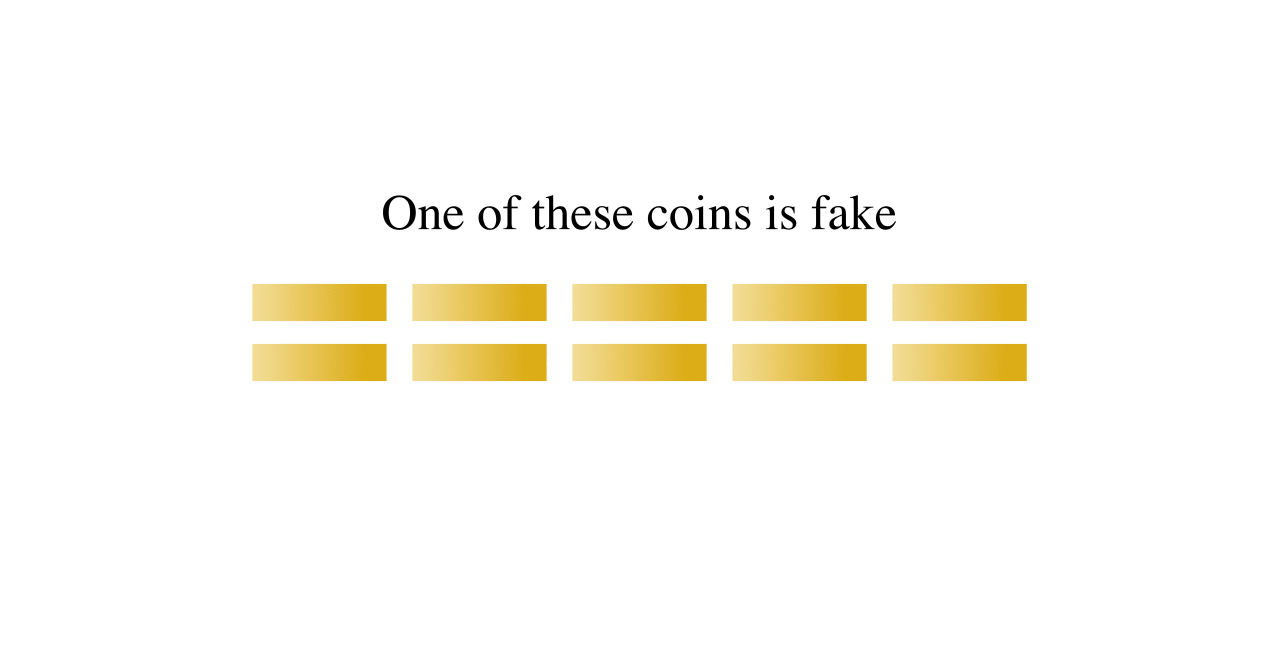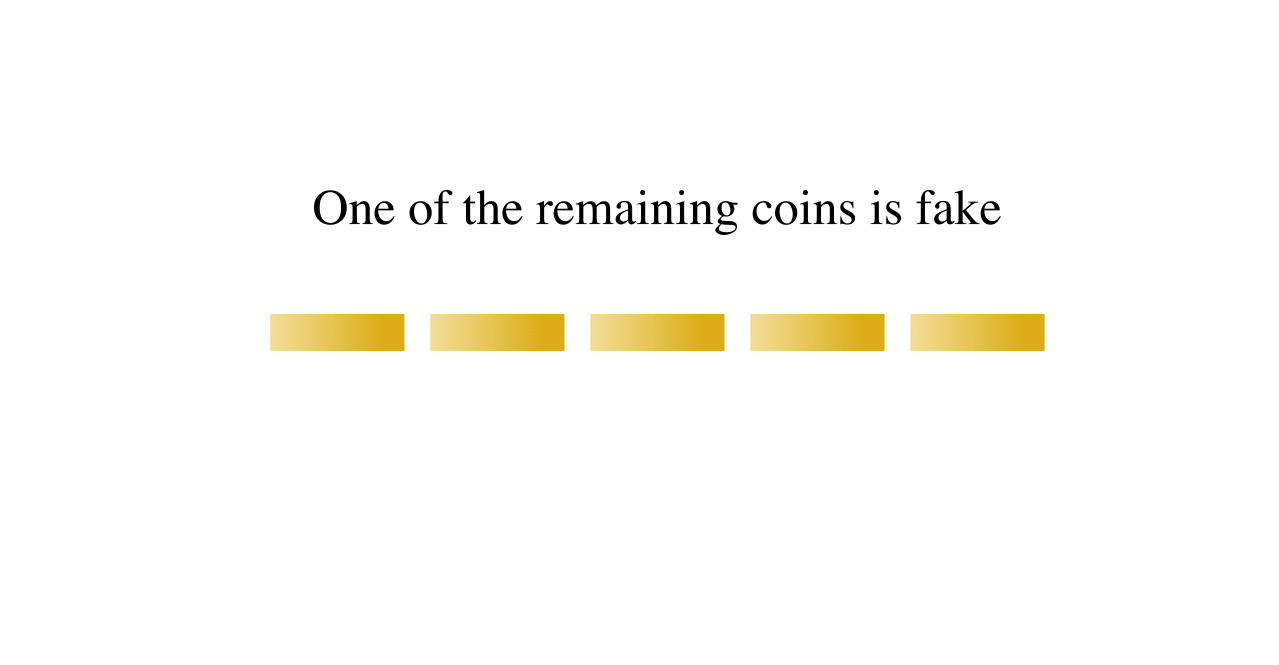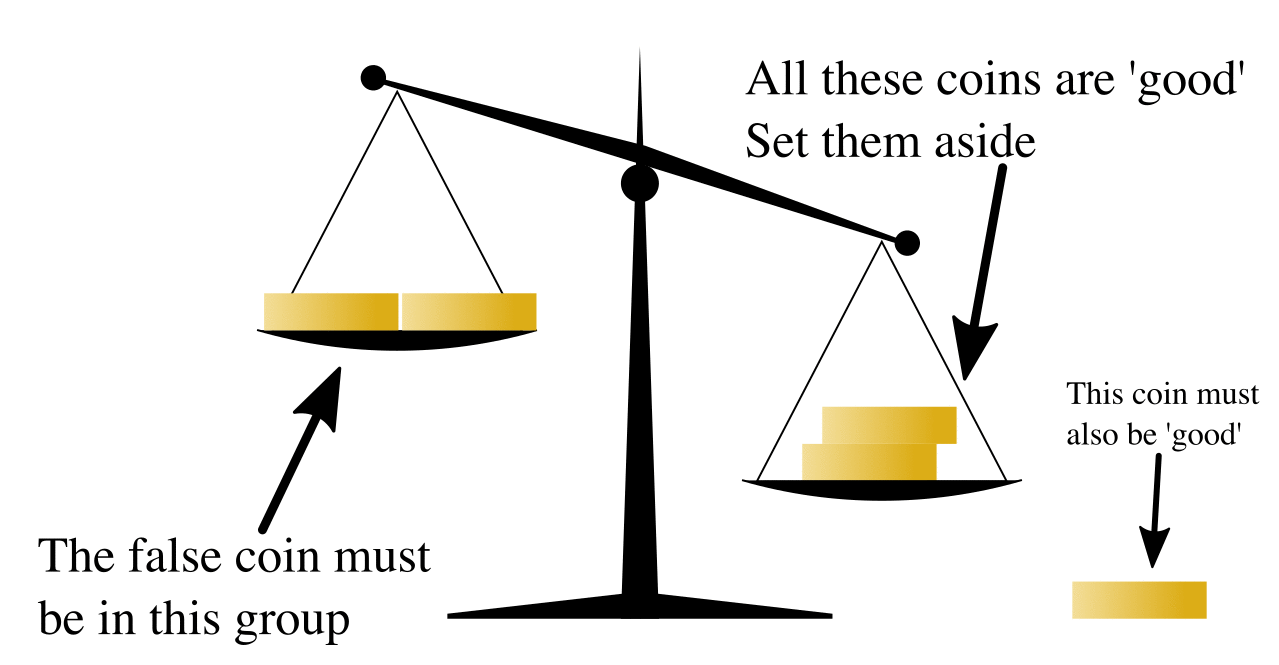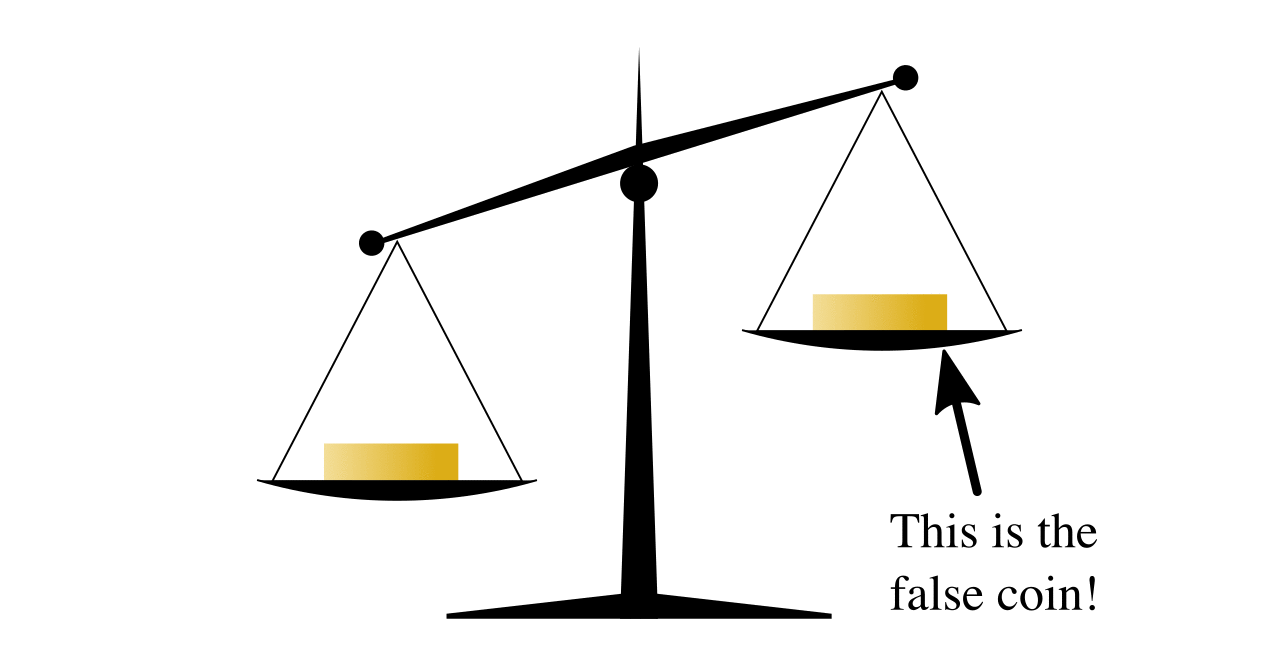|
OFAT
The one-factor-at-a-time method, also known as one-variable-at-a-time, OFAT, OF@T, OFaaT, OVAT, OV@T, OVaaT, or monothetic analysis is a method of design of experiments, designing experiments involving the testing of factors, or causes, one at a time instead of multiple factors simultaneously. Advantages OFAT is favored by non-experts, especially in situations where the data is cheap and abundant. There exist cases where the mental effort required to conduct a complex multi-factor analysis exceeds the effort required to acquire extra data, in which case OFAT might make sense. Furthermore, some researchers have shown that OFAT can be more effective than Fractional factorial design, fractional factorials under certain conditions (number of runs is limited, primary goal is to attain improvements in the system, and experimental error is not large compared to factor effects, which must be additive and independent of each other).Friedman, M., and Savage, L. J. (1947), “Planning Experi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factorial Design
In statistics, a full factorial experiment is an experiment whose design consists of two or more factors, each with discrete possible values or "levels", and whose experimental units take on all possible combinations of these levels across all such factors. A full factorial design may also be called a fully crossed design. Such an experiment allows the investigator to study the effect of each factor on the response variable, as well as the effects of interactions between factors on the response variable. For the vast majority of factorial experiments, each factor has only two levels. For example, with two factors each taking two levels, a factorial experiment would have four treatment combinations in total, and is usually called a ''2×2 factorial design''. In such a design, the interaction between the variables is often the most important. This applies even to scenarios where a main effect and an interaction is present. If the number of combinations in a full factorial design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Of Experiments
The design of experiments (DOE, DOX, or experimental design) is the design of any task that aims to describe and explain the variation of information under conditions that are hypothesized to reflect the variation. The term is generally associated with experiments in which the design introduces conditions that directly affect the variation, but may also refer to the design of quasi-experiments, in which natural conditions that influence the variation are selected for observation. In its simplest form, an experiment aims at predicting the outcome by introducing a change of the preconditions, which is represented by one or more independent variables, also referred to as "input variables" or "predictor variables." The change in one or more independent variables is generally hypothesized to result in a change in one or more dependent variables, also referred to as "output variables" or "response variables." The experimental design may also identify control variables that must b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractional Factorial Design
In statistics, fractional factorial designs are experimental designs consisting of a carefully chosen subset (fraction) of the experimental runs of a full factorial design. The subset is chosen so as to exploit the sparsity-of-effects principle to expose information about the most important features of the problem studied, while using a fraction of the effort of a full factorial design in terms of experimental runs and resources. In other words, it makes use of the fact that many experiments in full factorial design are often redundant, giving little or no new information about the system. Notation Fractional designs are expressed using the notation ''l''k − p, where ''l'' is the number of levels of each factor investigated, ''k'' is the number of factors investigated, and ''p'' describes the size of the fraction of the full factorial used. Formally, ''p'' is the number of ''generators'', assignments as to which effects or interactions are ''confounded'', ''i.e.'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balance Puzzle
A balance puzzle or weighing puzzle is a logic puzzle about balancing items—often coins—to determine which holds a different value, by using balance scales a limited number of times. These differ from puzzles that assign weights to items, in that only the relative mass of these items is relevant. For example, in detecting a dissimilar coin in three weighings (n = 3), the maximum number of coins that can be analyzed is = 13. Note that with 3 weighs and 13 coins, it is not always possible to determine the identity of the last coin (whether it is heavier or lighter than the rest), but merely that the coin is different. In general, with ''n'' weighs, you can determine the identity of a coin if you have - 1 or less coins. In the case n = 3, you can truly discover the identity of the different coin out of 12 coins. Nine-coin problem A well-known example has up to nine items, say coins (or balls), that are identical in weight except one, which is lighter than the others—a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronald Fisher
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher (17 February 1890 – 29 July 1962) was a British polymath who was active as a mathematician, statistician, biologist, geneticist, and academic. For his work in statistics, he has been described as "a genius who almost single-handedly created the foundations for modern statistical science" and "the single most important figure in 20th century statistics". In genetics, his work used mathematics to combine Mendelian genetics and natural selection; this contributed to the revival of Darwinism in the early 20th-century revision of the theory of evolution known as the modern synthesis. For his contributions to biology, Fisher has been called "the greatest of Darwin’s successors". Fisher held strong views on race and eugenics, insisting on racial differences. Although he was clearly a eugenist and advocated for the legalization of voluntary sterilization of those with heritable mental disabilities, there is some debate as to whether Fisher supported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficiency (statistics)
In statistics, efficiency is a measure of quality of an estimator, of an experimental design, or of a hypothesis testing procedure. Essentially, a more efficient estimator, needs fewer input data or observations than a less efficient one to achieve the Cramér–Rao bound. An ''efficient estimator'' is characterized by having the smallest possible variance, indicating that there is a small deviance between the estimated value and the "true" value in the L2 norm sense. The relative efficiency of two procedures is the ratio of their efficiencies, although often this concept is used where the comparison is made between a given procedure and a notional "best possible" procedure. The efficiencies and the relative efficiency of two procedures theoretically depend on the sample size available for the given procedure, but it is often possible to use the asymptotic relative efficiency (defined as the limit of the relative efficiencies as the sample size grows) as the principal compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceteris Paribus
' (also spelled '; () is a Latin phrase, meaning "other things equal"; some other English translations of the phrase are "all other things being equal", "other things held constant", "all else unchanged", and "all else being equal". A statement about a causal, empirical, or logical relation between two states of affairs is ''ceteris paribus'' if it is acknowledged that the statement, although usually accurate in expected conditions, can fail because of, or the relation can be abolished by, intervening factors. chapter 2 A ''ceteris paribus'' assumption is often key to scientific inquiry, because scientists seek to eliminate factors that perturb a relation of interest. Thus epidemiologists, for example, may seek to control independent variables as factors that may influence dependent variables—the outcomes of interest. Likewise, in scientific modeling, simplifying assumptions permit illustration of concepts considered relevant to the inquiry. An example in economics is " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |