|
Outbreak Intensity Score
Thomas P. Grazulis (born August 17, 1942) is an American meteorologist who has written extensively about tornadoes and produced documentaries as head of ''The Tornado Project''. Biography Early career Thomas Grazulis grew up in Worcester, Massachusetts and first confronted the power of a tornado at age 11 following the violent 1953 Worcester tornado, an F4 which killed 94 people and passed approximately north of his childhood home. Grazulis earned a bachelor's degree in meteorology from Florida State University (FSU) and was briefly a broadcaster, in part presenting the weather. He was a science teacher in New Jersey and worked on the "Earth Science Curriculum Project" with the National Science Foundation (NSF). He and his wife Doris, also a teacher and a small business operator, then moved to the St. Johnsbury, Vermont area in 1970. In 1972, they released ''Approaching the Unapproachable'', a documentary film on tornadoes that was the first to consider tornadoes in a sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Worcester, Massachusetts
Worcester ( , ) is the List of municipalities in Massachusetts, second-most populous city in the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the list of United States cities by population, 113th most populous city in the United States. Named after Worcester, England, the city had 206,518 people at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, also making it the second-List of cities in New England by population, most populous city in New England, after Boston, Massachusetts. Worcester is about west of Boston, east of Springfield, Massachusetts, and north-northwest of Providence, Rhode Island. Because it is near the geographic center of Massachusetts, Worcester is known as the "Heart of the Commonwealth"; a heart is the official symbol of the city. Worcester is the historical county seat, seat of Worcester County, Massachusetts, Worcester County. Worcester developed as an industrial city in the 19th century because the Blackstone Canal and railways facilitated the import of raw materials and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
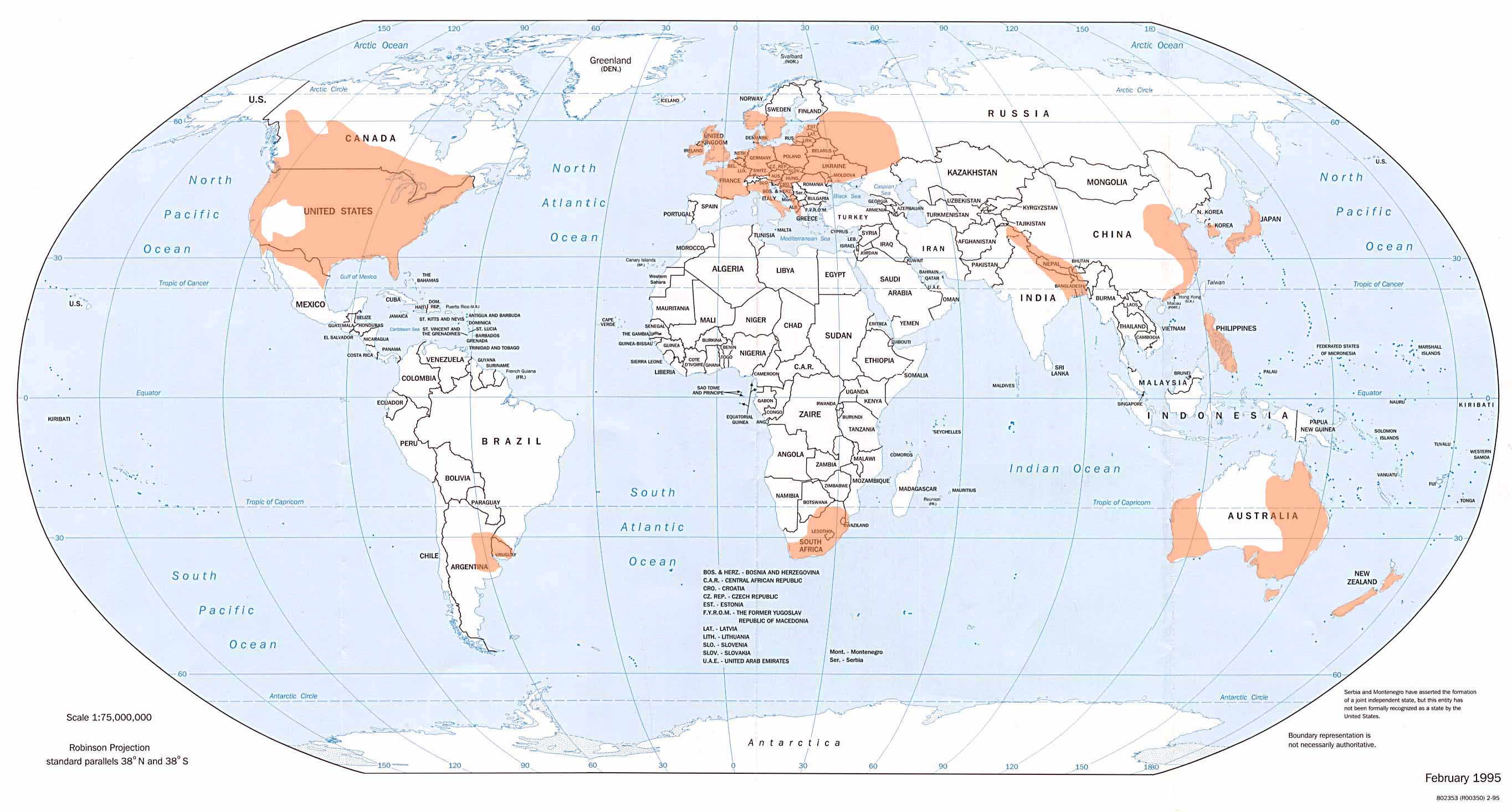
Tornado Climatology
Tornadoes have been recorded on all continents except Antarctica. They are most common in the middle latitudes where conditions are often favorable for convective storm development. The United States has the most tornadoes of any country, as well as the strongest and most violent tornadoes. A large portion of these tornadoes form in an area of the central United States popularly known as Tornado Alley. Canada experiences the second most tornadoes. Ontario and the Prairie Provinces see the highest frequency. Other areas of the world that have frequent tornadoes include significant portions of Europe, South Africa, Philippines, Bangladesh, parts of Argentina, Uruguay, southern and southeastern Brazil, northern Mexico, eastern and western Australia, New Zealand, and far eastern Asia. Tornado reports in the U.S. have been officially collated since 1950. These reports have been gathered by the National Climatic Data Center (NCDC), based in Asheville, North Carolina. A tornado can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Earth Sciences
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres: the biosphere, hydrosphere/ cryosphere, atmosphere, and geosphere (or lithosphere). Earth science can be considered to be a branch of planetary science but with a much older history. Geology Geology is broadly the study of Earth's structure, substance, and processes. Geology is largely the study of the lithosphere, or Earth's surface, including the crust and rocks. It includes the physical characteristics and processes that occur in the lithosphere as well as how they are affected by geothermal energy. It incorporates aspects of chemistry, physics, and biology as elements of geology interact. Historical geology is the application of geology to interpret Earth history and how it has changed over time. Geochemistry studies the che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
American Meteorological Society
The American Meteorological Society (AMS) is a scientific and professional organization in the United States promoting and disseminating information about the atmospheric, oceanic, and hydrologic sciences. Its mission is to advance the atmospheric and related sciences, technologies, specifications, applications and services for the benefit of society. Background Founded on December 29, 1919, by Charles F. Brooks, at a meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in St. Louis, and incorporated on January 21, 1920, the American Meteorological Society has a membership of more than 13,000 weather, water, and climate scientists, professionals, researchers, educators, students, and enthusiasts. AMS publishes 12 atmospheric and related oceanic and hydrologic journals (in print and online), sponsors as many as twelve conferences annually, and administers professional certification programs and awards. The AMS Policy and Education programs promote scientific kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Enhanced Fujita Scale
The Enhanced Fujita scale (abbreviated EF-Scale) is a scale that rates tornado intensity based on the severity of the damage a tornado causes. It is used in the United States and France, among other countries. The EF scale is also unofficially used in other countries, including China and Brazil. The rating of a tornado is determined by conducting a tornado damage survey. The scale has the same basic design as the original Fujita scale—six intensity categories from zero to five, representing increasing degrees of damage. It was revised to reflect better examinations of tornado damage surveys, in order to align wind speeds more closely with associated storm damage. Better standardizing and elucidating what was previously subjective and ambiguous, it also adds more types of structures and vegetation, expands degrees of damage, and better accounts for variables such as differences in construction quality. An "EF-Unknown" (EFU) category was later added for tornadoes that cannot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tornado Outbreak
A tornado outbreak is the occurrence of multiple tornadoes spawned by the same Synoptic scale meteorology, synoptic scale weather system. The number of tornadoes required to qualify as an outbreak typically are at least six to ten, with at least two rotational locations (if squall line) or at least two supercells producing Tornado family, multiple tornadoes. The tornadoes usually occur within the same day or continue into the early morning hours of the succeeding day, and within the same region. Most definitions allow for a break in tornado activity (time elapsed from the end of the last tornado to the beginning of the next tornado) of six hours. If tornado activity indeed resumes after such a lull, many definitions consider the event to be a new outbreak. A series of continuous or nearly continuous tornado outbreak days is a tornado outbreak sequence. In the United States and Canada, tornado outbreaks usually occur from March through June in the Great Plains, the Midwestern Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Climate Change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is Scientific consensus on climate change, driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, Deforestation and climate change, deforestation, and some Greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, agricultural and Environmental impact of concrete, industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases greenhouse effect, absorb some of the heat that the Earth Thermal radiation, radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, has increased in concentratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vortex
In fluid dynamics, a vortex (: vortices or vortexes) is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in the wake of a boat, and the winds surrounding a tropical cyclone, tornado or dust devil. Vortices are a major component of turbulent flow. The distribution of velocity, vorticity (the curl of the flow velocity), as well as the concept of circulation are used to characterise vortices. In most vortices, the fluid flow velocity is greatest next to its axis and decreases in inverse proportion to the distance from the axis. In the absence of external forces, viscous friction within the fluid tends to organise the flow into a collection of irrotational vortices, possibly superimposed to larger-scale flows, including larger-scale vortices. Once formed, vortices can move, stretch, twist, and interact in complex ways. A moving vortex carries s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tulsa, Oklahoma
Tulsa ( ) is the List of municipalities in Oklahoma, second-most-populous city in the U.S. state, state of Oklahoma, after Oklahoma City, and the List of United States cities by population, 48th-most-populous city in the United States. The population was 413,066 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is the principal municipality of the Tulsa Metropolitan Area, Tulsa metropolitan area, a region with 1,034,123 residents. The city serves as the county seat of Tulsa County, Oklahoma, Tulsa County, the most densely populated county in Oklahoma, with Urban Development, urban development extending into Osage County, Oklahoma, Osage, Rogers County, Oklahoma, Rogers and Wagoner County, Oklahoma, Wagoner counties. Tulsa was settled between 1828 and 1836 by the Lochapoka band of Creek people, Creek Native Americans, and was formally incorporated in 1898. Most of Tulsa is still part of the territory of the Muscogee (Creek) Nation. Northwest Tulsa lies in the Osage Nation wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Storm Chasing
Storm chasing is broadly defined as the deliberate pursuit of any severe weather phenomenon, regardless of motive, but most commonly for curiosity, adventure, scientific investigation, or for news or media coverage. A person who chases storms is known as a storm chaser (or "chaser" for short). While witnessing a tornado is the single biggest objective for most chasers, many chase thunderstorms and delight in viewing cumulonimbus and related cloud structures, watching a barrage of hail and lightning, and seeing what skyscapes unfold. A smaller number of storm chasers attempt to intercept tropical cyclones, waterspouts, blizzards, and other weather phenomena. Nature of and motivations for chasing Storm chasing is chiefly a recreational endeavor, with chasers usually giving their motives as photographing or video recording a storm, or for various personal reasons. These can include the beauty of the views afforded by the sky and land, the mystery of not knowing precisely what ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
TLC (TV Network)
TLC is an American multinational cable television, cable and satellite television, satellite television network owned by the Warner Bros. Discovery Networks, Networks division of Warner Bros. Discovery. First established in 1980 as The Learning Channel, it initially focused on educational and instructional programming. By the late 1990s, after an acquisition by Discovery, Inc. earlier in the decade, the network began to pivot towards reality television programming—predominantly focusing on programming involving Lifestyle (social sciences), lifestyles and personal stories—to the point that the previous name with "The Learning Channel" spelled out was orphaned initialism, phased out in favor of its initialism. , with its programming primarily dedicated to the nine-series ''90 Day Fiancé'' universe, comprising 31% of the shows carried by the channel, TLC is available to approximately 71,000,000 pay television households in the United States—down from its 2011 peak of 100, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Glossary Of Tornado Terms
The following is a glossary of tornado terms. It includes scientific as well as selected informal terminology. A * ''Advanced Radar Research Center'' (ARRC) * ''Advection'' * ''Air parcel'' * ''American Geophysical Union'' (AGU) * ''American Meteorological Society'' (AMS) * ''Anticipated convection'' (AC) – A convective outlook. * ''Angular momentum'' * ''Anticyclone'' * ''Anticyclonic rotation'' * ''Anticyclonic tornado'' * ''Anticyclogenesis'' * ''Arcus cloud'' * ''Atmosphere'' * ''Atmospheric pressure'' B * ''Baroclinity'' or ''baroclinicity'' – baroclinic * '' Barotropity or ''barotropicity'' – barotropic * Bear's cage – (tornado chaser slang) The precipitation that wraps around a mesocyclone, possibly hiding a tornado on the ground. * ''Beaufort scale'' * ''Bernoulli's principle'' * Blob – Informal term coined by Erik N. Rasmussen for a descending reflectivity core (DRC). * Boundary * ''Bounded weak echo region'' (BWER) * ''Bow echo'' * BRN shear * '' Bulk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |