|
Oława River
Oława (, , ) is a historic town in south-western Poland with 33,029 inhabitants (2019). It is situated in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, within the Wrocław metropolitan area. It is the seat of Oława County and of the smaller administrative district of Gmina Oława (although it is not part of the territory of the latter, as the town is an urban gmina in its own right). Etymology The name of the city comes from the Polish word root el-, ol-, which in Polish lands took also the form of oła-, meaning "water". The association with water refers to the location of the settlement between two rivers: the Oder and the Oława, which are close to each other, but only connect in Wrocław, which is away. The location of the city between rivers, pools and forests, and at the same time in the place of crossing the Oder River, favored the creation of a market settlement of Ślęża, and later a stronghold, a town. The locality was mentioned in the Old Polish, Latinized form of Oleva in a Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
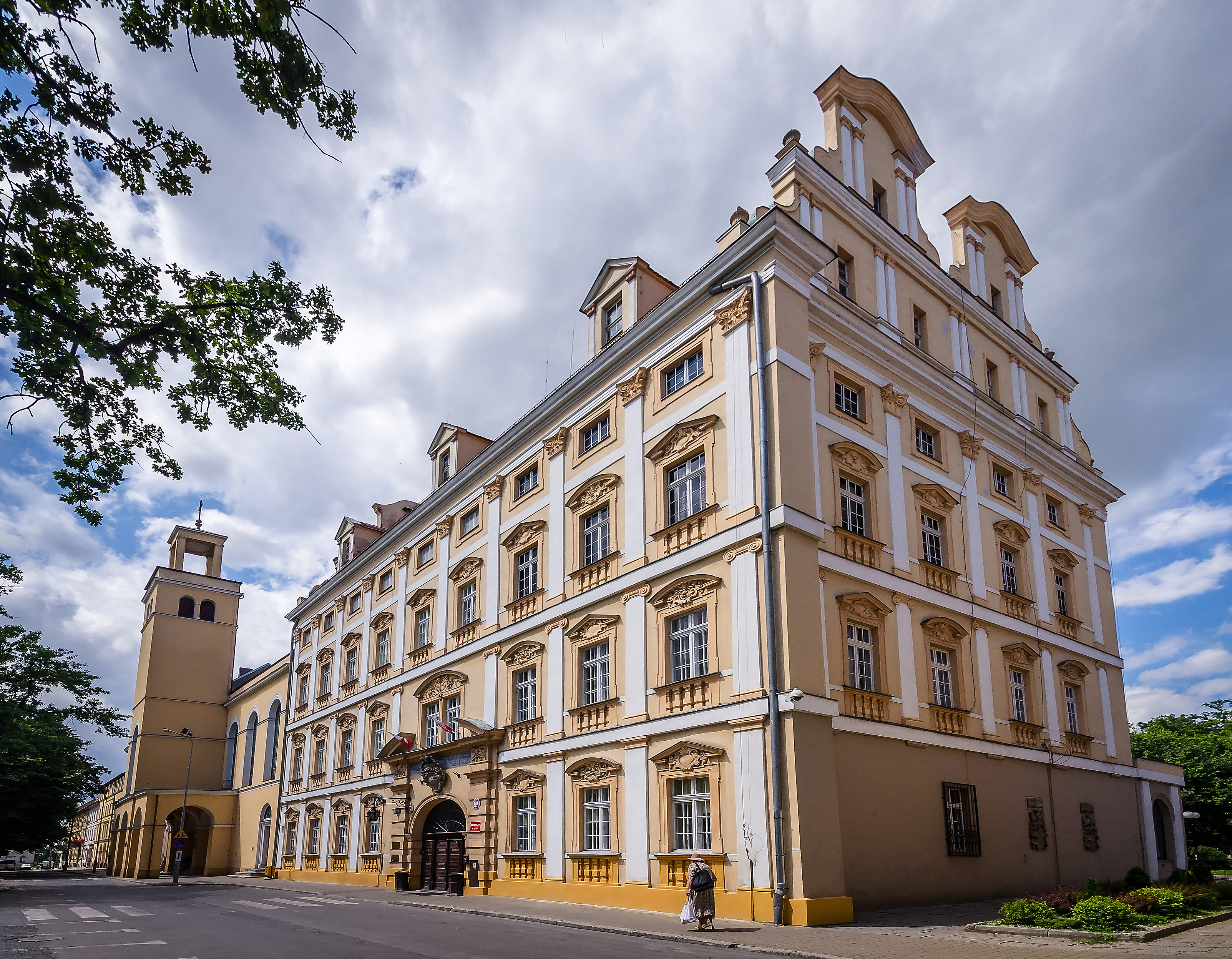
Oława Castle
Sobieski's Castle in Oława is a Renaissance-Baroque architecture, Baroque style castle located in the site of a former Gothic architecture, Gothic castle. The original castle had been built by Ludwik III of Oława, Duke Ludwik I built in the second half of the fourteenth century. It was the third castle structure in Oława, the first being the seat of the castellans, located in the south-east of the town. It remained an integral part of the town's defenses until the Hussite Wars, wars with the Hussites. Construction The Renaissance castle was built by master Jakub of Milan (most likely with the surname Pahr, builder of the Bolków Castle), continued by his brother-in-law Niuron, Bernard Niuron in 1588. After various reconstructions, this part of the castle now houses the local parish church's rectory of St. Apostle Peter and Paul. The reconstruction covered the whole of the Gothic architecture, Gothic castle, this included the now former west and northern wings of the castle-chur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
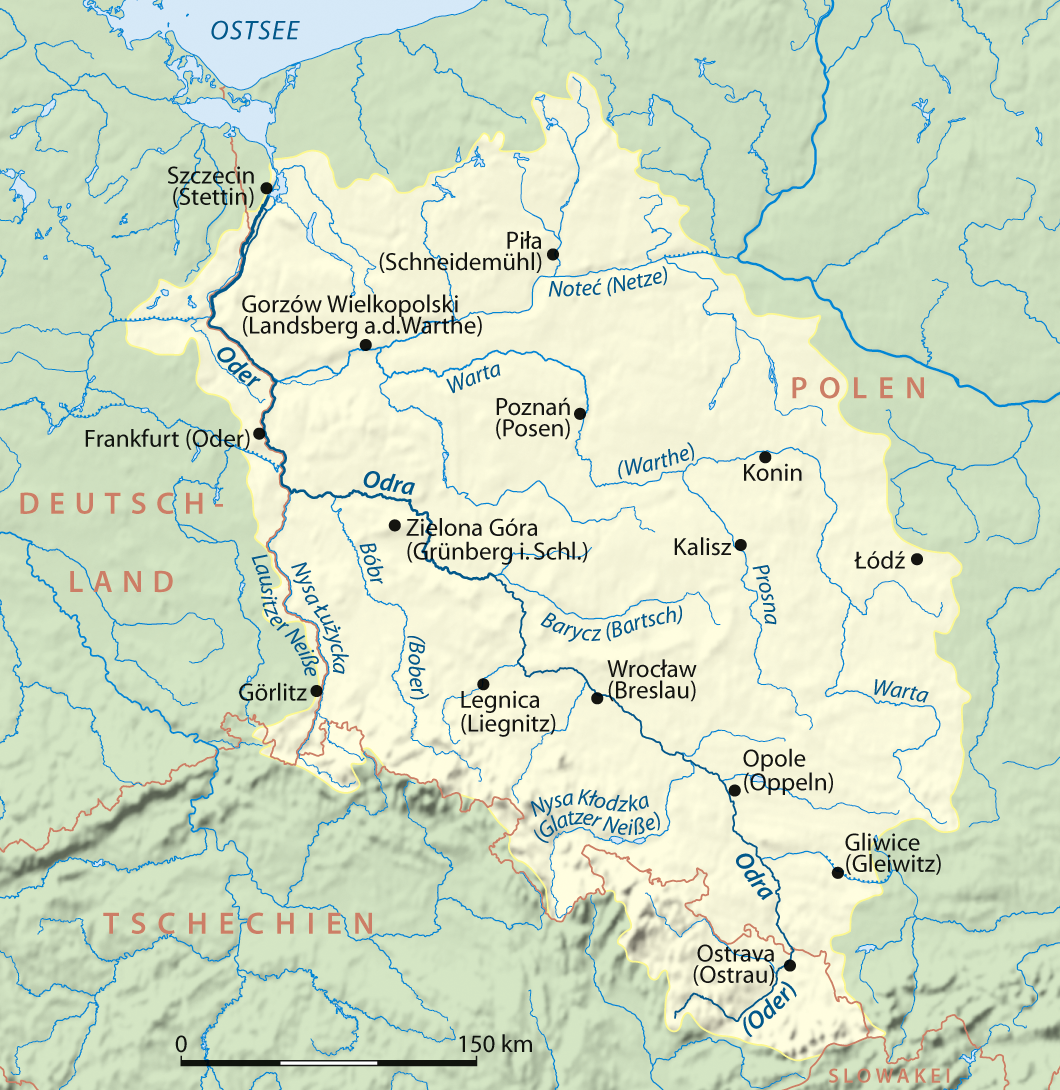
Oder
The Oder ( ; Czech and ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and its largest tributary the Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through western Poland, later forming of the border between Poland and Germany as part of the Oder–Neisse line. The river ultimately flows into the Szczecin Lagoon north of Szczecin and then into three branches (the Dziwna, Świna and Peene) that empty into the Bay of Pomerania of the Baltic Sea. Names The Oder is known by several names in different languages, but the modern ones are very similar: English and ; Czech, Polish, and , ; (); ; Medieval Latin: ''Od(d)era''; Renaissance Latin: ''Viadrus'' (invented in 1534). The origin of this name is said by onomastician Jürgen Udolph to come from the Illyrian word ''*Adra'' (“water vein”). Ptolemy knew the modern Oder as the Συήβος (''Suebos''; Latin ''Suevus''), a name apparen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casimir III Of Poland
Casimir III the Great (; 30 April 1310 – 5 November 1370) reigned as the King of Poland from 1333 to 1370. He also later became King of Ruthenia in 1340, retaining the title throughout the Galicia–Volhynia Wars. He was the last Polish king from the Piast dynasty. Casimir inherited a kingdom weakened by war and under his rule it became relatively prosperous and wealthy. He reformed the Polish army and doubled the size of the kingdom. He reformed the judicial system and introduced several undying codified statutes, gaining the title "the Polish Justinian". Casimir built extensively and founded the Jagiellonian University (back then simply called the University of Krakow),Saxton, 1851, p. 535 the oldest Polish university and one of the oldest in the world. He also confirmed privileges and protections previously granted to Jews and encouraged them to settle in Poland in great numbers. Casimir left no legitimate sons. When he died in 1370 from an injury received while hunting, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine, or disease, while parts of Germany reported population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659), Franco-Spanish War, the Torstenson War, the Dutch-Portuguese War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. The war had its origins in the 16th-century Reformation, which led to religious conflict within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Catholic and Lutheran states, but the settlement was destabilised by the subsequent expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries. Combined with differences over the limits of imperial authority, religion was thus an important factor in star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
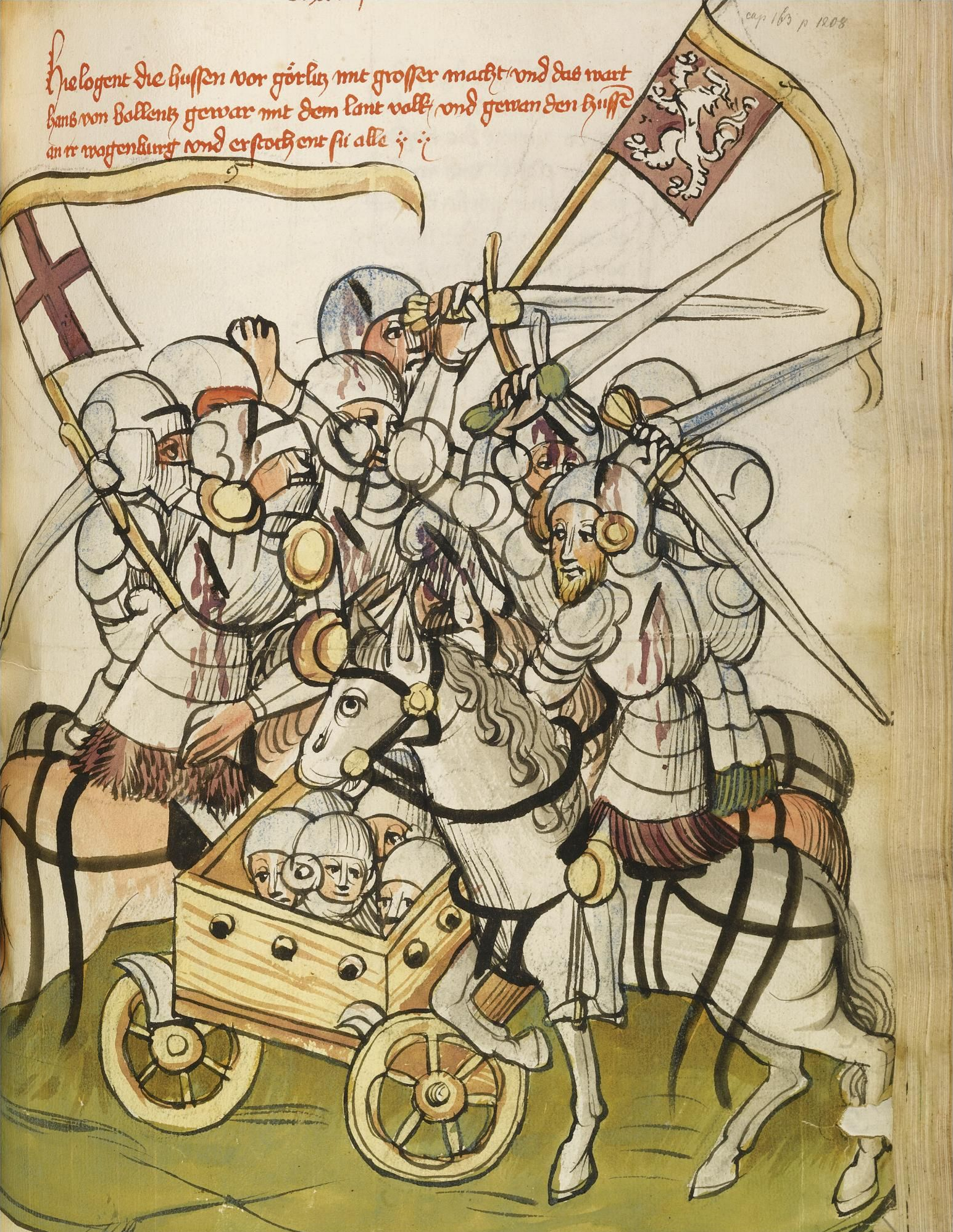
Hussites
upright=1.2, Battle between Hussites (left) and Crusades#Campaigns against heretics and schismatics, Catholic crusaders in the 15th century upright=1.2, The Lands of the Bohemian Crown during the Hussite Wars. The movement began during the Prague.html" ;"title="Renaissance in Prague">Renaissance in Prague and quickly spread south and then through the rest of the Kingdom of Bohemia. Eventually, it expanded into the remaining domains of the Bohemian Crown as well. The Hussites (Czech: ''Husité'' or ''Kališníci'', "Chalice People"; Latin: ''Hussitae'') were a Czech Proto-Protestantism, proto-Protestant Christian movement influenced by both the Byzantine Rite and John Wycliffe that followed the teachings of reformer Jan Hus (fl. 1401–1415), a part of the Bohemian Reformation. The Czech lands had originally been Christianized by Byzantine Greek missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius, who introduced the Byzantine Rite in the Old Church Slavonic liturgical language and the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Mongol Invasion Of Poland
The Mongol invasion of Poland from late 1240 to 1241 culminated in the Battle of Legnica, where the Mongols defeated an alliance which included forces from Testament of Bolesław III Wrymouth, fragmented Poland and their allies, led by Henry II the Pious, the Duke of Silesia and High Duke of Poland. The first invasion's intention was to secure the flank of the main Mongolian army attacking the Kingdom of Hungary. The Mongols neutralized any potential help to King Béla IV of Hungary, Béla IV being provided by the Poles or any military orders. Background The Mongol invasion of Europe, Mongols invaded Europe with three armies. One of the three armies was tasked with distracting Poland, before joining the main Mongol force invading Hungary. The Mongol general in charge, Subutai, did not want the Polish forces to be able to threaten his flank during the primary invasion of Hungary. Thus, the Mongol goal was to use a small detachment to prevent the Poles from assisting Hungary un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Bernhard Werner Zamek W Oławie
Friedrich may refer to: Names *Friedrich (given name), people with the given name ''Friedrich'' *Friedrich (surname), people with the surname ''Friedrich'' Other *Friedrich (board game), a board game about Frederick the Great and the Seven Years' War * ''Friedrich'' (novel), a novel about anti-semitism written by Hans Peter Richter *Friedrich Air Conditioning, a company manufacturing air conditioning and purifying products *, a German cargo ship in service 1941-45 See also *Friedrichs (other) *Frederick (other) *Nikolaus Friedreich Nikolaus Friedreich (1 July 1825 in Würzburg – 6 July 1882 in Heidelberg) was a German pathologist and neurologist, and a third generation physician in the Friedreich family. His father was psychiatrist Johann Baptist Friedreich (1796–18 ... {{disambig ja:フリードリヒ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
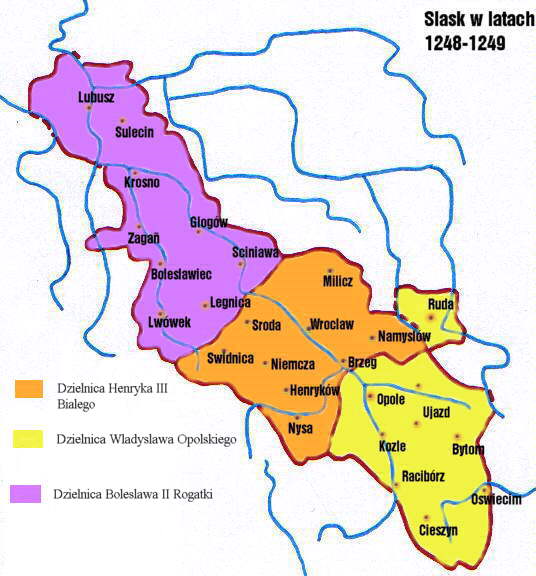
Duchy Of Brzeg
The Duchy of Brzeg () or Duchy of Brieg (; ) was one of the Duchies of Silesia, created in 1311 during the fragmentation of the Duchy of Legnica. A Bohemian fief from 1329, it was ruled by the Silesian Piasts until their extinction in 1675. Its capital was Brzeg in Lower Silesia. History When the Piast duke Henry V of Wrocław and Legnica died in 1296, his sons and heirs were still minors and his estates were ruled by their uncle Duke Bolko I the Strict of Świdnica, succeeded by their maternal uncle King Wenceslaus II of Bohemia in 1301 and by the Wrocław bishop Henry of Wierzbno in 1305. Finally in 1311, Henry's bequests were divided among his sons: Bolesław III the Generous, the eldest brother, received the southeastern lands around Brzeg and Grodków. Soon after however, Bolesław insisted on his rights as the firstborn son and ousted his younger brother Władysław from the Duchy of Legnica. He maintained good relations with his brother-in-law, the Luxembourg king John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Legnica
The Duchy of Legnica (, ) or Duchy of Liegnitz () was one of the Duchies of Silesia, formed during the fragmentation of Poland into smaller provincial duchies, ruled by a local line of the Piast dynasty between 1248 and 1675. Its capital was Legnica in Lower Silesia. Legnica Castle had become a residence of the Silesian dukes in 1163 and from 1248 was the seat of a principality in its own right, ruled by the Silesian branch of the Piast dynasty until the extinction of the line in 1675. Formed by Bolesław II the Bald, Duke of Lower Silesia at Wrocław, Legnica shared the fate of most of the others Silesian duchies, falling into Bohemian, Austrian and eventually—after the First Silesian War— Prussian spheres of influence. States and territories disestablished in the 1670s History The town of Legnica became famous for the Battle of Legnica that took place at the nearby village of Legnickie Pole on 9 April 1241, during the first Mongol invasion of Poland. A Christian army ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Silesia
The Duchy of Silesia (, ) with its capital at Wrocław was a medieval provincial duchy of Poland located in the region of Silesia. Soon after it was formed under the Piast dynasty in 1138, it fragmented into various Silesian duchies. In 1327, the remaining Duchy of Wrocław as well as most other duchies ruled by the Silesian Piasts passed under the suzerainty of the Kingdom of Bohemia as the Duchies of Silesia. The acquisition was completed when King Casimir III the Great of Poland renounced his rights to Silesia in the 1335 Treaty of Trentschin. Geography During the time of its establishment, the Silesian lands covered the basin of the upper and middle Oder river. In the south the Sudetes mountain range up to the Moravian Gate formed the border with the lands of Bohemia – including Kłodzko Land – and Moravia. After a more than century-long struggle, the boundary had just been determined by an 1137 agreement with the Bohemian duke Soběslav I. In the west Lower S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, roughly from the Sudetes, Sudeten Mountains to the north. In 2023, the official population of Wrocław was 674,132, making it the third-largest city in Poland. The population of the Wrocław metropolitan area is around 1.25 million. Wrocław is the historical capital of Silesia and Lower Silesia. The history of the city dates back over 1,000 years; at various times, it has been part of the Kingdom of Poland, the Kingdom of Bohemia, the Kingdom of Hungary, the Habsburg monarchy of Austria, the Kingdom of Prussia and German Reich, Germany, until it became again part of Poland in 1945 immediately after World War II. Wrocław is a College town, university city with a student population of over 130,000, making it one of the most yo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piotr Włostowic
Herb ŁabędźPiotr Włostowic (or Włost; 1080 – 1153), also known as Peter Wlast, was a Polish noble, castellan of Wrocław, and a ruler (''możnowładca'') of part of Silesia. From 1117 he was voivode (''palatyn'') of the Duke of Poland Bolesław III Wrymouth. Part of the Łabędzie family, and son of Włost, he is likely to have been related to older princes of Silesia. His lands included the territories near Mount Ślęża and Piasek Island near Wrocław. The Dunin clan of noble families claims descent from him. His most famous deed is the capture of Volodar (Wołodar) of Peremyshl (Przemyśl). Later he married Maria, a daughter of Sviatopolk II of Kiev. For this marriage and his adventure in Rus', he was ordered by the Church to reconcile. He was ordered to construct seventy churches. Włostowic, a loyal subject of Bolesław III, had much more negative relations with Bolesław's son, Władysław II the Exile, and especially his wife, Agnes of Babenberg, who co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |