|
Ouali II
Mansa Uli II ( French: "Oualy II"), also known as Gbèré, was a mansa ("king of kings") of the Mali Empire. He ruled during the second half of the 15th century. According to the oral traditions preserved in Dioma, Gbèré was the younger of two brothers from Niani who liberated Dioma from a Fula invasion. Gbèré is a Mandinka name meaning "red" in reference to one's skin tone. After this success, his brother was crowned mansa. Gbèré ascended to the throne under the royal name Uli II following his brother Musa III's death. Other sources claim that Musa was his father. Uli was in turn succeeded, perhaps not directly, by his son Mahmud II. See also *Mali Empire *Keita Dynasty The Keita dynasty ruled pre-imperial and imperial Mali from the 11th century into the early 17th century. It was a Muslim dynasty, and its rulers claimed descent from Bilal ibn Rabah. The early history is entirely unknown, outside of legends and ... References Mansas of the Mali Empire 15t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansa (title)
''Mansa'' (; ''mansaw'') is a Maninka and Mandinka language, Mandinka word for a hereditary ruler, commonly translated as "king". It is particularly known as the title of the rulers of the Mali Empire, such as Mansa Musa, and in this context is sometimes translated as "emperor". It is also a title held by traditional village rulers, and in this context is translated as "chief". ''Mansa'' contrasts with another Manding word for ruler, ''faama''. ''Faama'' emphasizes the military, coercive authority of a ruler, and can be translated as "tyrant", whereas ''mansa'' refers to a hereditary ruler whose authority is derived from tradition and mystical power. A ruler can be both a ''faama'' and a ''mansa'', but a ''mansa'' was not necessarily a ''faama''. The word ''mansa'' () was recorded in Arabic during the 14th century by North African writers such as Ibn Battuta and Ibn Khaldun, who explained it as meaning "sultan". Cognates of ''mansa'' exist in other Mandé languages, such as S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mali Empire
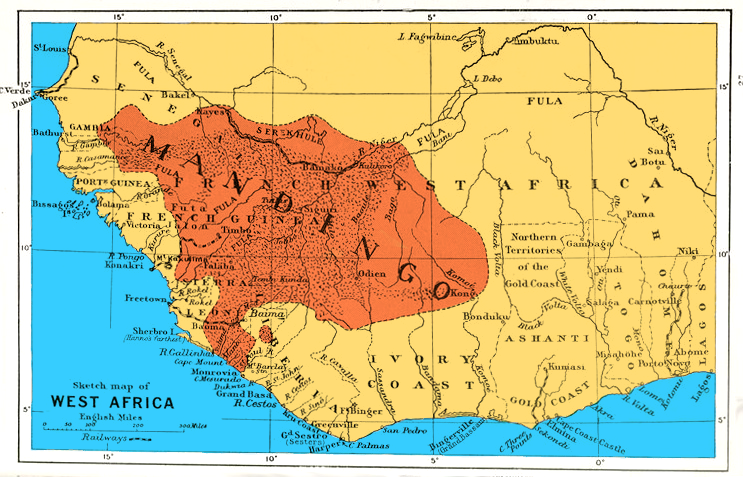
The Mali Empire (Manding languages, Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or ''Manden Duguba''; ) was an empire in West Africa from 1226 to 1610. The empire was founded by Sundiata Keita () and became renowned for the wealth of its rulers, especially Mansa Musa (Musa Keita). At its peak, Mali was the largest empire in West Africa, widely influencing the culture of the region through the spread of Manding languages, its language, laws, and customs. The empire began as a small Mandinka people, Mandinka kingdom at the upper reaches of the Niger River, centered around the Manding region. It began to develop during the 11th and 12th centuries as the Ghana Empire, or Wagadu, declined and trade epicentres shifted southward. The Pre-imperial Mali, history of the Mali Empire before the 13th century is unclear, as there are conflict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musa III
Mansa Musa III, also known as Foamed Musa or Sérébandjougou was a mansa (emperor) of the Mali Empire, probably ruling in the second quarter of the 15th century. Little is known about him or his reign. He first enters recorded history during the empire's war against the Fula; Wassoulounké in the 1440s.Niane, D.T.: "Recherches sur l’Empire du Mali au Moyen âge". Presence Africaine. Paris, 1975 He and his younger brother liberated the newly settled area of Dioma, and Sérébandjougou was crowned mansa shortly after. He was succeeded, perhaps immediately or with other kings in between, by his son or brother Ouali II. See also *Mali Empire *Keita Dynasty The Keita dynasty ruled pre-imperial and imperial Mali from the 11th century into the early 17th century. It was a Muslim dynasty, and its rulers claimed descent from Bilal ibn Rabah. The early history is entirely unknown, outside of legends and ... References Mansas of the Mali Empire 15th-century monarchs in Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahmud II (mansa)
Mansa Mahmud II, also known as Muhammad or Mamadou, was mansa ("king of kings") of the Mali Empire from 1481 to 1496. He was the son, but not necessarily the immediate successor, of Mansa Uli II. Mansa Mahmud II's rule was characterized by crisis. The rise of Tenguella in the 1480s and 90s put pressure on Mali's western provinces, particularly Futa Jallon that was occupied by Koli Tenguella. The growing trade in Mali's western provinces with Portugal witnessed the exchange of envoys between the two nations. Mansa Mahmud II received the Portuguese envoy Pedro da Évora in 1484.Niane, D.T.: "Recherches sur l'Empire du Mali au Moyen âge". Presence Africaine. Paris, 1975 In the letter he sent back to King John II of Portugal, Mahmud claimed to be exceeded in power by only the sultans of Yemen, Baghdad, Cairo and Takrur.M. Ly-Tall"The Decline of the Mali Empire" in D. T. Niane (ed.), ''General History of Africa, IV: Africa from theTwelfth to the Sixteenth Century'' (UNESCO, 1984 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keita Dynasty
The Keita dynasty ruled pre-imperial and imperial Mali from the 11th century into the early 17th century. It was a Muslim dynasty, and its rulers claimed descent from Bilal ibn Rabah. The early history is entirely unknown, outside of legends and myths. The first Keita ''mansa'' was Sundiata Keita. This is when Mari Jata is crowned and Keita becomes a clan name. A couple of generations after him, his great-nephew, Mansa Musa Keita I of Mali, made a celebrated pilgrimage to Mecca. The dynasty remained a major power in West Africa from the early 13th century until the breakup of the Mali Empire around 1610. Rivals from within the clan founded smaller kingdoms within contemporary Mali and Guinea. Of the members of these modern "daughter dynasties", the late politician Modibo Keita and the musician Salif Keita are arguably the most famous. Legendary Ancestors According to Muslim tradition, Bilal ibn Rabah was a freed slave, possibly of Abyssinian descent, who accepted Islam and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world's Major religious groups, second-largest religious population after Christians. Muslims believe that Islam is the complete and universal version of a Fitra, primordial faith that was revealed many times through earlier Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets and messengers, including Adam in Islam, Adam, Noah in Islam, Noah, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, and Jesus in Islam, Jesus. Muslims consider the Quran to be the verbatim word of God in Islam, God and the unaltered, final revelation. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Torah in Islam, Tawrat (the Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Gospel in Islam, Injil (Gospel). They believe that Muhammad in Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family. Like all other Romance languages, it descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. French evolved from Northern Old Gallo-Romance, a descendant of the Latin spoken in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien language, Francien) largely supplanted. It was also substratum (linguistics), influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul and by the Germanic languages, Germanic Frankish language of the post-Roman Franks, Frankish invaders. As a result of French and Belgian colonialism from the 16th century onward, it was introduced to new territories in the Americas, Africa, and Asia, and numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole, were established. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niani, Mali
Niani is a village in Guinea. It is located in the Kankan Prefecture of the Kankan Region, in the east of the country. It lies on the left bank of the Sankarani River. Geography The village is situated in extreme eastern Guinea, on the west bank of the Sankarani River. The river is accessible all year round and rocky peaks surround the village. The village is also on the edge of the forest, which is a source of gold, kola nuts, palm oil and ivory. History Niani is often considered one of the ancient capitals of the Mali Empire. Some scholars believe that the village became the capital in the early 12th century after the former capital of Dioliba was abandoned. Niani is mentioned by the 16th-century traveler Leo Africanus. While some scholars believe that Kangaba was one of the capitals of the empire, others believe that Niani remained continuously the capital through the 14th to 16th centuries. 14th century Arab historian Shihab al-Umari reported the village as ''Nyeni'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fula People
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people are an ethnic group in Sahara, Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, and regions near the Red Sea coast in Sudan. The approximate number of Fula people is unknown, due to clashing definitions regarding Fula ethnicity. Various estimates put the figure between 25 and 40 million people worldwide. A significant proportion of the Fula – a third, or an estimated 7 to 10 million – are pastoralism, pastoralists, and their ethnic group has the largest nomadic pastoral community in the world., Quote: The Fulani form the largest pastoral nomadic group in the world. The Bororo'en are noted for the size of their cattle herds. In addition to fully nomadic groups, however, there are also semisedentary Fulani – Fulbe Laddi – who also farm, although they argue that they do so out of necessity, not choice. The major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, The Gambia, southern Senegal and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the List of ethnic groups of Africa, largest ethnolinguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family, which are a ''lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. They are predominantly Subsistence agriculture, subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahmud II
Mahmud II (, ; 20 July 1785 – 1 July 1839) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1808 until his death in 1839. Often described as the "Peter the Great of Turkey", Mahmud instituted extensive administrative, military, and fiscal reforms. His disbandment of the conservative Janissary, Janissary Corps removed a major obstacle to his and his successors' reforms in the Empire, creating the foundations of the subsequent Tanzimat era. Mahmud's reign was also marked by further Ottoman military defeats and loss of territory as a result of nationalist uprisings and European intervention. Mahmud ascended the throne following an Ottoman coups of 1807–1808, 1808 coup that deposed his half-brother Mustafa IV. Early in his reign, the Ottoman Empire ceded Bessarabia to Russia at the end of the Russo-Turkish War (1806–1812), 1806–1812 Russo-Turkish War. Greece waged a Greek War of Independence, successful war of independence that started in 1821 with British, French and Russian su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |