|
Orobates
''Orobates'' is an extinct genus of diadectid reptiliomorphs that lived during the Early Permian. Its fossilised remains were found in Germany. A combination of primitive and derived traits (i.e. autapomorphic and plesiomorphic) distinguish it from all other well-known members of Diadectidae, a family of herbivorous reptiliomorphs. It weighed about 4 kg and appears to have been part of an upland fauna, browsing on high fibre plants. Locomotion The trace fossil species ''Ichniotherium sphaerodactylum'', from Bromacker in Germany, has been attributed to ''Orobates''. A study in 2015 found that the genus was characterized by a long body and tail, with fairly short legs and a short skull compared to the more derived ''Diadectes''. This indicates ''Orobates'' was less specialised for long treks compared to ''Diadectes''. A three-dimensional digital reconstruction of the holotype specimen allowed further analysis of the postcranium. An analysis of the mobility of the hip joi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orobates BW
''Orobates'' is an extinct genus of diadectid reptiliomorphs that lived during the Early Permian. Its fossil, fossilised remains were found in Germany. A combination of primitive and derived traits (i.e. autapomorphic and plesiomorphic) distinguish it from all other well-known members of Diadectidae, a family of herbivorous reptiliomorphs. It weighed about 4 kg and appears to have been part of an upland fauna, browsing on high fibre plants. Locomotion The trace fossil species ''Ichniotherium sphaerodactylum'', from Bromacker in Germany, has been attributed to ''Orobates''. A study in 2015 found that the genus was characterized by a long body and tail, with fairly short legs and a short skull compared to the more derived ''Diadectes''. This indicates ''Orobates'' was less specialised for long treks compared to ''Diadectes''. A three-dimensional digital reconstruction of the holotype specimen allowed further analysis of the postcranium. An analysis of the mobility of the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
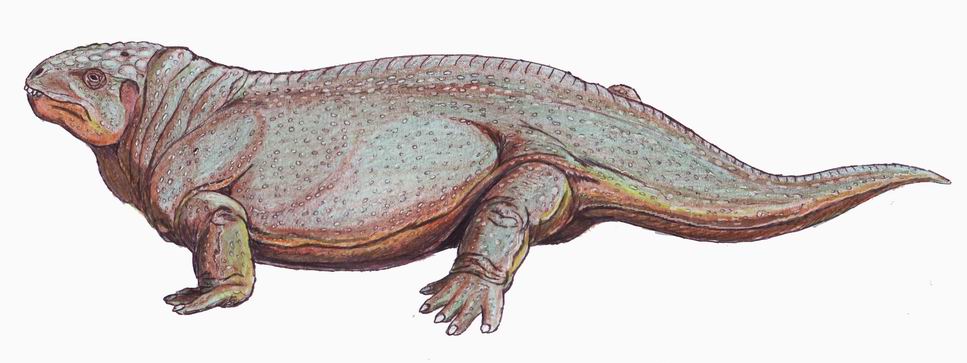
Orobates Pabsti-3
''Orobates'' is an extinct genus of diadectid reptiliomorphs that lived during the Early Permian. Its fossilised remains were found in Germany. A combination of primitive and derived traits (i.e. autapomorphic and plesiomorphic) distinguish it from all other well-known members of Diadectidae, a family of herbivorous reptiliomorphs. It weighed about 4 kg and appears to have been part of an upland fauna, browsing on high fibre plants. Locomotion The trace fossil species ''Ichniotherium sphaerodactylum'', from Bromacker in Germany, has been attributed to ''Orobates''. A study in 2015 found that the genus was characterized by a long body and tail, with fairly short legs and a short skull compared to the more derived ''Diadectes''. This indicates ''Orobates'' was less specialised for long treks compared to ''Diadectes''. A three-dimensional digital reconstruction of the holotype specimen allowed further analysis of the postcranium. An analysis of the mobility of the hip join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diadectid
Diadectidae is an extinct family of early tetrapods that lived in what is now North America and Europe during the Late Carboniferous and Early Permian in Asia during the Late Permian. They were the first herbivorous tetrapods, and also the first fully terrestrial animals to attain large sizes. Footprints indicate that diadectids walked with an erect posture. They were the first to exploit plant material in terrestrial food chains, making their appearance an important stage in both vertebrate evolution and the development of terrestrial ecosystems. The best known and largest representative of the family is ''Diadectes'', a heavily built animal that attained a maximum length of several metres. Several other genera and various fragmentary fossil remains are also known. Although well known genera like ''Diadectes'' first appear in the Late Pennsylvanian, fragmentary remains of possible diadectids are known from much earlier deposits, including a piece of lower jaw found in Missis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diadectes
''Diadectes'' (meaning ''crosswise-biter'') is an extinct genus of large reptiliomorphs or synapsids that lived during the early Permian period (Artinskian-Kungurian stages of the Cisuralian epoch, between 290 and 272 million years ago). ''Diadectes'' was one of the first herbivorous tetrapods, and also one of the first fully terrestrial vertebrates to attain large size. Description ''Diadectes'' was a heavily built animal, up to long, with a thick-boned skull, heavy vertebrae and ribs, massive limb girdles, and short, robust limbs. The nature of the limbs and vertebrae clearly indicates a terrestrial animal. The rib cage was assumed to be barrel-shaped, but new fossils show the ribs were actually sticking out to the sides. Paleobiology It possesses some characteristics of reptilians and amphibians, combining a reptile-like skeleton with a more primitive, seymouriamorph-like skull. ''Diadectes'' has been classified as belonging to the sister group of the amniotes. Among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisuralian
The Cisuralian is the first Series (stratigraphy), series/Epoch (geology), epoch of the Permian. The Cisuralian was preceded by the Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian and followed by the Guadalupian. The Cisuralian Epoch is named after the western slopes of the Ural Mountains in Russia and Kazakhstan and dates between 298.9 ± 0.15 – 272.3 ± 0.5 Mya. The Cisuralian is often synonymous with the informal terms early Permian or lower Permian. It corresponds approximately with the Wolfcampian in southwestern North America. The series saw the appearance of beetles and Fly, flies and was a relatively stable warming period of about 21 million years. Name and background The Cisuralian is the first series or epoch of the Permian. The Cisuralian was preceded by the last Pennsylvanian epoch (Gzhelian) and is followed by the Permian Guadalupian Epoch. The name "Cisuralian" was proposed in 1982, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. The Ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown-tetrapods (last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Carboniferous, 350 million years ago. The specific aquatic ancestors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Motion Analysis
X-ray motion analysis is a technique used to track the movement of objects using X-rays. This is done by placing the subject to be imaged in the center of the X-ray beam and recording the motion using an image intensifier and a high-speed camera, allowing for high quality videos sampled many times per second. Depending on the settings of the X-rays, this technique can visualize specific structures in an object, such as bones or cartilage. X-ray motion analysis can be used to perform gait analysis, analyze joint movement, or record the motion of bones obscured by soft tissue. The ability to measure skeletal motions is a key aspect to one's understanding of vertebrate biomechanics, energetics, and motor control. Imaging Methods Planar Many X-ray studies are performed with a single X-ray emitter and camera. This type of imaging allows for tracking movements in the two-dimensional plane of the X-ray. Movements are performed parallel to the camera's imaging plane in order for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axolotl
The axolotl (; from nci, āxōlōtl ), ''Ambystoma mexicanum'', is a paedomorphic salamander closely related to the tiger salamander. Axolotls are unusual among amphibians in that they reach adulthood without undergoing metamorphosis. Instead of taking to the land, adults remain aquatic and gilled. The species was originally found in several lakes underlying what is now Mexico City, such as Lake Xochimilco and Lake Chalco. These lakes were drained by Spanish settlers after the conquest of the Aztec Empire, leading to the destruction of much of the axolotl’s natural habitat. Axolotls should not be confused with the larval stage of the closely related tiger salamander (''A. tigrinum''), which are widespread in much of North America and occasionally become paedomorphic. Neither should they be confused with mudpuppies (''Necturus'' spp.), fully aquatic salamanders from a different family that are not closely related to the axolotl but bear a superficial resemblance. , wild ax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue-tongued Skink
Blue-tongued skinks comprise the Australasian genus ''Tiliqua'', which contains some of the largest members of the skink family (Scincidae). They are commonly called blue-tongued lizards or simply blue-tongues or blueys in Australia. As suggested by these common names, a prominent characteristic of the genus is a large blue tongue that can be bared as bluff-warning to potential enemies. The type of predator/threat that is near will determine the intensity of colour present in the tongue. In addition, their blue tongue will produce a response in the prey which will in turn diminish the attack. The tongue can also deform itself and produce a thick mucus in order to catch prey. They are relatively shy in comparison with other lizards, and also significantly slower due to their shorter legs. Systematics and distribution Blue-tongued skinks are closely related to the genera ''Cyclodomorphus'' and '' Hemisphaeriodon''. All species are found on mainland Australia with the exception of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw-Hill Connect. Webp.274/ref> They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement (only during birth) in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally. Classification The number of joints depends on if sesamoids are included, age of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_3069938647.jpg)
