skin and pneumonia although it may be used for a variety of other infections including drug-resistant tuberculosis. It is used either by injection into a vein or by mouth. When given for short periods, linezolid is a relatively safe antibiotic. It can be used in people of all ages and in people with liver disease or poor kidney function. Common side effects with short-term use include headache, diarrhea, rash, and nausea. Serious side effects may include serotonin syndrome, bone marrow suppression, and high blood lactate levels, particularly when used for more than two weeks. If used for longer perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxazolidinones
2-Oxazolidone is a heterocyclic organic compound containing both nitrogen and oxygen in a 5-membered ring. Oxazolidinones Evans auxiliaries Oxazolidinones are a class of compounds containing 2-oxazolidone in the structure. In chemistry, they are useful as Evans auxiliaries, which are used for chiral synthesis. Usually, the acid chloride substrate reacts with the oxazolidinone to form an imide. Substituents at the 4 and 5 position of the oxazolidinone direct any aldol reaction to the alpha position of the carbonyl of the substrate. Pharmaceuticals Oxazolidinones are mainly used as antimicrobials. The antibacterial effect of oxazolidinones is by working as protein synthesis inhibitors, targeting an early step involving the binding of N-formylmethionyl-tRNA to the ribosome. (See Linezolid#Pharmacodynamics) Some of the most important oxazolidinones are antibiotics. Examples of antibiotic oxazolidinones include: *Linezolid (Zyvox), which is available for intravenous administr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Synthesis Inhibitor
A protein synthesis inhibitor is a compound that stops or slows the growth or proliferation of cells by disrupting the processes that lead directly to the generation of new proteins. While a broad interpretation of this definition could be used to describe nearly any compound depending on concentration, in practice, it usually refers to compounds that act at the molecular level on translational machinery (either the ribosome itself or the translation factor), taking advantages of the major differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosome structures. Mechanism In general, protein synthesis inhibitors work at different stages of bacterial mRNA translation into proteins, like initiation, elongation (including aminoacyl tRNA entry, proofreading, peptidyl transfer, and bacterial translocation) and termination: Earlier stages * Rifamycin inhibits bacterial DNA transcription into mRNA by inhibiting DNA-dependent RNA polymerase by binding its beta-subunit. * alpha-Amanitin is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tedizolid
Tedizolid (formerly torezolid, trade name Sivextro), is an oxazolidinone-class antibiotic. Tedizolid phosphate is a phosphate ester prodrug of the active compound tedizolid. It was developed by Cubist Pharmaceuticals, following acquisition of Trius Therapeutics (originator: Dong-A Pharmaceuticals), and is marketed for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (also known as complicated skin and skin-structure infections (cSSSIs)). The most common side effects include nausea (feeling sick), headache, diarrhoea and vomiting. These side effects were generally of mild or moderate severity. Tedizolid was approved for medical use in the United States in June 2014, and for medical use in the European Union in March 2015. Medical uses Tedizolid was approved by the U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on June 20, 2014, with the indication for the treatment of acute bacterial Skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused by certain susceptible bacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posizolid
Posizolid is an oxazolidinone antibiotic under investigation by AstraZeneca for the treatment of bacterial infections. At a concentration of 2 mg/L it inhibited 98% of all Gram-positive bacteria tested in vitro ''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology .... Clinical trials References Oxazolidinone antibiotics Isoxazoles Ethers Fluoroarenes Tetrahydropyridines Carboxamides Vicinal diols {{antibiotic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AZD2563
Posizolid is an oxazolidinone antibiotic under investigation by AstraZeneca for the treatment of bacterial infections. At a concentration of 2 mg/L it inhibited 98% of all Gram-positive bacteria tested in vitro ''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology .... Clinical trials References Oxazolidinone antibiotics Isoxazoles Ethers Fluoroarenes Tetrahydropyridines Carboxamides Vicinal diols {{antibiotic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxazolidine
An oxazolidine is a five-membered ring compound consisting of three carbon atoms, a nitrogen atom and an oxygen atom. The O atom and NH group are the 1 and 3 positions, respectively. In oxazolidine derivatives, there is always a carbon atom between the O and N atoms (or it would be an ''isoxazolidine''). All of the carbon atoms in oxazolidines are reduced (compare to oxazole and oxazoline). Some of their derivatives, the 2,4-Oxazolidinedione, oxazolidinediones, are used as anticonvulsants. Oxazolidines were first synthesized over 100 years ago. Monooxazolidines Oxazolidines that are the precursor to bisoxazolidines are in effect mono-oxazolidines. They are also used as moisture scavengers in polyurethane and other systems. Dioxooxazolidines Oxazolidines where the carbon centers at the 1 and 3 positions are carbonyl group, carbonyls are called dioxooxazolidines. Some of these are commercial fungicides including chlozolinate, vinclozolin, and famoxadone. Bisoxazolidines Bisoxazol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posizolid
Posizolid is an oxazolidinone antibiotic under investigation by AstraZeneca for the treatment of bacterial infections. At a concentration of 2 mg/L it inhibited 98% of all Gram-positive bacteria tested in vitro ''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology .... Clinical trials References Oxazolidinone antibiotics Isoxazoles Ethers Fluoroarenes Tetrahydropyridines Carboxamides Vicinal diols {{antibiotic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radezolid
Radezolid (INN, codenamed RX-1741) is a novel oxazolidinone 2-Oxazolidone is a heterocyclic organic compound containing both nitrogen and oxygen in a 5-membered ring. Oxazolidinones Evans auxiliaries Oxazolidinones are a class of compounds containing 2-oxazolidone in the structure. In chemistry, they are ... antibiotic being developed by Melinta Therapeutics, Inc. for the treatment of bacterial acne. References Further reading * * * * * * Oxazolidinone antibiotics Triazoles Fluoroarenes Acetamides Biphenyls {{antibiotic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldol Reaction
The aldol reaction is a means of forming carbon–carbon bonds in organic chemistry. Discovered independently by the Russian chemist Alexander Borodin in 1869 and by the French chemist Charles-Adolphe Wurtz in 1872, the reaction combines two carbonyl compounds (the original experiments used aldehydes) to form a new β-hydroxy carbonyl compound. These products are known as '' aldols'', from the ''ald''ehyde + alcoh''ol'', a structural motif seen in many of the products. Aldol structural units are found in many important molecules, whether naturally occurring or synthetic. For example, the aldol reaction has been used in the large-scale production of the commodity chemical pentaerythritol and the synthesis of the heart disease drug Lipitor (atorvastatin, calcium salt). The aldol reaction unites two relatively simple molecules into a more complex one. Increased complexity arises because up to two new stereogenic centers (on the α- and β-carbon of the aldol adduct, marked wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldol Reaction
The aldol reaction is a means of forming carbon–carbon bonds in organic chemistry. Discovered independently by the Russian chemist Alexander Borodin in 1869 and by the French chemist Charles-Adolphe Wurtz in 1872, the reaction combines two carbonyl compounds (the original experiments used aldehydes) to form a new β-hydroxy carbonyl compound. These products are known as '' aldols'', from the ''ald''ehyde + alcoh''ol'', a structural motif seen in many of the products. Aldol structural units are found in many important molecules, whether naturally occurring or synthetic. For example, the aldol reaction has been used in the large-scale production of the commodity chemical pentaerythritol and the synthesis of the heart disease drug Lipitor (atorvastatin, calcium salt). The aldol reaction unites two relatively simple molecules into a more complex one. Increased complexity arises because up to two new stereogenic centers (on the α- and β-carbon of the aldol adduct, marked wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |