|
Ostróg
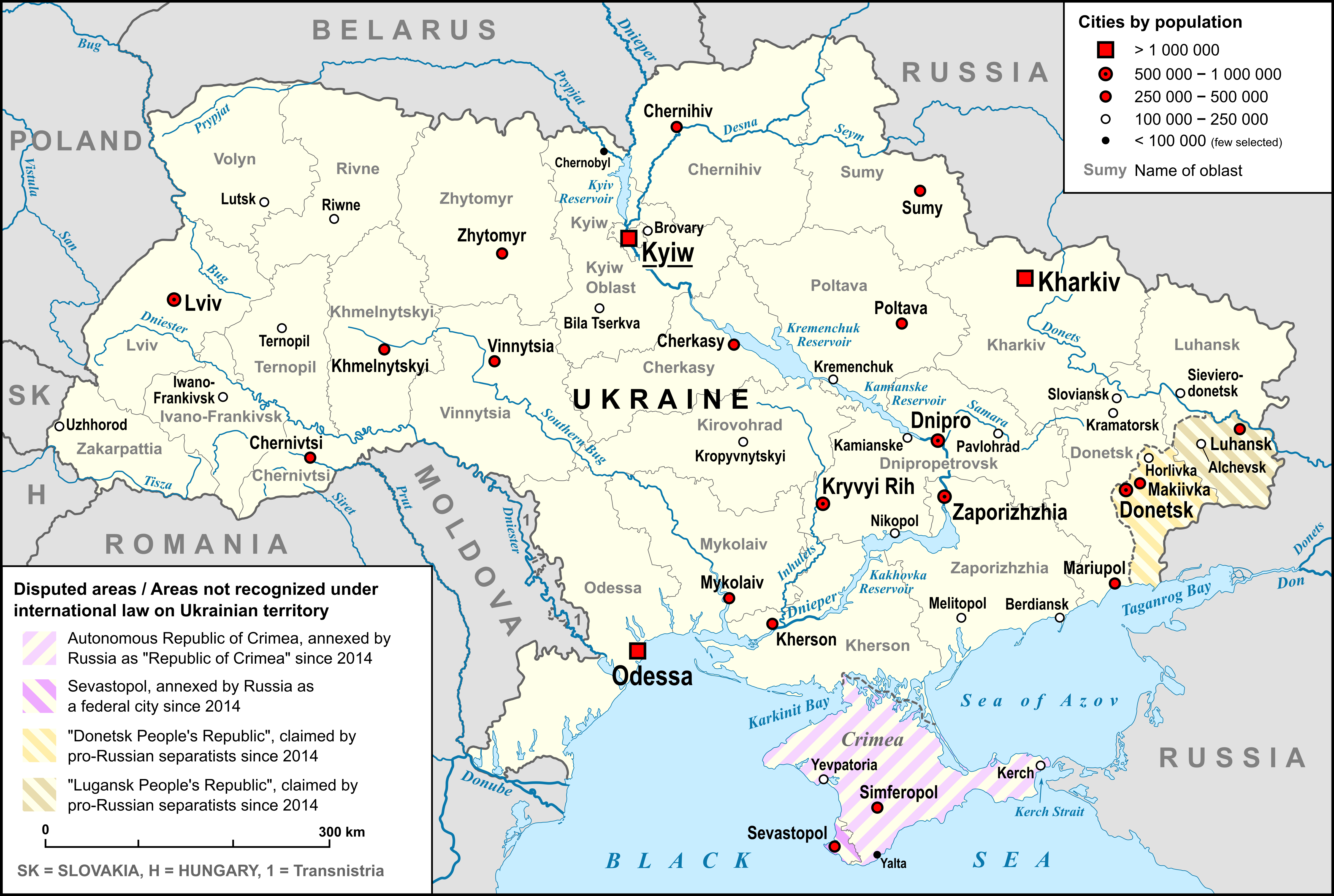
Ostroh ( , ) is a city in Rivne Oblast, western Ukraine. It is situated on the Horyn, Horyn River. Ostroh was the administrative center of Ostroh Raion until 2020, but as a city of regional significance (Ukraine), city of oblast significance did not belong to the raion. Currently the city is the centre of Ostroh urban hromada. Population: The Ostroh Academy was established here in 1576, the first higher educational institution in modern Ukraine. Furthermore, in the 16th century, the first East Slavic books, notably the Ostrog Bible, were printed there. History The Hypatian Codex first mentions Ostroh in 1100, as a fortress of the Volhynian princes. Since the 14th century, it was the seat of the powerful Ostrogski princely family, who developed their town into a great centre of learning and commerce. Upon the family's demise in the 17th century, Ostroh passed to the Zasławski and then Lubomirski families. In the second half of the 14th century, Ostroh, together with the whole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostroh Urban Hromada
Ostroh ( , ) is a city in Rivne Oblast, western Ukraine. It is situated on the Horyn River. Ostroh was the administrative center of Ostroh Raion until 2020, but as a city of oblast significance did not belong to the raion. Currently the city is the centre of Ostroh urban hromada. Population: The Ostroh Academy was established here in 1576, the first higher educational institution in modern Ukraine. Furthermore, in the 16th century, the first East Slavic books, notably the Ostrog Bible, were printed there. History The Hypatian Codex first mentions Ostroh in 1100, as a fortress of the Volhynian princes. Since the 14th century, it was the seat of the powerful Ostrogski princely family, who developed their town into a great centre of learning and commerce. Upon the family's demise in the 17th century, Ostroh passed to the Zasławski and then Lubomirski families. In the second half of the 14th century, Ostroh, together with the whole of Volhynia, was administratively integrated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrogski Princely Family
The House of Ostrogski (; ; ) was one of the more prominent families in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The family spanned from the 14th century Ruthenian noble Daniil Ostrogski to the 17th century Polish members. After the death of Janusz Ostrogski, the last male heir, most of the family's possessions passed to the Zasławski family. The family played a crucial role in preserving the Eastern Orthodoxy, particularly during the Union of Brest signing in 1595. Members contributed to printing books in Church Slavonic (Kyiv uthenianrecession) and supporting the Orthodox brotherhoods. By the 17th century almost all members turn to Catholicism and became fully associated with the Polish nation (Polonization). Many of their possessions were passed on or inherited by members of Sanguszko family. History The Ostrogski family was most likely of Rurikid stock and descended from Sviatopolk II of Kiev. Some scholars however ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Ukraine
There are 463 populated places in Ukraine, populated places in Ukraine that have been officially granted city status () by the Verkhovna Rada, the country's parliament, as of 23 April 2025. Settlements with more than 10,000 people are eligible for city status although the status is typically also granted to settlements of historical or regional importance. Smaller settlements are Populated places in Ukraine#Rural settlements, rural settlements () and villages (). Historically, there were systems of city rights, granted by the territorial lords, which defined the status of a place as a ''misto'' or ''selo''. In the past, cities were self-governing and had several privileges. The list of cities is roughly ordered by population and the 2022 estimates are compared to the 2001 Ukrainian census, except for Chernobyl for which the population is an unofficial estimate. The City with special status, cities with special status are shown in ''italic''. The average population size is 62,000. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torre Del Greco
Torre del Greco (; ; "Greek man's Tower") is a ''comune'' in the Metropolitan City of Naples in Italy, with a population of c. 85,000 . The locals are sometimes called ''Corallini'' because of the once plentiful coral in the nearby sea, and because the city has been a major producer of coral jewellery and cameo (carving), cameo brooches since the seventeenth century. History Ancient period Tracing the history of Torre del Greco is difficult given the almost complete lack of historical documentary sources. Based on archaeological evidence, in ancient Rome, Roman times Torre del Greco was probably a suburb of Herculaneum and, like elsewhere on the Bay of Naples such as at Oplontis and Stabiae, many patricians' villas would have lined the coast. In 79 AD the eruption of Vesuvius buried the area under volcanic ash. The nearby Roman Villa Sora was a large and sumptuous residence with terraces down to the beach and overlooking the sea from its 150m-long frontage, dating from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
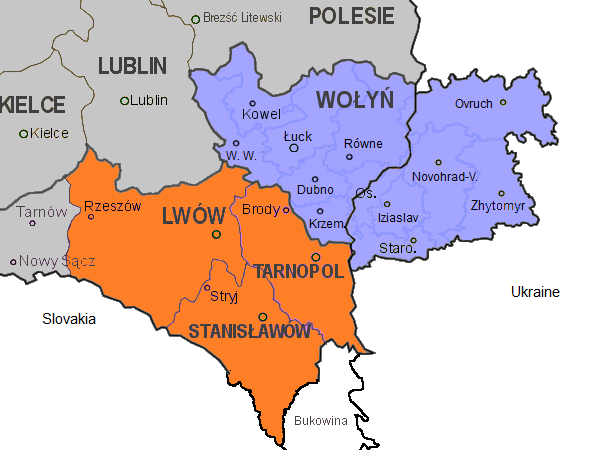
Volhynia
Volhynia or Volynia ( ; see #Names and etymology, below) is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between southeastern Poland, southwestern Belarus, and northwestern Ukraine. The borders of the region are not clearly defined, but in Ukraine it is roughly equivalent to Volyn Oblast, Volyn and Rivne Oblasts; the territory that still carries the name is Volyn Oblast. Volhynia has changed hands numerous times throughout history and been divided among competing powers. For centuries it was part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. After the Russian annexation during the Partitions of Poland, all of Volhynia was made part of the Pale of Settlement on the southwestern border of the Russian Empire. Important cities include Rivne, Lutsk, Zviahel, and Volodymyr (city), Volodymyr. Names and etymology *, ; * ; *, ; * or ; *; * ; *; *; * or (both ); Volhynian German: , , or (all ); *, or . The alternative name for the region is Lodomeria after the city of Volodymyr (city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypatian Codex
The ''Hypatian Codex'', also known as Hypatian Letopis or Ipatiev Letopis, is a compendium of three Rus' chronicle, Rus' chronicles: the ''Primary Chronicle'', ''Kievan Chronicle'' and ''Galician-Volhynian Chronicle''. It is the most important source of historical data about Kievan Rus'. The language of this work is Old Church Slavonic with many East Slavic languages, East Slavisms. Provenance The codex was discovered in Ukraine in 1617 by Zacharias Kopystensky, and was then copied by monks in 1621. The codex later known as the ''Hypatian Codex'' was most likely acquired from the Ipatievsky Monastery (Hypatian Monastery) in Kostroma on 15 May 1767. This would have happened during the May–June 1767 Volga voyage of Empress Catherine the Great, Catherine II (), who was highly interested in reading Rus' chronicles, and collecting them all at the capital city of Saint Petersburg (one of the goals of her voyage). Count Vladimir Grigorievich Orlov (1743–1831), then director of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrog Bible
The Ostrog Bible (; ) was the first complete printed edition of the Bible in Church Slavonic, published in Ostrog (now Ostroh, Ukraine) in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by the printer Ivan Fyodorov in 1581 with the assistance of Konstantin Ostrogski. It was based on Gennady's Bible and was the primary source for the Moscow Bible published in 1663 under Alexis of Russia. Description The main source for the Ostrog Bible was Gennady's Bible, which was completed in 1499 in Novgorod, Russia. The Ostrog Bible was translated not from the (Hebrew) Masoretic text, but from the (Greek) Septuagint. This translation comprised seventy-six books of the Old and New Testaments and a manuscript of the ''Codex Alexandrinus''. Some parts were based on Francysk Skaryna's translations. The Ostrog Bible was printed on two dates: 12 July 1580, and 12 August 1581. The second version differs from the 1580 original in composition, ornamentation, and correction of misprints. In the printing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostroh Academy
The Ostroh Academy (; ) was an influential institute of higher learning located in Ostroh in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It is considered the first institution of higher education in the Eastern Slavic world, dating to 1576 and founded by the wealthy Ruthenian magnate Konstanty Wasyl Ostrogski. The academy was at the centre of what historians have dubbed the "Ostroh Renaissance", an Orthodox cultural revival led by the Rus’ magnates of Poland-Lithuania in resistance to the dominant Reformation and Counter-Reformation. Its crowning achievement was the publication of the Ostroh Bible in 1581, the first complete print of the Bible in a Slavic language, and an "epochal event in the life of the whole Orthodox world." History In the late 16th century, all higher schools of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth were under influence of Catholic or Protestant nobles. The Council of Trent (1545–63) and the activities of the Jesuits, under the guardianship of Sigism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of Regional Significance (Ukraine)
A city of regional significance () in Ukraine was a type of second-level Administrative divisions of Ukraine, administrative division or municipality, the other type being Raions of Ukraine, raions (districts). In the first-level division of Oblasts of Ukraine, oblasts, they were referred to as ''cities of oblast significance''; in the first-level autonomous republic of Autonomous Republic of Crimea, Crimea, they were ''cities of republican significance''. The designation was created with the introduction of oblasts in 1932. It was abolished in a 2020 reform that merged raions together and integrated the city municipalities into them. Such city municipality was complex and usually combined the city proper and adjacent populated places. The city of regional (oblast) significance was governed by a city council known as ''mis'krada'', which was chaired by a mayor. There were instances where a municipality might have included only the city alone (city proper), while in others instanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostroh Raion
Ostroh Raion () was a raion in Rivne Oblast in western Ukraine. Its administrative center An administrative centre is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune, is located. In countries with French as the administrative language, such as Belgiu ... was the city of Ostroh which was administratively incorporated as a city of oblast significance and did not belong to the raion. The raion was abolished and its territory was merged into Rivne Raion on 18 July 2020 as part of the administrative reform of Ukraine, which reduced the number of raions of Rivne Oblast to four. The last estimate of the raion population was See also * Subdivisions of Ukraine References External links rv.gov.ua Former raions of Rivne Oblast 1940 establishments in Ukraine Ukrainian raions abolished during the 2020 administrative reform {{Rivne-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Center
An administrative centre is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune, is located. In countries with French as the administrative language, such as Belgium, Luxembourg, Switzerland and many African countries, a (, , ) is a town or city that is important from an administrative perspective. Algeria The capitals of Algerian provinces, districts, and communes are called . Belgium The in Belgium is the administrative centre of each of the ten provinces of Belgium. Three of these cities also give their name to their province (Antwerp, Liège and Namur). France The of a French department is known as the prefecture (). This is the town or city where the prefect of the department (and all services under their control) are situated, in a building also known as the prefecture. In every French region, one of the departments has preeminence over the others, and the prefect carries the tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |