|
Oscar Ljungström
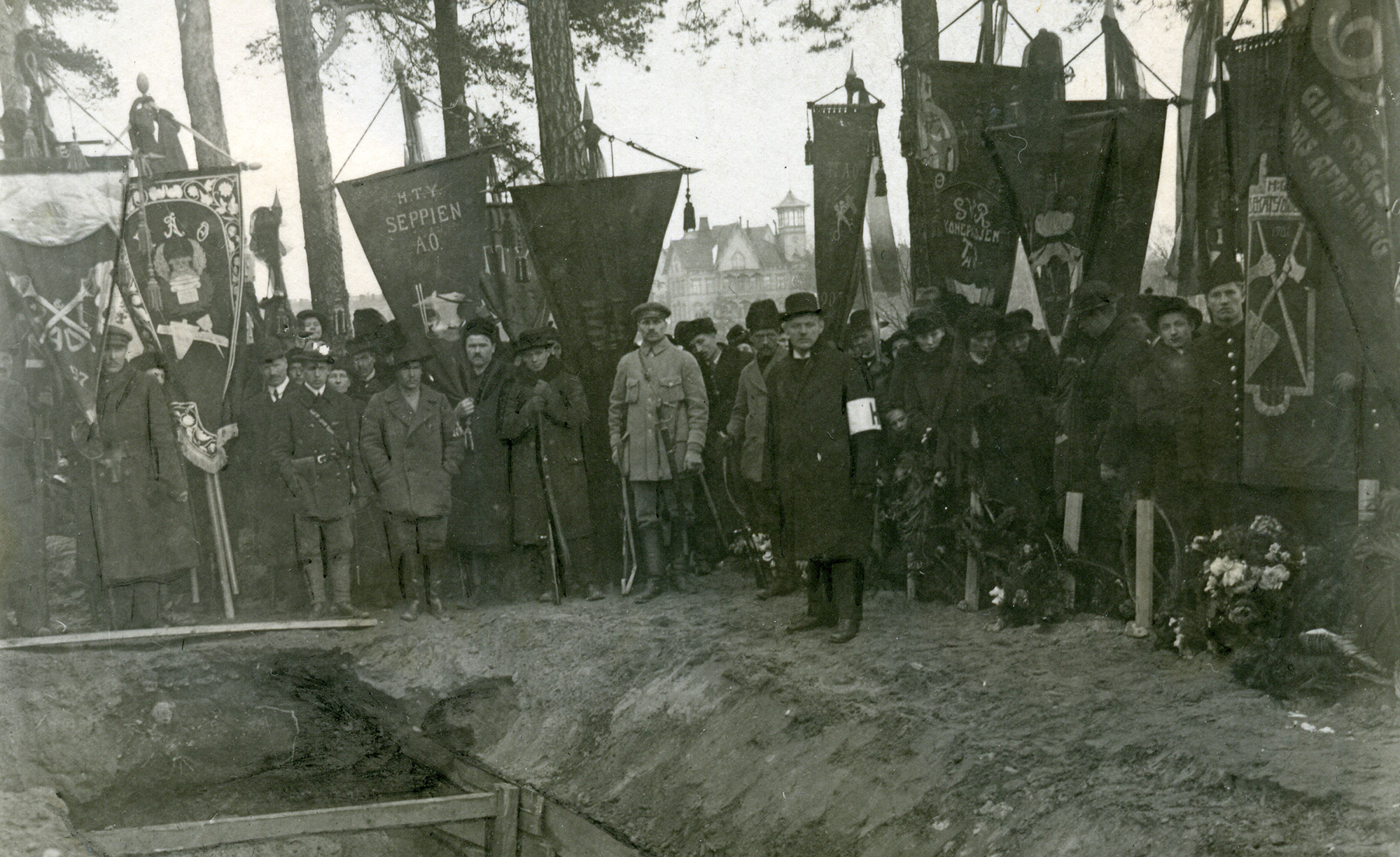
Oscar Ljungström (7 November 1868 – 17 August 1943) was a Swedish archivist, officer, and author. Biography Oscar Ljungström was born in 1868 to the cartographer Jonas Patrik Ljungström, and Amalia (née Falck). Among his siblings were Fredrik Ljungström, Birger Ljungström, and Georg Ljungström. Oscar Ljungstrom served as an archivist in the urban engineering office of Stockholm. With a background as an officer in the ''Swedish Landstorm'' of the Swedish Army, and a determined anti-communist, he joined the White forces under Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim in Finland after the outbreak of the Finnish Civil War in 1918. He served as a platoon commander during the war, which the Whites eventually won against the Reds. Oscar Ljungström had artistic interests and made several visual artworks, working mainly with oil paintings. Yet, writing became his primary element. Of a family background partly of Christians outside of the mainline Lutheran Church of Sweden, Ljungström ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Civil War
The Finnish Civil War was a civil war in Finland in 1918 fought for the leadership and control of the country between Whites (Finland), White Finland and the Finnish Socialist Workers' Republic (Red Finland) during the country's transition from a Grand Duchy of Finland, grand duchy ruled by the Russian Empire to a fully independent state. The clashes took place in the context of Aftermath of World War I, the national, political, and social turmoil caused by World War I (Eastern Front (World War I), Eastern Front) in Europe. The war was fought between the Red Guards (Finland), Red Guards, led by a section of the Social Democratic Party of Finland, Social Democratic Party with backup of the Russian bolsheviks and the White Guard (Finland), White Guards of the Senate of Finland, senate and those who opposed socialism, with major assistance by the German Army (German Empire), German Imperial Army, along the German goal to control Fennoscandia. The paramilitary Red Guards, which wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Socialist Workers' Republic
The Finnish Socialist Workers' Republic (FSWR), more commonly referred to as Red Finland, was a self-proclaimed socialist state in Finland during the Finnish Civil War from January to May 1918. The FSWR was established by the Finnish People's Delegation, a government formed by members of the Social Democratic Party to rival the existing Government of Finland, with support of the Red Guards. The FSWR controlled the capital Helsinki and most of southern Finland until March. Kullervo Manner served as its sole leader as Chairman of the Central Committee of the Finnish People's Delegation. The FSWR collapsed when the Red Guards were defeated by the White Finns and Germany, with Manner and most of the Finnish People's Delegation fleeing to Soviet Russia. The name "Finnish Socialist Workers' Republic" () appeared only in the Treaty between Finnish People's Delegation and Russian Council of People's Commissars, signed on 1 March 1918. The People's Delegation had earlier used th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lomaland
Lomaland was a Theosophical community in Point Loma in San Diego, California, from 1900 to 1942. Theosophical Society leader Katherine Tingley founded it in 1900 as a school, cultural center, and residential facility for her followers. The American headquarters of the Theosophical Society Pasadena was also situated there. The facility was important to the growing city of San Diego for its cultural offerings, and it left a lasting legacy in its campus (now Point Loma Nazarene University) which still retains many of the unique architectural features of the original Lomaland. The residents of Lomaland also transformed their Point Loma neighborhood by planting so many trees, orchards and shrubs that the formerly barren neighborhood is now known as the " Wooded Area". Led by Katherine Tingley, the group came to Point Loma to establish a community that would model the philosophical and humanitarian goals of Theosophy. The "White City" envisioned by Tingley was to be located on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theosophical Society Pasadena
The Theosophical Society (Pasadena) is a branch of Theosophy based in Pasadena, California. It claims to be the successor organization to the original Theosophical Society founded by Helena Petrovna Blavatsky and others in 1875 in New York City. It is the second largest Theosophical group in members and international reach after the Theosophical Society Adyar. It traces its roots to the line of William Quan Judge established Leader in 1895 was recognized by a portion of The Society after Blavatsky's death due to a dispute surrounding Annie Besant regarding the existence of The Masters. The juxtaposed positions are put as this: he was either "faithful to the teachings of the Mahatmas" (the stance of the modern Pasadena organization) or as Besant claimed, had forged the letters claiming them to be from the Mahatmas (the stance of the modern Adyar organization). The corresponding faction led by Henry Steel Olcott and Annie Besant, whose organization, based in India, is known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Philosophy
Eastern philosophy (also called Asian philosophy or Oriental philosophy) includes the various philosophies that originated in East and South Asia, including Chinese philosophy, Japanese philosophy, Korean philosophy, and Vietnamese philosophy, which are dominant in East Asia; and Indian philosophy (including Hindu philosophy, Jain philosophy, Buddhist philosophy), which are dominant in South Asia, Southeast Asia, Tibet, Japan and Mongolia. Indian philosophy Indian philosophy refers to ancient philosophical traditions (; 'world views', 'teachings') of the Indian subcontinent. Hinduism may have roots dating back to the times of the Indus Valley civilization. The major orthodox schools arose sometime between the start of the Common Era and the Gupta Empire. These Hindu schools developed what has been called the "Hindu synthesis" merging orthodox Brahmanical and unorthodox elements from Buddhism and Jainism. Hindu thought also spread east to the Indonesian Srivijaya empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syncretism
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various school of thought, schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or religious assimilation, assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thus asserting an underlying unity and allowing for an Inclusivism, inclusive approach to other faiths. While syncretism in art and culture is sometimes likened to eclecticism, in the realm of religion, it specifically denotes a more integrated merging of beliefs into a unified system, distinct from eclecticism, which implies a selective adoption of elements from different traditions without necessarily blending them into a new, cohesive belief system. Etymology The English word is first attested in the early 17th century. It is from Neo-Latin, Modern Latin , drawing on the (), supposedly meaning "Cretan federation". However, this is a spurious etymology derived from the naive idea in Plutarch's 1st- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secularism
Secularism is the principle of seeking to conduct human affairs based on naturalistic considerations, uninvolved with religion. It is most commonly thought of as the separation of religion from civil affairs and the state and may be broadened to a similar position seeking to remove or to minimize the role of religion in any public sphere. Secularism may encapsulate anti-clericalism, atheism, naturalism, non-sectarianism, neutrality on topics of religion, or antireligion. Secularism is not necessarily antithetical to religion, but may be compatible with it. As a philosophy, secularism seeks to interpret life based on principles derived solely from the material world, without recourse to religion. It shifts the focus from religion towards "temporal" and material concerns. There are distinct traditions of secularism like the French, Turkish, American and Indian models. These differ greatly, from the American emphasis on avoiding an established religion and the freedom of bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclectic Approach
Eclectic approach is a method of language education that combines various approaches and methodologies to teach language depending on the aims of the lesson and the abilities of the learners. Different teaching methods are borrowed and adapted to suit the requirement of the learners. It breaks the monotony of the class. In addition, It is a conceptual approach that does not merely include one paradigm or a set of assumptions. Instead, eclecticism adheres to or is constituted from several theories, styles, and ideas in order to gain a thorough insight about the subject, and draws upon different theories in different cases. ‘Eclecticism’ is common in many fields of study such as psychology, martial arts, philosophy, teaching, religion and drama Approaches and methods There are varied approaches and methods used for language teaching. In eclectic approach, the teacher can choose from these different methods and approaches: * Grammar-translation Method: It is a method of teaching ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Esotericism
Western esotericism, also known as the Western mystery tradition, is a wide range of loosely related ideas and movements that developed within Western society. These ideas and currents are united since they are largely distinct both from orthodox Judeo-Christian, Judeo-Christian religion and Age of Enlightenment rationalism. It has influenced, or contributed to, various forms of Western philosophy, mysticism, Western religions, religion, science, pseudoscience, Western art history, art, Western literature, literature, and Western culture#Music, music. The idea of grouping a wide range of Western traditions and philosophies together under the term ''esotericism'' developed in 17th-century Europe. Various academics have debated numerous definitions of Western esotericism. One view adopts a definition from certain esotericist schools of thought themselves, treating "esotericism" as a perennial philosophy, perennial hidden inner tradition. A second perspective sees esotericism as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theosophy (Blavatskian)
Theosophy is a religious movement established in the United States in the late 19th century. Founded primarily by the Russian Helena Blavatsky and based largely on her writings, it draws heavily from both older European philosophies such as Neoplatonism and Indian religions such as Hinduism and Buddhism. Although many adherents maintain that Theosophy is not a religion, it is variably categorized by religious scholars as both a new religious movement and a form of occultism from within Western esotericism. As presented by Blavatsky, Theosophy teaches that there is an ancient and secretive brotherhood of spiritual adepts known as the Masters, who are found around the world but primarily centered in Tibet. These Masters were alleged by Blavatsky to have cultivated great wisdom and supernatural powers, and Theosophists believe they initiated the modern Theosophical movement through disseminating their teachings via Blavatsky. Theosophists believe that these Masters are attemp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |