|
Overprinting (geology)
In this orthogneiss from the Czech Republic the original igneous rock">igneous rock texture has been overprinted by foliation (geology), foliation associated with metamorphism. Overprinting is a geology, geological process that superimposes a set of characteristics on rock that partially obscure earlier characteristics. Examples include metamorphic overprinting (superimposed metamorphism), in which new structure, texture, or mineral composition is imposed on existing rock. For example, the Tauern window of Alps contains beds that were originally metamorphosed to eclogite but have since been overprinted to the blueschist and then the greenschist facies. Likewise, deformation associated with the Mazatzal orogeny in Arizona and New Mexico, US, was subsequently overprinted by deformation associated with the Picuris orogeny The Picuris orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now the Southwestern United States from 1.43 to 1.3 billion years ago in the Calymmian Period of the Mes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthogneiss Geopark
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures and pressures than schist. Gneiss nearly always shows a banded texture characterized by alternating darker and lighter colored bands and without a distinct cleavage. Gneisses are common in the ancient crust of continental shields. Some of the oldest rocks on Earth are gneisses, such as the Acasta Gneiss. Description Orthogneiss from the Czech Republic In traditional English and North American usage, a gneiss is a coarse-grained metamorphic rock showing compositional banding (gneissic banding) but poorly developed schistosity and indistinct cleavage. In other words, it is a metamorphic rock composed of mineral grains easily seen with the unaided eye, which form obvious compositional layers, but which has only a weak tendency to fracture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tauern Window
The Hohe Tauern window is a geological structure in the Austrian Central Eastern Alps. It is a window (in German ''fenster'') in the Austroalpine nappes where high-grade metamorphic rocks of the underlying Penninic nappes crop out. The structure is caused by a large dome-like antiform in the nappe stacks of the Alps. The relatively hard rocks of the Hohe Tauern window are more resistant to erosion, so the window has a high relief. The mountain chains thus formed are called the Hohe Tauern. Most of Austria's highest mountains are in the Hohe Tauern, among them the Großglockner (3798 m) and Großvenediger (3674 m). See also * References External links * * Geology of the Alps Structural geology Geology of Austria Geology of Italy Window A window is an opening in a wall, door, roof, or vehicle that allows the exchange of light and may also allow the passage of sound and sometimes air. Modern windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia. The Alpine arch generally extends from Nice on the western Mediterranean to Trieste on the Adriatic and Vienna at the beginning of the Pannonian Basin. The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrusting and folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains 128 peaks higher than . The altitude and size of the range affect the climate in Europe; in the mountains, precipitation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclogite
Eclogite () is a metamorphic rock containing garnet (almandine-pyrope) hosted in a matrix of sodium-rich pyroxene (omphacite). Accessory minerals include kyanite, rutile, quartz, lawsonite, coesite, amphibole, phengite, paragonite, zoisite, dolomite, corundum and, rarely, diamond. The chemistry of primary and accessory minerals is used to classify three types of eclogite (A, B, and C). The broad range of eclogitic compositions has led a longstanding debate on the origin of eclogite xenoliths as subducted, altered oceanic crust. Origins Eclogites typically result from high to ultrahigh pressure metamorphism of mafic rock at low thermal gradients of < as it is subducted to the lower crust to depths in a subduction zone. Class ...
|
Blueschist
Blueschist (), also called glaucophane schist, is a metavolcanic rock that forms by the metamorphism of basalt and rocks with similar composition at high pressures and low temperatures (), approximately corresponding to a depth of . The blue color of the rock comes from the presence of the predominant minerals glaucophane and lawsonite. Blueschists are schists typically found within orogenic belts as terranes of lithology in faulted contact with greenschist or rarely eclogite facies rocks. Petrology Blueschist, as a rock type, is defined by the presence of the minerals glaucophane + ( lawsonite or epidote ) +/- jadeite +/- albite or chlorite +/- garnet +/- muscovite in a rock of roughly basaltic composition. Blueschist often has a lepidoblastic, nematoblastic or schistose rock microstructure defined primarily by chlorite, phengitic white mica, glaucophane, and other minerals with an elongate or platy shape. Grain size is rarely coarse, as mineral growth is retarded b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenschist
Greenschists are metamorphic rocks that formed under the lowest temperatures and pressures usually produced by regional metamorphism, typically and 2–10 kilobars (). Greenschists commonly have an abundance of green minerals such as chlorite, serpentine, and epidote, and platy minerals such as muscovite and platy serpentine. The platiness gives the rock schistosity (a tendency to split into layers.) Other common minerals include quartz, orthoclase, talc, carbonate minerals and amphibole (actinolite). Greenschist is a general field petrologic term for metamorphic or altered mafic volcanic rock. In Europe, the term ''prasinite'' is sometimes used. A ''greenstone'' is sometimes a greenschist but can also be rock types without any schistosity, especially metabasalt (spilite). However, basalts may remain quite black if primary pyroxene does not revert to chlorite or actinolite. To qualify for the name a rock must also exhibit schistosity or some foliation or layering. The rock i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphic Facies
A metamorphic facies is a set of mineral assemblages in metamorphic rocks formed under similar pressures and temperatures.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak The assemblage is typical of what is formed in conditions corresponding to an area on the two dimensional graph of temperature vs. pressure (See diagram in Figure 1). Rocks which contain certain minerals can therefore be linked to certain tectonics, tectonic settings, times and places in the geological history of the area. The boundaries between facies (and corresponding areas on the temperature v. pressure graph) are wide because they are gradational and approximate. The area on the graph corresponding to rock formation at the lowest values of temperature and pressure is the range of formation of sedimentary rocks, as opposed to metamorphic rocks, in a process called diagenesis. Historic definition The name ''facies'' was first used for specific Sedimentary depositional environment, sedimentary environments i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
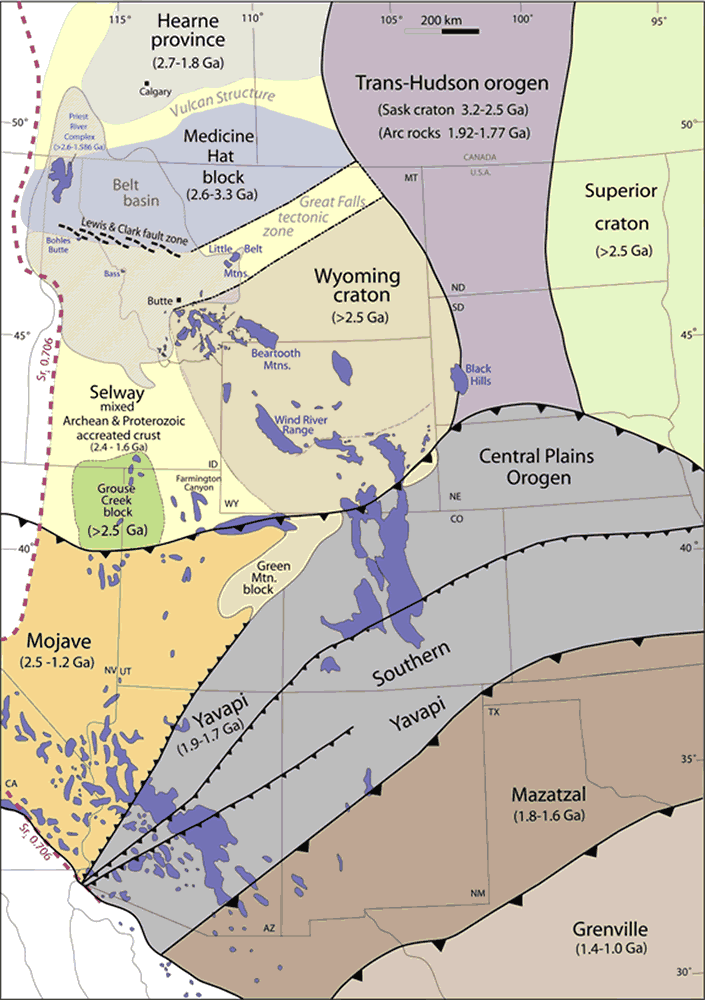
Mazatzal Orogeny
The Mazatzal orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now the Southwestern United States from 1650 to 1600 Mya in the Statherian Period of the Paleoproterozoic. Preserved in the rocks of New Mexico and Arizona, it is interpreted as the collision of the 1700-1600 Mya age Mazatzal island arc terrane with the proto-North American continent. This was the second in a series of orogenies within a long-lived convergent boundary along southern Laurentia that ended with the ca. 1200–1000 Mya Grenville orogeny during the final assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia, which ended an 800-million-year episode of convergent boundary tectonism. Description Age and isotope data show that southern North America is composed of a series of northeast-trending provinces representing island arc terranes accreted onto the 1800 Mya core of Laurentia. These are the Yavapai province (1800–1700 Mya), the Mazatzal province (1700–1650 Mya), the Granite-Rhyolite province (1500–1300 Mya), and the Llan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Four Corners region with Utah to the north, Colorado to the northeast, and New Mexico to the east; its other neighboring states are Nevada to the northwest, California to the west and the Mexican states of Sonora and Baja California to the south and southwest. Arizona is the 48th state and last of the contiguous states to be admitted to the Union, achieving statehood on February 14, 1912. Historically part of the territory of in New Spain, it became part of independent Mexico in 1821. After being defeated in the Mexican–American War, Mexico ceded much of this territory to the United States in 1848. The southernmost portion of the state was acquired in 1853 through the Gadsden Purchase. Southern Arizona is known for its desert cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Mexico
) , population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano) , seat = Santa Fe , LargestCity = Albuquerque , LargestMetro = Tiguex , OfficialLang = None , Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Keres, Zuni , Governor = , Lieutenant Governor = , Legislature = New Mexico Legislature , Upperhouse = Senate , Lowerhouse = House of Representatives , Judiciary = New Mexico Supreme Court , Senators = * * , Representative = * * * , postal_code = NM , TradAbbreviation = N.M., N.Mex. , area_rank = 5th , area_total_sq_mi = 121,591 , area_total_km2 = 314,915 , area_land_sq_mi = 121,298 , area_land_km2 = 314,161 , area_water_sq_mi = 292 , area_water_km2 = 757 , area_water_percent = 0.24 , population_as_of = 2020 , population_rank = 36th , 2010Pop = 2,117,522 , population_density_rank = 45th , 2000DensityUS = 17.2 , 2000Density = 6.62 , MedianHouseholdIncome = $51,945 , IncomeRank = 45th , AdmittanceOrder = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picuris Orogeny
The Picuris orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now the Southwestern United States from 1.43 to 1.3 billion years ago in the Calymmian Period of the Mesoproterozoic. The event is named for the Picuris Mountains in northern New Mexico and interpreted either as the suturing of the Granite-Rhyolite crustal province to the southern margin of the proto-North American continent Laurentia or as the final suturing of the Mazatzal crustal province onto Laurentia. According to the former hypothesis, this was the second in a series of orogenies within a long-lived convergent boundary along southern Laurentia that ended with the ca. 1200–1000 Mya Grenville orogeny during the final assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia, which ended an 800-million-year episode of convergent boundary tectonism. Description Age and isotope data show that southern North America is composed of a series of northeast-trending provinces representing island arc terranes accreted onto the 1800 Mya core of Lauren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |