|
Overton Corners–Lacolle 221 Border Crossing
The Overton Corners–Lacolle 221 Border Crossing connects the towns of Lacolle, Quebec to Champlain, New York on the Canada–United States border. This crossing is open 24 hours per day, 365 days per year. Because the village of Lacolle, Quebec has two border crossings, this one is called 221 to indicate it is the crossing on Quebec Route 221. The other crossing is the Rouses Point–Lacolle 223 Border Crossing immediately to the east. Conversely, the US Border station is sometimes called 276 because it is located on New York State Route 276. During the era of Prohibition in the United States, this crossing was one of the busiest on the US-Canada border. The roads leading to it in both the US and Canada were in good condition and was a popular route for traffic traveling between Montreal and New York City. During that era, it was common for large queues of southbound traffic to build up approaching US Customs, as people attempted to smuggle alcohol into the United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Office Of The Supervising Architect
The Office of the Supervising Architect was an agency of the United States Treasury Department that designed federal government buildings from 1852 to 1939. About The office handled some of the most important architectural commissions of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. Among its creations are the well-known State, War, and Navy building (now the Eisenhower Executive Office Building) in Washington, DC, the San Francisco Mint Building, and smaller post offices that have served communities for decades, many recognized as National Historic Landmarks, listed in the National Register of Historic Places, or designated as local landmarks. Tarsney Act Until 1893 the office used in-house architects. In 1893 Missouri congressman John Charles Tarsney introduced a bill that allowed the Supervisory Architect to have competitions among private architects for major structures. Competitions were held for the Alexander Hamilton U.S. Custom House, Cleveland Federal Building, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Clinton County, New York
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. Geography has been called "a bridge between natural science and social science disciplines." Origins of many of the concepts in geography can be traced to Greek Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who may have coined the term "geographia" (). The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as the title of a book by Greek scholar Claudius Ptolemy (100 – 170 AD). This work created the so-called "Ptolemaic tradition" of geography, which included "Ptolemaic cartographic theory." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places Listings In Clinton County, New York
List of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Clinton County, New York This is intended to be a complete list of National Register of Historic Places in Clinton County, New York Clinton County is the northeasternmost county in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 79,843. Its county seat is the city of Plattsburgh. The county lies just south of the border with the Cana .... The locations of National Register properties and districts for which the latitude and longitude coordinates are included below, may be seen in a map.The latitude and longitude information provided is primarily from the National Register Information System, and has been found to be fairly accurate for about 99% of listings. For 1%, the location info may be way off. We seek to correct the coordinate information wherever it is found to be erroneous. Please leave a note in the Discussion page for this article if you believe any specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Canada–United States Border Crossings
This article includes lists of border crossings, ordered from west to east (north to south for Alaska crossings), along the Canada–United States border. Each port of entry (POE) in the tables below links to an article about that crossing. On the U.S. side, each crossing has a three-letter Port of entry, Port of Entry code. This code is also seen on Passport stamp#United States, passport entry stamp or Parole (United States immigration), parole stamp. The list of codes is administered by the United States Department of State, Department of State. Note that one code may correspond to multiple crossings. Land ports of entry Port of entry hours of service for road crossings, except where noted, are open year-round during the day. Unstaffed road crossings This is a list of roads that cross the U.S.–Canada border that do not have border inspection services, but where travelers are legally allowed to cross the border in one or both directions. In prior years, there were do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trout River Border Crossing
Trout River is a border crossing connecting Elgin, Quebec to Constable, New York on the Canada–US border, most prominently featuring the Trout River Border Inspection Station. The crossing can be reached by New York State Route 30 on the American side and by Quebec Route 138 on the Canadian side. Historically, Trout River was the primary crossing of the Trout River, NY port of Entry. This distinction is due to the fact that the U.S. Customs and Border Protection defines a port of entry as 'any designated place at which a CBP officer is authorized to accept entries of merchandise to collect duties, and to enforce the various provisions of the customs and navigation laws'. This means that the border stations of Fort Covington and Churubusco are facilities of the Trout River Port of Entry. There are several buildings near this crossing that were built prior to the establishment of the US-Canada border in 1842. These include a former duty-free shop and two residences. US Borde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plattsburgh, New York
Plattsburgh is a city in and the county seat of Clinton County, New York, United States, situated on the north-western shore of Lake Champlain. The population was 19,841 at the United States Census, 2020, 2020 census. The population of the surrounding (and separately incorporated) Plattsburgh (town), New York, Town of Plattsburgh was 11,886 as of the United States Census, 2020, 2020 census, making the combined population of Plattsburgh to be 31,727. Plattsburgh lies just to the northeast of Adirondack Park, immediately outside of the park boundaries. It is the second largest community in the North Country (New York), North Country region (after Watertown, New York, Watertown), and serves as the main commercial hub for the sparsely populated northern Adirondack Mountains. The land around Plattsburgh was previously inhabited by the Iroquois, Western Abenaki, Mohican, and Mohawk people. Samuel de Champlain was the first ever recorded European that sailed into Champlain Valley and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
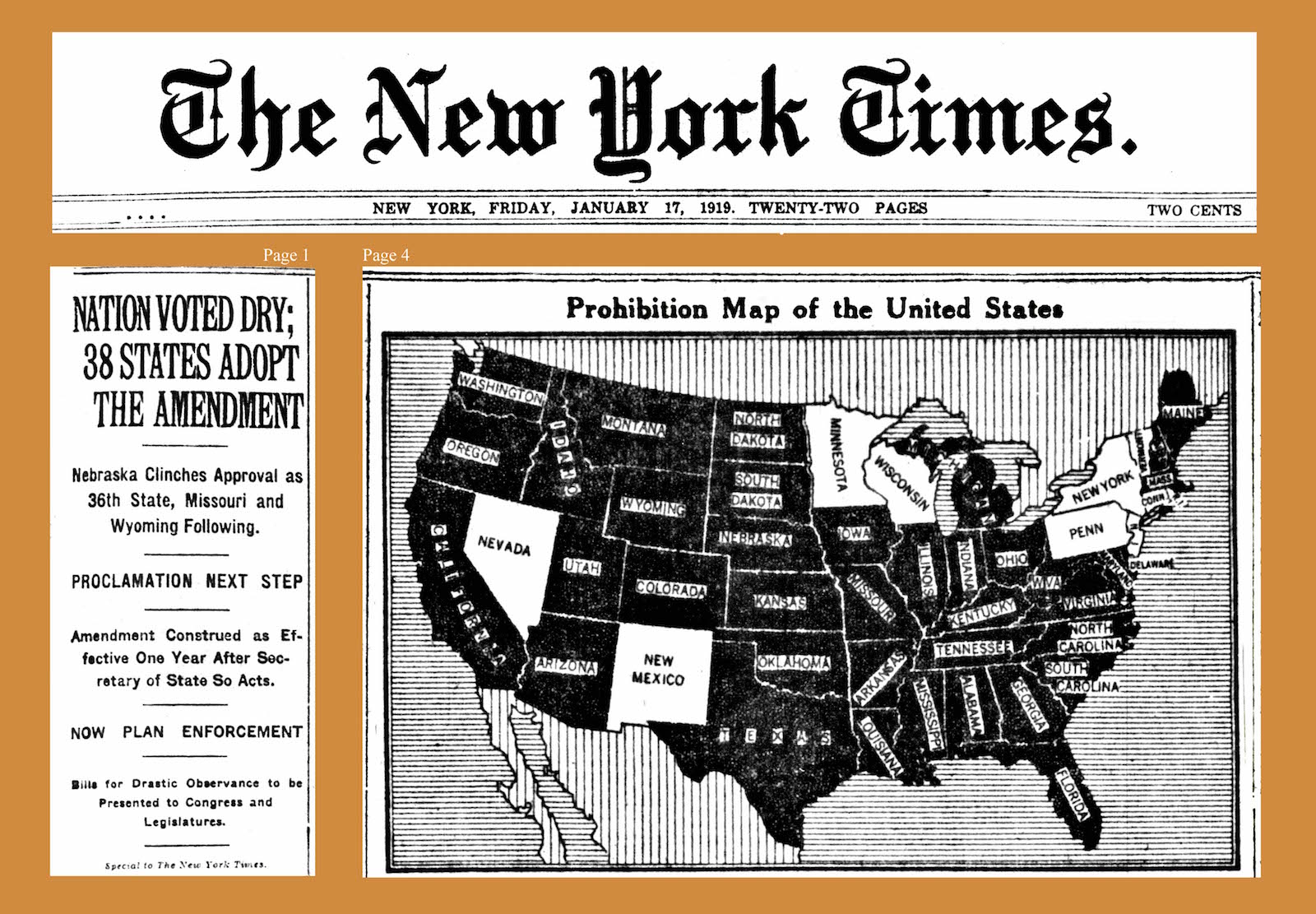
Eighteenth Amendment To The United States Constitution
The Eighteenth Amendment (Amendment XVIII) to the United States Constitution established the prohibition of alcohol in the United States. The amendment was proposed by Congress on December 18, 1917, and ratified by the requisite number of states on January 16, 1919. The Eighteenth Amendment was repealed by the Twenty-first Amendment on December 5, 1933, making it the only constitutional amendment in American history to be repealed. The Eighteenth Amendment was the product of decades of efforts by the temperance movement, which held that a ban on the sale of alcohol would ameliorate poverty and other societal problems. The Eighteenth Amendment declared the production, transport and sale of intoxicating liquors illegal, although it did not outlaw the actual consumption of alcohol. Shortly after the amendment was ratified, Congress passed the Volstead Act to provide for the federal enforcement of Prohibition. The Volstead Act declared that liquor, wine and beer qualified as in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volstead Act
The National Prohibition Act, known informally as the Volstead Act, was an act of the 66th United States Congress designed to execute the 18th Amendment (ratified January 1919) which established the prohibition of alcoholic drinks. The Anti-Saloon League's Wayne Wheeler conceived and drafted the bill, which was named after Andrew Volstead, chairman of the House Judiciary Committee, who managed the legislation. Historical context The Volstead Act had a number of contributing factors that led to its ratification in 1919. For example, the formation of the Anti-Saloon League in 1893. The league used the after effects of World War I to push for national prohibition because there was a lot of prejudice and suspicion of foreigners following the war. Many reformers used the war to get measures passed and a major example of this was national prohibition. The league was successful in getting many states to ban alcohol prior to 1917 by claiming that to drink was to be pro-German an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Ford
Henry Ford (July 30, 1863 – April 7, 1947) was an American Technological and industrial history of the United States, industrialist and business magnate. As the founder of the Ford Motor Company, he is credited as a pioneer in making automobiles affordable for middle-class Americans through the system that came to be known as Fordism. In 1911, he was awarded a patent for the transmission mechanism that would be used in the Ford Model T and other automobiles. Ford was born in a farmhouse in Springwells Township, Michigan, and left home at the age of 16 to find work in Detroit. It was a few years before this time that Ford first experienced automobiles, and throughout the later half of the 1880s, he began repairing and later constructing engines, and through the 1890s worked with DTE Electric Company, a division of Edison Electric. He founded the Ford Motor Company in 1903 after prior failures in business, but success in constructing automobiles. The introduction of the Ford M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Buildings Act
The Public Buildings Act of 1926, also known as the Elliot–Fernald Act, was a statute which governed the construction of federal buildings throughout the United States, and authorized funding for this construction. Its primary sponsor in the House of Representatives was Representative Richard N. Elliott of Indiana (who served on the House Committee on Public Buildings and Grounds), and its primary sponsor in the Senate was Bert M. Fernald of Maine (who served on the Senate Committee on Public Buildings and Grounds. Congress had provided funding for no federal buildings between 1913 and 1926. The U.S. federal government had struggled with the need to build a number of large governmental office buildings since the mid-1910s, but little had been done. In January 1924, the Public Buildings Commission (an independent agency of the executive branch) recommended that a new series of federal office buildings be built near the White House. President Calvin Coolidge asked the United S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |