|
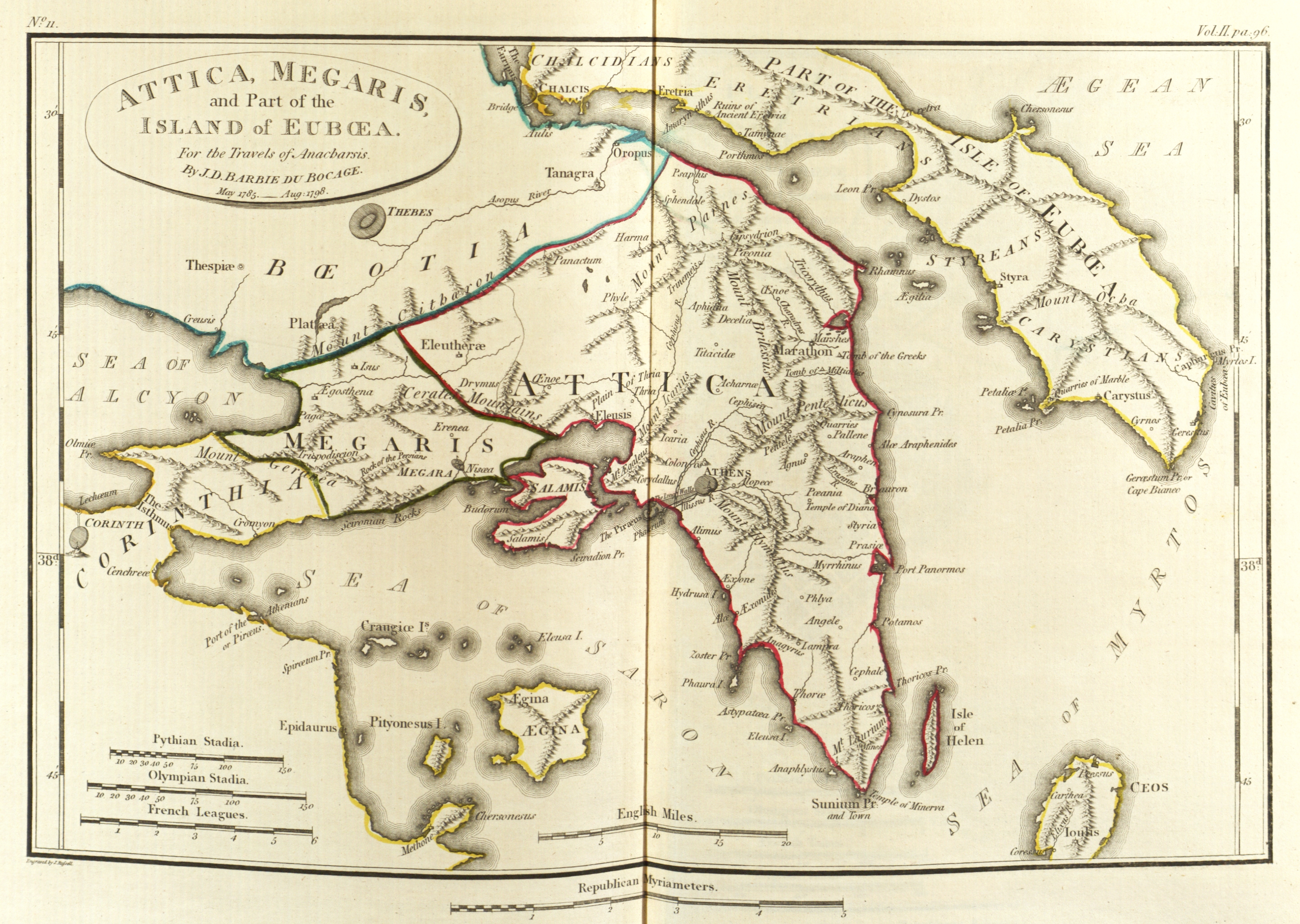
Oenoe (Attica)
Oenoe or Oinoe ( grc, Οἰνόη) was a deme of Athens, situated upon the confines of Boeotia and Attica, near Eleutherae, and upon the regular road to Plataea and Thebes. Hysiae and Oenoe are mentioned as the frontier demi of Attica in 507 BC, when they were both taken by the Boeotians. From this time Hysiae continued to be a Boeotian town; but Oenoe was recovered by the Athenians, and was fortified by them before the commencement of the Peloponnesian War. In 411 BC, the Boeotians again obtained possession of Oenoe; but it must have been recovered a second time by the Athenians, as it continues to be mentioned as an Attic demus down to the latest times. Oenoe was situated on the Pythian Way, so called because it led from Athens to Delphi: this road apparently branched off from the Sacred Way to Eleusis, near the tomb of Strato. Near Oenoe was a Pythium, or temple of Apollo Pythius, in consequence of the sanctity of which Oenoe obtained the epithet of the Sacred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deme
In Ancient Greece, a deme or ( grc, δῆμος, plural: demoi, δημοι) was a suburb or a subdivision of Athens and other city-states. Demes as simple subdivisions of land in the countryside seem to have existed in the 6th century BC and earlier, but did not acquire particular significance until the reforms of Cleisthenes in 508 BC. In those reforms, enrollment in the citizen-lists of a deme became the requirement for citizenship; prior to that time, citizenship had been based on membership in a phratry, or family group. At this same time, demes were established in the main city of Athens itself, where they had not previously existed; in all, at the end of Cleisthenes' reforms, Athens was divided into 139 demes, to which one can be added Berenikidai (established in 224/223 BC), Apollonieis (201/200 BC), and Antinoeis (added in 126/127). The establishment of demes as the fundamental units of the state weakened the ''gene'', or aristocratic family groups, that had dominated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleusis
Elefsina ( el, Ελευσίνα ''Elefsina''), or Eleusis (; Ancient Greek: ''Eleusis'') is a suburban city and municipality in the West Attica regional unit of Greece. It is situated about northwest from the centre of Athens and is part of its metropolitan area. It is located in the Thriasio Plain, at the northernmost end of the Saronic Gulf. North of Elefsina are Mandra and Magoula, while Aspropyrgos is to the northeast. It is the site of the Eleusinian Mysteries and the birthplace of Aeschylus. Today, Elefsina is a major industrial centre, with the largest oil refinery in Greece as well as the home of the Aeschylia Festival, the longest-lived arts event in the Attica Region. On 11 November 2016, Elefsina was named the European Capital of Culture for 2021. Etymology The word Eleusis first appears at the Orphic hymn «Δήμητρος Ελευσινίας, θυμίαμα στύρακα». Also Hesychius of Alexandria reports that the older name for Eleusis was Saesa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Ancient Attica
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Cithaeron
Cithaeron or Kithairon (Κιθαιρών, -ῶνος) is a mountain and mountain range about sixteen kilometres (ten miles) long in Central Greece. The range is the physical boundary between Boeotia in the north and Attica in the south. It is mainly composed of limestone and rises to . The north-east side of the range is formed by the mountain Pastra. The range was the scene of many events in Greek mythology and was especially sacred to Dionysus. In Euripides' ''Bacchae'', Dionysus carries out his dances and rites with his bacchants, his priestesses, on Cithaeron. Oedipus was exposed on the mountain, while Actaeon and Pentheus were both dismembered on its slopes. It was also the place where Heracles or Alcathous hunted and killed the Lion of Cithaeron. In historic times, the mountain acted as a backdrop to the Battle of Plataea of 479 BC and was the scene of much skirmishing before the battle itself. In later times, fortifications were built both at Plataea and Erythrai as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandion II
In Greek mythology, Pandion II ( or ; Ancient Greek: Πανδίων) was a legendary King of Athens, the son and heir of King Cecrops II and his wife Metiadusa, daughter of Eupalamus. Family Pandion was the father of Aegeus, Pallas, Nisos, Lycus and the wife of Sciron by Pylia, daughter of King Pylas of Megara. Mythology Pandion II was the eighth king of Athens in the traditional line of succession as given by the third century BC Parian Chronicle, the chronographer Castor of Rhodes (probably from the late third-century Eratosthenes) and the '' Bibliotheca''. He was preceded by Cecrops I, Cranaus, Amphictyon, Erichthonius, Pandion I, Erechtheus, and Cecrops II, and succeeded by Aegeus and Theseus. Castor gives his reign as 25 years (1307/6–1282/1). Originally there may have been a single Pandion, and either Pandion I or Pandion II may have been a later invention in order to fill a gap in the mythical history of Athens. Pausanias calls this Pandion the father of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaris
:''This is also the ancient Greek name of a small island off Naples, site of the Castel dell'Ovo.'' Megaris ( grc, Μεγαρίς) was a small but populous state of ancient Greece, west of Attica and north of Corinthia, whose inhabitants were adventurous seafarers, credited with deceitful propensities. The capital, Megara, was famous for white marble and fine clay. Mount Geraneia dominates the center of the region. The island of Salamis was originally under the control of Megara, before it was lost to Athens in the late 7th century BCE. Province The province of Megaris or Megarida ( el, Επαρχία Μεγαρίδας or ) was one of the provinces of the East Attica Prefecture. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipalities Aspropyrgos, Eleusis, Mandra-Eidyllia Mandra-Eidyllia ( el, Μάνδρα-Ειδύλλια) is a municipality in the West Attica regional unit, Attica, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Mandra. The municipality has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nisos
In Greek mythology, Nisos or Nisus (Ancient Greek: Νῖσος) was a King of Megara. Family Nisos was one of the four sons of Pandion II, King of Athens, and Pylia, daughter of King Pylas of Megara. He was the brother of Aegeas, Pallas, Lykos and the wife of Sciron. According to Hyginus, Nisus's father was the god Ares while other authors affirmed that he was the offspring of Deion.Hyginus, ''Fabulae'198/ref> Nisos was married to Abrota, sister of Megareus, and when she died, Nisos commanded that the Megarian women should wear clothes like she had. His daughter Eurynome, with Poseidon, had the famous son Bellerophon. The second daughter Iphinoe married Megareus, her maternal uncle. Lastly, the third princess Scylla was responsible for Nisos' death. Mythology Early days Metion, the uncle of Nisos, had seized the throne from Pandion II. However, upon their father's death, Nisos and his brothers returned to Athens and took back control. They drove out the sons of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label= Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label=genitive, , ; , is one of the Olympian deities in classical Greek and Roman religion and Greek and Roman mythology. The national divinity of the Greeks, Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, music and dance, truth and prophecy, healing and diseases, the Sun and light, poetry, and more. One of the most important and complex of the Greek gods, he is the son of Zeus and Leto, and the twin brother of Artemis, goddess of the hunt. Seen as the most beautiful god and the ideal of the ''kouros'' (ephebe, or a beardless, athletic youth), Apollo is considered to be the most Greek of all the gods. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as ''Apulu''. As the patron deity of Delphi (''Apollo Pythios''), Apollo is an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strato Of Lampsacus
Strato of Lampsacus (; grc-gre, Στράτων ὁ Λαμψακηνός, Strátōn ho Lampsakēnós, – ) was a Peripatetic philosopher, and the third director (scholarch) of the Lyceum after the death of Theophrastus. He devoted himself especially to the study of natural science, and increased the naturalistic elements in Aristotle's thought to such an extent, that he denied the need for an active god to construct the universe, preferring to place the government of the universe in the unconscious force of nature alone. Life Strato, son of Arcesilaus or Arcesius, was born at Lampsacus between 340 and 330 BCE. He might have known Epicurus during his period of teaching in Lampsacus between 310 and 306 BCE. He attended Aristotle's school in Athens, after which he went to Egypt as tutor to Ptolemy, where he also taught Aristarchus of Samos. He returned to Athens after the death of Theophrastus (c. 287 BCE), succeeding him as head of the Lyceum. He died sometime between 270 and 268 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred Way
The Sacred Way ( grc, Ἱερὰ Ὁδός, ''Hierá Hodós''), in ancient Greece, was the road from Athens to Eleusis. It was so called because it was the route taken by a procession celebrating the Eleusinian Mysteries. The procession to Eleusis began at the Sacred Gate in the Kerameikos (the Athenian cemetery) on the 19th Boedromion. In the present day, the road from central Athens to Aegaleo and Chaidari (the old route to Eleusis) is called the Iera Odos after the ancient road. Mythos of Eleusis The sacred rites of Demeter were performed in Eleusis in Ancient Greece beginning as far back as the 15th Century BCE, according to some sources. According to the Homeric Hymns of the Archaic period, Demeter stopped at Eleusis during her quest for Persephone. The story describes how Demeter, persuaded to stay at the palace of Eleusis by its prince, Celeus, was given the task of raising Celeus's son Demophon. When she is discovered to be a Goddess by the queen Metaneira after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |